- N - 바꿀 숫자의 최대값
- K - 자리수
- P - 바꿀 수 있는 LED 최대 값
- X - 현재 층
풀이방법
📢크게 보면 1부터 N까지의 수 중 변경할 숫자를 하나 정하고, 변경할 수 있는 갯수 P 안에 변경할 수 있다면, count를 증가시킨다.
코드
0 ~ 9까지 디지털로 표현한 배열 저장
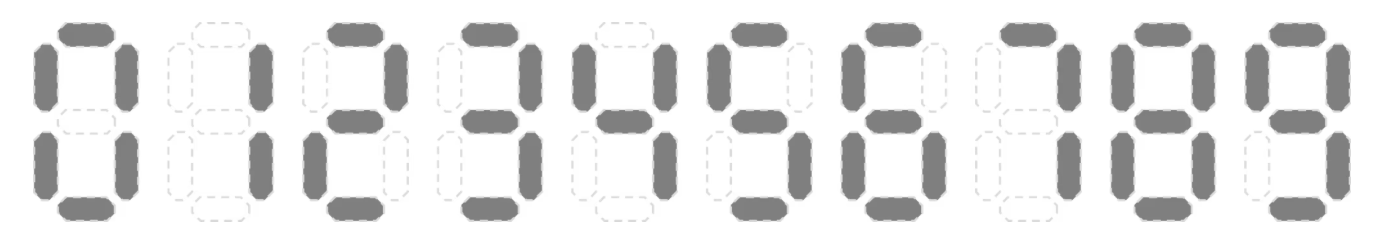
static int[][] display = {{1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, //0
{0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1}, //1
{0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0}, //2
{0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1}, //3
{1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1}, //4
{1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1}, //5
{1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1}, //6
{0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1}, //7
{1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}, //8
{1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1}}; //9숫자를 디지털 배열로 바꾸는 함수
public static int[] num_to_digit(int x) {
int[] result = new int[k];
for (int i = k - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
result[i] = x % 10;
x /= 10;
}
return result;
}예를 들어, 입력된 수가 1234라고 가정해봅시다. 이 경우 1, 2, 3, 4의 각 자리의 숫자를 분리하여 디스플레이에 표시된 LED 상태를 확인할 수 있습니다.
1 ~ N 까지 순회
-
check 메서드
check 메서드는 입력된 수와 다른 모든 수에 대해 LED 디스플레이의 상태를 비교하고, LED를 반전시킬 수 있는 경우의 수를 계산합니다. -
can_reverse 메서드:
can_reverse 메서드는 두 수의 각 자리의 LED 상태를 비교하여 LED를 반전시킬 수 있는지를 판단합니다.
public static void check(int num, int[] x_digit) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (i == x) continue;
if (can_reverse(i, x_digit)) count++;
}
}
public static boolean can_reverse(int target, int[] x_digit) {
int[] target_digit = num_to_digit(target);
int diff_count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 7; j++) {
if (display[x_digit[i]][j] != display[target_digit[i]][j]) {
diff_count++;
if (diff_count > p) return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}전체코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main { //문제유형: 브루트포스 , 메모리 제한: 512MB, 시간 제한: 1초
static int n, k, p, x;
static int[][] display = {{1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1}, //0
{0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1}, //1
{0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0}, //2
{0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1}, //3
{1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1}, //4
{1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1}, //5
{1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1}, //6
{0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1}, //7
{1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}, //8
{1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1}}; //9
static long count = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String s = br.readLine();
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(s);
n = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
k = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
p = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
x = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int[] x_digit = num_to_digit(x);
check(0, x_digit);
System.out.println(count);
}
public static void check(int num, int[] x_digit) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (i == x) continue;
if (can_reverse(i, x_digit)) count++;
}
}
public static boolean can_reverse(int target, int[] x_digit) {
int[] target_digit = num_to_digit(target);
int diff_count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 7; j++) {
if (display[x_digit[i]][j] != display[target_digit[i]][j]) {
diff_count++;
if (diff_count > p) return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
public static int[] num_to_digit(int x) {
int[] result = new int[k];
for (int i = k - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
result[i] = x % 10;
x /= 10;
}
return result;
}
}
