1. 1차원 배열의 선언

2. 2차원 배열 선언
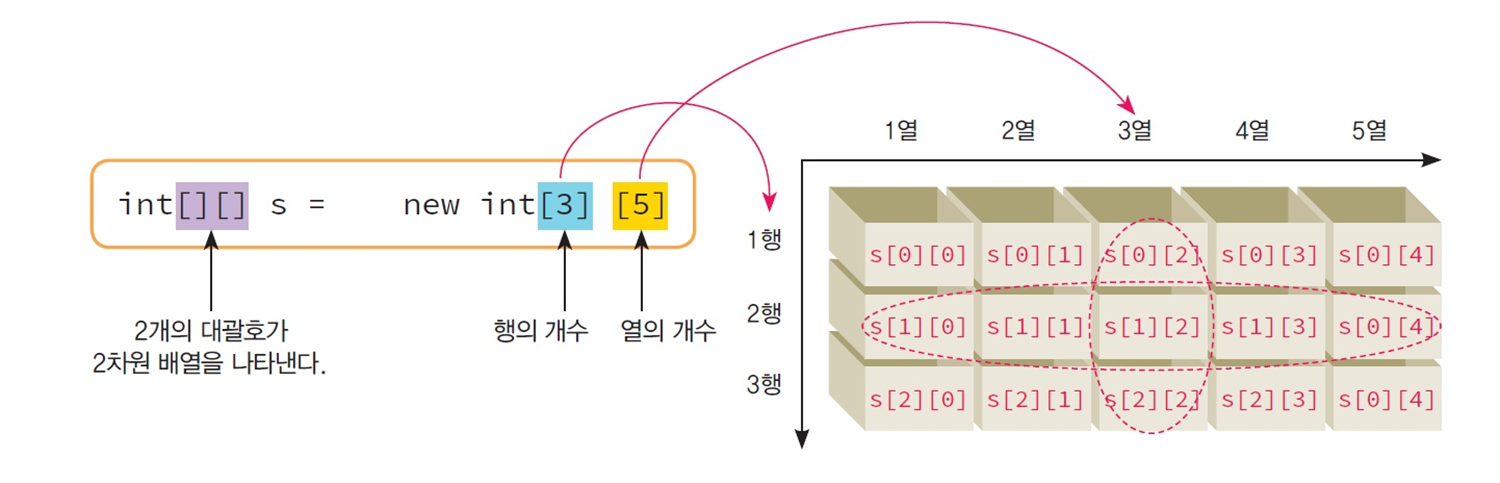
예제 1) 2차원 배열의 접근
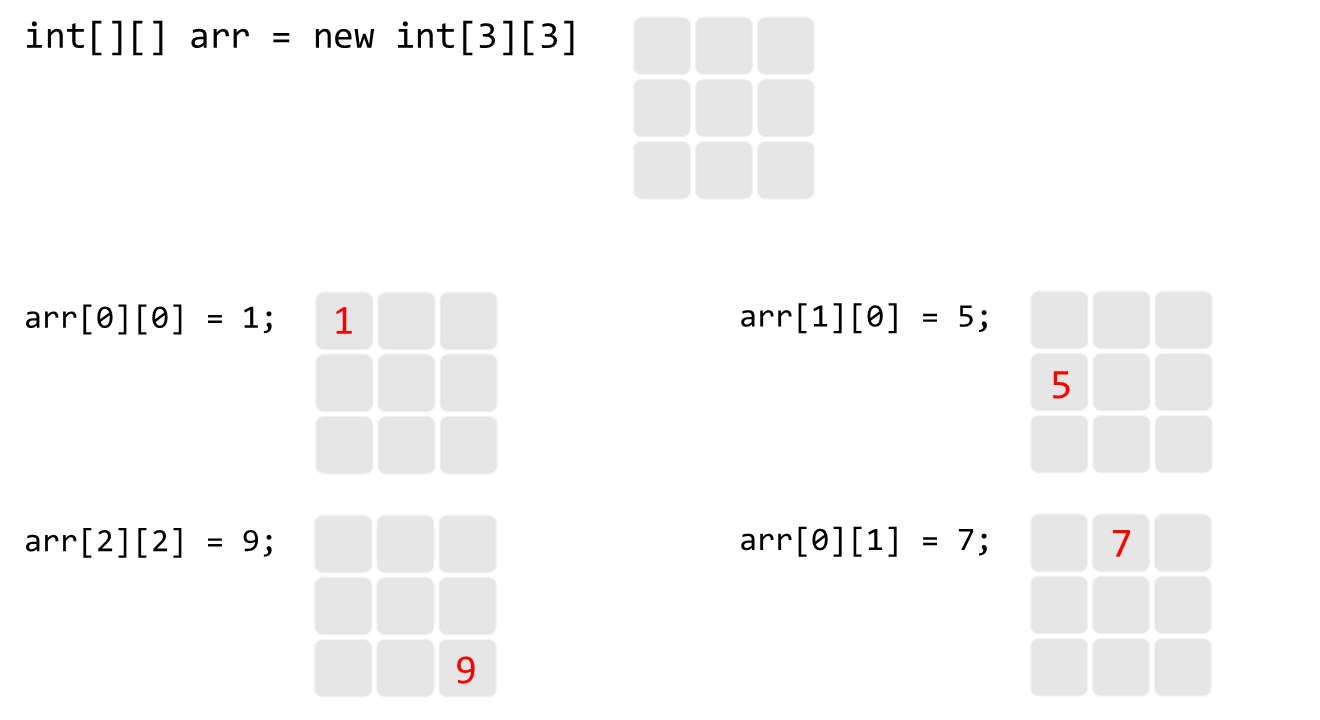
예제 2) 2차원 배열의 접근
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = new int[3][4];
int num = 1;
// 배열에 값을 저장
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
arr[i][j] = num;
num++;
}
}
// 배열에 저장된 값을 출력
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}예제 3) 2차원 배열의 실제 구조
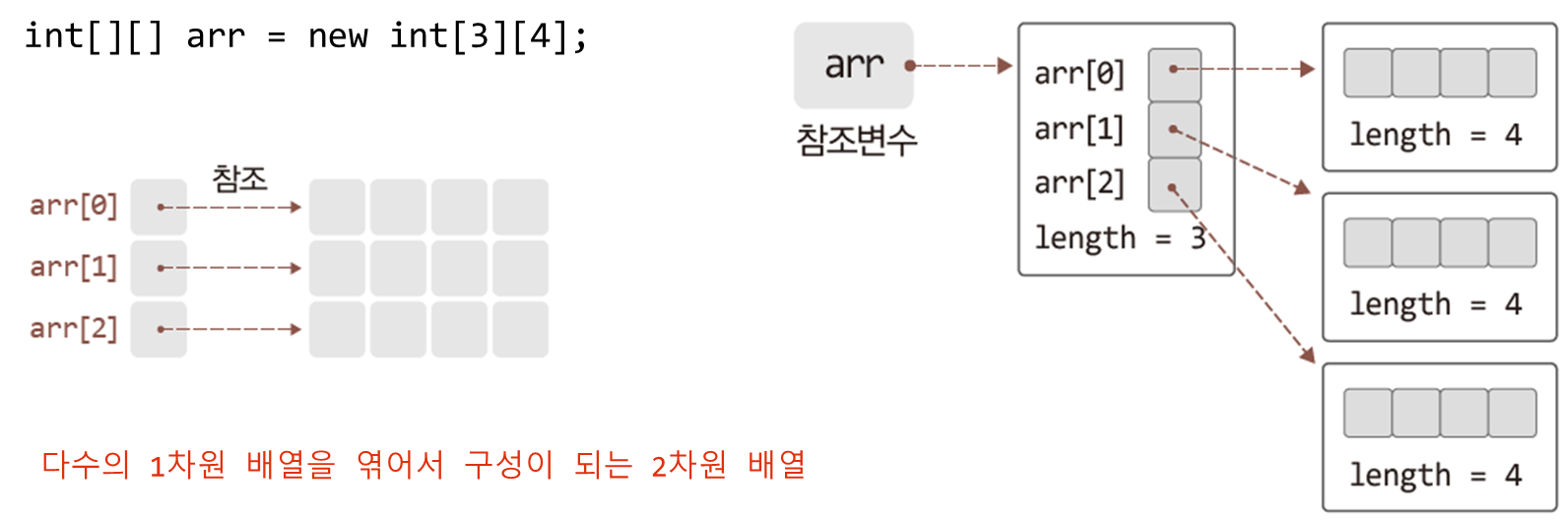
위의 그림을 이해 하는것이 핵심
예제 4) 2차원 배열의 초기화

public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = {
{11},
{22, 33},
{44, 55, 66}
};
// 배열의 구조대로 내용 출력
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}실습 문제
문자형 2차원 배열 5행 5열을 만들과 행과 열을 입력 받아 해당 좌표의 값을 'X'로 변환해 2차원 배열을 출력하시오. 또한 계속해서 반복 실행하도록 구현하고 행이나 열 입력 시 0미만 5이상의 수가 입력되면 프로그램을 종료하시오.
입출력 예시

소스코드
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 문제 2 2차원 배열 행, 열 입력 받아 해당 좌표 값 변환 출력
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
char[][] arr = new char[5][5];
int row;
int col;
while (true) {
System.out.print("행 인덱스 입력 >> ");
row = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("열 인덱스 입력 >> ");
col = sc.nextInt();
if (row < 0 || row > 4 || col < 0 || col > 4) {
System.out.print("프로그램을 종료합니다.");
break;
}
arr[row][col] = 'X';
System.out.println(" 0 1 2 3 4");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++)
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
sc.close();
}
}문제 2)
다음 멤버를 가지고 직사각형을 표현하는 Rectangle 클래스를 작성하라.
-
int 타입의 x, y, width, height 필드: 사각형을 구성하는 점과 크기 정보
-
x, y, width, height 값을 매개변수로 받아 필드를 초기화하는 생성자
-
int square() : 사각형 넓이 리턴
-
void show() : 사각형의 좌표와 넓이를 화면에 출력
-
boolean contatins(Rectangle r) : 매개변수로 받은 r이 현 사각형 안에 있으면 true 리턴
-
main() 메소드의 코드와 실행 결과는 다음과 같다
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle r = new Rectangle(2, 2, 8, 7);
Rectangle s = new Rectangle(5, 5, 6, 6);
Rectangle t = new Rectangle(1, 1, 10, 10);r.show();
System.out.println("s의 면적은 "+s.square());
if(t.contains(r)) System.out.println("t는 r을 포함합니다.");
if(t.contains(s)) System.out.println("t는 s를 포함합니다.");
}
(2,2)에서 크기가 8x7인 사각형
s의 면적은 36
t는 r을 포함합니다.
class Rectangle {
private int x, y, width, height; // 1번 조건에 제시돼 있듯이 네가지 멤버변수를 private으로 설정.
public Rectangle() {
}
public Rectangle(int x, int y, int width, int height){
// 2번 조건에 제시되어 있듯이 매개변수로 값 4개를 받아 각각 초기화해 주는 생성자.
this.x = x; // this 포인터를 사용한다. 이렇게 하면 변수이름을 헷갈리게 두번 설정해줄 필요없다.
this.y = y;
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
public int square(){
return (this.width * this.height);
}
public void show(){
System.out.println( "( " + this.x + " , " + this.y + " )에서 크기가 " + this.width + " x" + this.height + "인 사각형" );
}
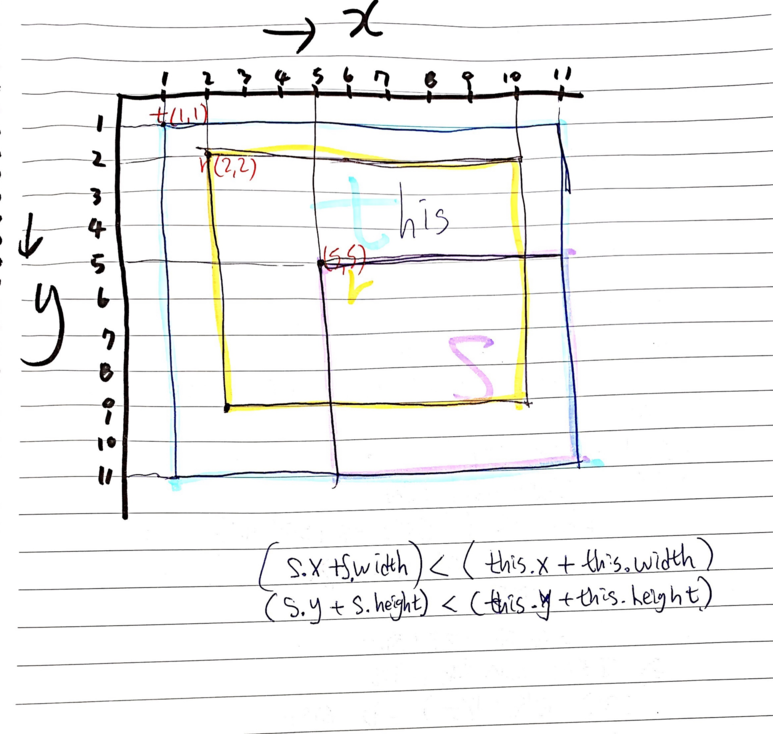
public boolean contains(Rectangle r){
if( ((r.x + r.width) < (this.x + this.width))
&& ((r.y + r.height) < (this.y + this.height))
&& (this.x < r.x) && (this.y < r.y)){
return true;
}else
return false;
}
}
public class RectangleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle r = new Rectangle(2, 2, 8 ,7 ); // r은 x = 2, y = 2
Rectangle s = new Rectangle(5, 5, 6 ,6 );// s는 x= 5, y =
Rectangle t = new Rectangle(1, 1, 10 ,10 );
r.show();
System.out.println("s면적은 " + s.square());
if(t.contains(r))
System.out.println("t는 r을 포함합니다.");
if(t.contains(s))
System.out.println("t는 s을 포함합니다.");
}
}
