77번. Recyclable and Low Fat Products
Write a solution to find the ids of products that are both low fat and recyclable.
(링크)
low_fats 테이블에서 Y는 low fat이라는 것을, N는 아니라는 것을 의미
recyclable에서 Y는 recyclable이라는 것을, N은 아니라는 것을 의미
SELECT
product_id
FROM
products
WHERE
(low_fats = 'Y')
AND (recyclable = 'Y')
;새로운 사이트로 넘어가서 그런지 난이도가 급감...
78번. Find Customer Referee
Find the names of the customer that are not referred by the customer with id = 2.
(링크)
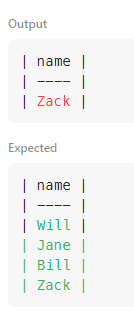
간단한 문제라 생각했고, 초안은 아래와 같다
SELECT
name
FROM
customer
WHERE
referee_id != 2
;하지만 답은 틀렸는데, referee_id가 null인 경우가 포함되지 않았기 때문
조건절이 문제인가 해서 not (referee_id = 2)로도 해보았지만 여전히 같은 문제 발생
조건절에 연산자를 넣으면 NULL을 제외한다
생각해보면, null은 연산을 할 수 없기 때문에 referee_id=2로 조건을 걸면 애초에 null값은 조건 양쪽에 모두 포함되지 않는다
SELECT
name
FROM
customer
WHERE
not (referee_id = 2)
OR referee_id is null
;결국 이 문제에서 핵심은
전처리 단계에서 referee_id에 null값이 있다는 것을 확인하고,
이를 기반으로 WHERE절을 적절하게 작성하는 것이었던 게 아닐까 싶다
79번. Big Countries
A country is big if:
-it has an area of at least three million (i.e., 3000000 km2), or
-it has a population of at least twenty-five million (i.e., 25000000).
Write a solution to find the name, population, and area of the big countries.
(링크)
country가 big하다는 조건 (1) area가 3000000 이상 (2) population이 25000000 이상
SELECT
name
, population
, area
FROM
world
WHERE
(area >= 3000000)
OR (population >= 25000000)
;3000000를 300000로 적어서 계속 wrong answer가 났었다;;
자리수라도 표기해줬으면..
80번 Article Views I
Write a solution to find all the authors that viewed at least one of their own articles.
Return the result table sorted by id in ascending order.
(링크)
table에 PK가 없고 중복된 row가 있을 수 있다 -> distinct가 필요할 것
author_id와 viewer_id가 동일한 경우 동일한 사람을 나타냄
자신의 article을 조회한 author들을 조회하라
-> author_id = view_id
"ID" 컬럼으로 오름차순 정렬해라
SELECT
distinct author_id as 'id'
FROM
views
WHERE
author_id = viewer_id
ORDER BY
author_id
;마지막에 출력할 컬럼명을 안 맞추면 그것도 오답 처리를 해서 살짝 헤맸다
당연히 코드에서 실수한 줄 알았네;
81. Invalid Tweets
Write a solution to find the IDs of the invalid tweets. The tweet is invalid if the number of characters used in the content of the tweet is strictly greater than 15.
Return the result table in any order.
(링크)
tweet_id가 PK
SNS 앱의 모든 트윗을 포함하고 있음
글자수가 15보다 크면 invalid tweet임
SELECT
tweet_id
FROM
tweets
WHERE
length(content) > 15
;len()인줄 알았는데 length()였다
len()은 파이썬이구나...
82번. Replace Employee ID With The Unique Identifier
Write a solution to show the unique ID of each user, If a user does not have a unique ID replace just show null.
Return the result table in any order.
(링크)
-employees 테이블
| id | name |
| -- | -------- |
| 1 | Alice |
| 7 | Bob |
| 11 | Meir |
| 90 | Winston |
| 3 | Jonathan |id가 PK
각 row에 id-name(of company)가 있다
-employeeUNI 테이블
| id | unique_id |
| -- | --------- |
| 3 | 1 |
| 11 | 2 |
| 90 | 3 |(id, unique_id)가 PK [Q. 튜플 형태로 PK가 가능한건가? 혹은 둘 다 PK라는 건가?]
각 row에 id와 그에 따른 unique_id가 있다
(기대 결과)
| unique_id | name |
| --------- | -------- |
| null | Alice |
| null | Bob |
| 2 | Meir |
| 3 | Winston |
| 1 | Jonathan |2개 테이블을 ID를 기준으로 JOIN해서
unique_id와 name을 출력하는 문제
SELECT
u.unique_id
, e.name
FROM
employees e
LEFT JOIN employeeuni u
ON u.id = e.id
;LEFT JOIN에서 어느 테이블을 왼쪽에 놓을 지 주의하자
기대 결과를 보면 alice, bob은 unique_id가 null이다
즉 unique_id가 없는 name값이 존재하는 테이블 = employees 테이블이 Left로 가야 한다
83번. Product Sales Analysis I
Write a solution to report the product_name, year, and price for each sale_id in the Sales table.
Return the resulting table in any order.
(링크)
Sales 테이블
| sale_id | product_id | year | quantity | price |
| ------- | ---------- | ---- | -------- | ----- |
| 1 | 100 | 2008 | 10 | 5000 |
| 2 | 100 | 2009 | 12 | 5000 |
| 7 | 200 | 2011 | 15 | 9000 |Product 테이블
| product_id | product_name |
| ---------- | ------------ |
| 100 | Nokia |
| 200 | Apple |
| 300 | Samsung |product_id를 기준으로 INNER JOIN하고
product_name, year, price를 출력하면 된다
84. Customer Who Visited but Did Not Make Any Transactions
Write a solution to find the IDs of the users who visited without making any transactions and the number of times they made these types of visits.
Return the result table sorted in any order.
(링크)
Visits 테이블
| visit_id | customer_id |
| -------- | ----------- |
| 1 | 23 |
| 2 | 9 |
| 4 | 30 |
| 5 | 54 |
| 6 | 96 |
| 7 | 54 |
| 8 | 54 |Transactions 테이블
| transaction_id | visit_id | amount |
| -------------- | -------- | ------ |
| 2 | 5 | 310 |
| 3 | 5 | 300 |
| 9 | 5 | 200 |
| 12 | 1 | 910 |
| 13 | 2 | 970 |방문은 했지만 거래를 하지 않은 user들의 ID를 찾고 (customer_id)
그들이 방문만 하고 거래를 하지 않은 횟수를 계산 (count_no_trans) -> LEFT JOIN
SELECT
v.customer_id as 'customer_id'
, count(v.customer_id) as 'count_no_trans'
FROM
visits v
LEFT JOIN transactions t
ON v.visit_id = t.visit_id
WHERE
t.transaction_id IS NULL
GROUP BY
v.customer_id
;85. Rising Temperature
(링크)
Write a solution to find all dates' id with higher temperatures compared to its previous dates (yesterday).
Return the result table in any order.
어제보다 temperature가 높은 date들의 ID를 출력
weather 테이블
| id | recordDate | temperature |
| -- | ---------- | ----------- |
| 1 | 2015-01-01 | 10 |
| 2 | 2015-01-02 | 25 |
| 3 | 2015-01-03 | 20 |
| 4 | 2015-01-04 | 30 |보다마자 떠오른 함수는 lead, lag()였다
temperature와 lag(temperature)를 뽑으면 쉽게 해결될 듯?
SELECT
id
# , temp
# , y_temp
FROM (
SELECT
id
, recordDate
, temperature as 'temp'
, lag(temperature , 1, null) over (order by recorddate) as 'y_temp'
FROM
weather
) a
WHERE
temp > y_temp
;LEAD() 함수와 LAG() 함수
다만 lag() 함수의 구성이 기억이 나지 않아 찾아봐야 했다
윈도우 함수였다는 사실도 잊고 있었으니...
(참고, 참고)
용법은 내가 기억하던 것과 동일하다
컬럼 하나를 찍고, 그 컬럼에서 n번째 이전/이후 값을 가져오는 것
LEAD(<expr>[,offset[,default_value]])
OVER ([PARTITION BY <expr>] ORDER BY <expr>)[..] 부분은 생략 가능하다.
offset : 지정시 N번째 값을 가져온다.
- default_value : N번째 값이 없을 경우 default_value값을 가져온다.
PARTITION BY : 지정시 GROUP 별로 행 값을 가져온다.
예제
SELECT location, continent, total_cases ,total_cases as 누적,
lag(total_cases) over(order by total_cases) as cases_lag,
lag(total_cases, 1, 0) over(order by total_cases) as cases_lag_1,
lag(total_cases, 2, 0) over(order by total_cases) as cases_lag_2
FROM corona_world
WHERE location = 'South Korea' ;내 식으로 풀어 쓰자면
lag(컬럼명, n번째 이전값, null이라면 반환값) over (파티션 컬럼 order by 컬럼)
# lead 함수도 동일이 중 n번째 이전값은 default = 1이고, 파티션은 필요하다면 넣고 아니면 생략 가능
데이터의 누락 가능성
문제가 발생했다
내가 작성한 코드는 매일의 데이터가 존재할 때는 성립하는데,
만약 중간에 누락된 날짜가 있으면 '하루 전'이 아닌 그 이전 값을 어제 데이터로 간주하여 계산하게 된다
즉 '어제 날짜 데이터'를 찾아내서 이걸 조건으로 해당하는 temperature를 뽑고 이와 비교하는 코드를 짜야하는 것
일단 하루 전의 날짜는 date_add() 함수로 쉽게 구할 수 있다
date_add(recorddate, interval -1 day) as 'y_date'문제는 하루 전 날짜에 맞는 온도를 다시 뽑는 것인데...
이건 떠오르지 않는다
대신 datediff() 함수를 사용해보기로 했다
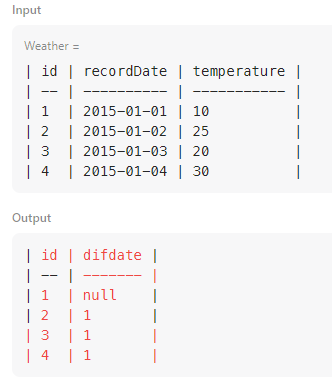
SELECT
id
, datediff(recorddate, lag_date) as 'difdate'
FROM (
SELECT
id
, recorddate
, temperature
, lag(recorddate, 1, null) over (order by recorddate) as 'lag_date'
FROM
weather
) a
;
이전 row의 날짜 데이터를 받아오는 새로운 컬럼을 만들고 (lag_date)
lag_date와 기존의 recorddate의 차이를 구해서 이것이 1일 때만 값을 출력하게 해보자
최종안
SELECT
id
FROM (
SELECT
id
, recorddate
, temperature
, lag(recorddate, 1, null) over (order by recorddate) as 'lag_date'
, lag(temperature, 1, null) over (order by recorddate) as 'lag_temp'
FROM
weather
) a
WHERE
# 이전 temperature 값보다 높을 때
(temperature > lag_temp)
# 이전 date와의 차이가 1day일 때 (==어제일 때)
AND (datediff(recorddate, lag_date) = 1)
;보다 효율적인 답안
다른 분들 답안을 보니, 내가 너무 복잡하게 생각했었나? 싶었다
SELECT
t.id
FROM
Weather t
CROSS JOIN Weather y #카데시안 곱
WHERE 1=1
AND (y.recordDate = DATE_ADD(t.recordDate, INTERVAL -1 DAY))
AND (t.temperature > y.temperature)
;
SELECT
t.id
FROM
Weather t
CROSS JOIN Weather y
WHERE
(DATEDIFF(t.recordDate, y.recordDate) = 1)
AND (t.temperature > y.temperature)
;weather 테이블을 '오늘=t'과 '내일=y' 2개의 테이블로 가정하여 카데시안 곱을 실행한다
그러면 아래처럼 t의 1개 row마다 y의 값들이 전부 매칭되게 된다
| id | recordDate | temperature | id | recordDate | temperature |
| -- | ---------- | ----------- | -- | ---------- | ----------- |
| 4 | 2015-01-04 | 30 | 1 | 2015-01-01 | 10 |
| 3 | 2015-01-03 | 20 | 1 | 2015-01-01 | 10 |
| 2 | 2015-01-02 | 25 | 1 | 2015-01-01 | 10 |
| 1 | 2015-01-01 | 10 | 1 | 2015-01-01 | 10 |
| 4 | 2015-01-04 | 30 | 2 | 2015-01-02 | 25 |
| 3 | 2015-01-03 | 20 | 2 | 2015-01-02 | 25 |
| 2 | 2015-01-02 | 25 | 2 | 2015-01-02 | 25 |
| 1 | 2015-01-01 | 10 | 2 | 2015-01-02 | 25 |
| 4 | 2015-01-04 | 30 | 3 | 2015-01-03 | 20 |
| 3 | 2015-01-03 | 20 | 3 | 2015-01-03 | 20 |
| 2 | 2015-01-02 | 25 | 3 | 2015-01-03 | 20 |
| 1 | 2015-01-01 | 10 | 3 | 2015-01-03 | 20 |이 때 조건에 맞게
1) t.recodedate가 y.recorddate보다 1 day 더 큰 경우 (datediff가 1인 경우)
2) t.temperature가 y.temperature보다 큰 경우
를 작성해주면 문제에서 의도하는 바만 남게 된다
