
기본 자료형을 감싸는 래퍼 클래스
Boolean public Boolean(boolean value)
Character public Character(char value)
Byte public Byte(byte value)
Short public Short(short value)
Integer public Integer(int value)
Long public Long(long value)
Float public Float(float value), public Float(double value)
Double public Double(double value)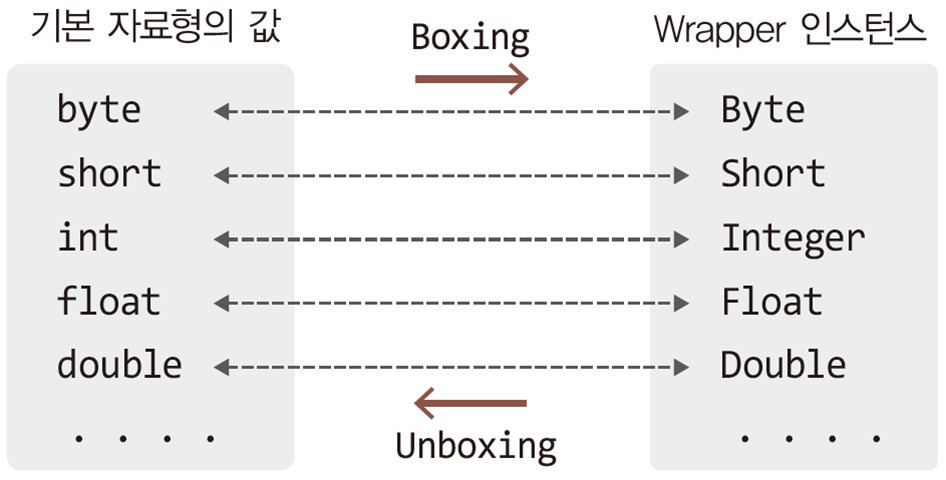
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer iObj = new Integer(10); // 박싱
Double dObj = new Double(3.14); // 박싱
. . . .
int num1 = iObj.intValue(); // 언박싱
double num2 = dObj.doubleValue(); // 언박싱
. . . .
// 래퍼 인스턴스 값의 증가 방법
iObj = new Integer(iObj.intValue() + 10);
dObj = new Double(dObj.doubleValue() + 1.2);
. . . .
}
오토박싱과 오토언박싱
class AutoBoxingUnboxing {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer iObj = 10; // 오토 박싱 진행
Double dObj = 3.14; // 오토 박싱 진행
. . . .
int num1 = iObj; // 오토 언박싱 진행
double num2 = dObj; // 오토 언박싱 진행
. . . .
}
}class AutoBoxingUnboxing {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer iObj = 10; // 오토 박싱 진행
Double dObj = 3.14; // 오토 박싱 진행
. . . .
int num1 = iObj; // 오토 언박싱 진행
double num2 = dObj; // 오토 언박싱 진행
. . . .
}
}public static void main(String[] args) {
// 클래스 메소드를 통한 인스턴스 생성 방법 두 가지
Integer n1 = Integer.valueOf(5); // 숫자 기반 Integer 인스턴스 생성
Integer n2 = Integer.valueOf("1024"); // 문자열 기반 Integer 인스턴스 생성
// 대소 비교와 합을 계산하는 클래스 메소드
System.out.println("큰 수: " + Integer.max(n1, n2));
System.out.println("작은 수: " + Integer.min(n1, n2));
System.out.println("합: " + Integer.sum(n1, n2));
System.out.println();
// 정수에 대한 2진, 8진, 16진수 표현 결과를 반환하는 클래스 메소드
System.out.println("12의 2진 표현: " + Integer.toBinaryString(12));
System.out.println("12의 8진 표현: " + Integer.toOctalString(12));
System.out.println("12의 16진 표현: " + Integer.toHexString(12));
}
