-
394. Decode String - 해결
class Solution: def decodeString(self, s: str) -> str: res = '' chars = '' stack_num = [] stack_str = [] stack_brace = [] for char in s: if char.isdigit(): stack_num.append(int(char)) elif char == "[": stack_brace.append("[") elif char == "]": stack_str.append(chars) stack_brace.pop() elif len(stack_num) == 0 and len(stack_brace) == 0 and len(stack_str) == 0: res += char else: chars += char if len(stack_num) > 0 and len(stack_str) > 0 and len(stack_brace) == 0: res += self.decode_str(stack_num, stack_str) stack_num = [] stack_str = [] chars = '' return res def decode_str (self, stack_num: list, stack_str: list) -> str: res = '' while len(stack_num) > 0: chars = stack_str.pop() num = stack_num.pop() if res == '': res = chars else: res += chars res = num * (res) return res처음에는 이런 식으로 해결하려고 했었지만
def test07(self): s = "3[a]2[b4[F]c]" ans = "aaabFFFFcbFFFFc" assert self.sl.decodeString(s) == ans이런 테스트를 통과하지 못했다. 😂
결국 생각을 다르게 하기로…
위에 문제를 풀려면 b4[F] → FFFF로 먼저 선행되어야 하는데 기존에 방식으로는 어렵다고 생각
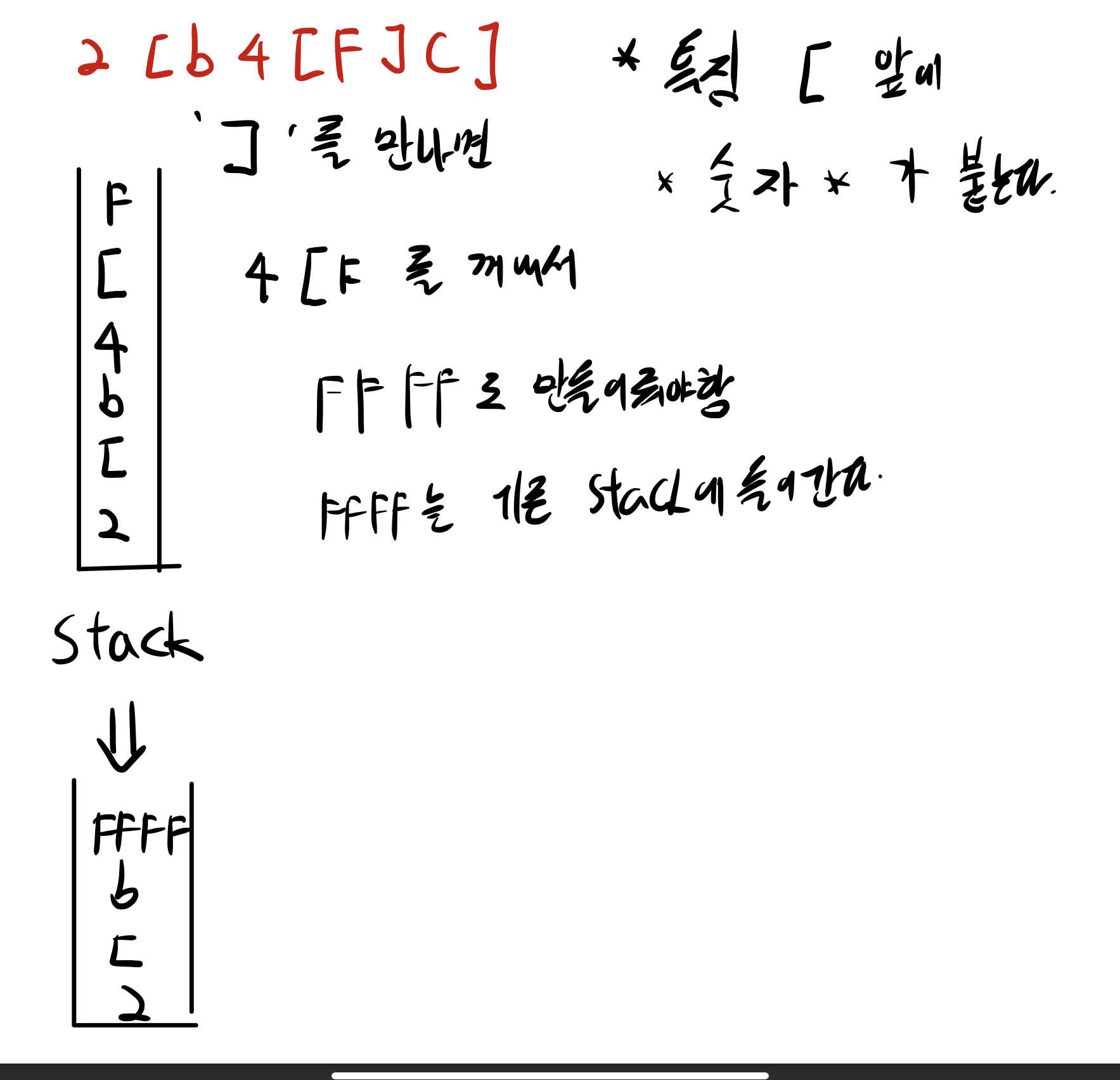
스택에 관련 char를 쌓으면서 처리하는 방법으로 구성
python은 언어 특성상 array를 reverse 하는 것이 편해서 코드를 짧게 구성할 수 있음
🚩해결
```python
class Solution:
def decodeString(self, s: str) -> str:
stack = []
for c in s:
if c != ']':
stack.append(c)
else:
tmp = []
while stack[-1] != "[":
tmp.append(stack.pop())
stack.pop()
chars = ''.join(tmp[::-1])
tmp = []
while stack and stack[-1].isdigit():
tmp.append(stack.pop())
times = tmp[::-1]
times = int(''.join(times))
chars = times * chars
stack.append(chars)
return ''.join(stack)
```