자료형
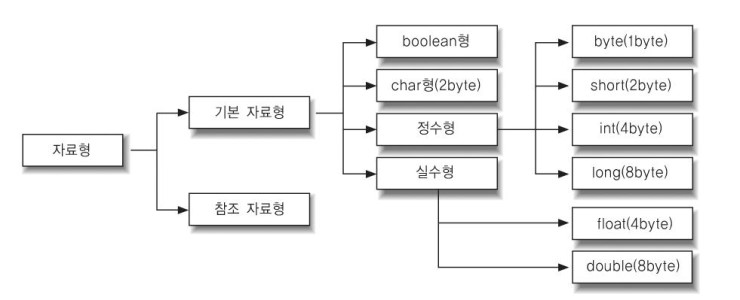
- 참조 자료형 : String, Array ..∞, 메모리 주소를 저장
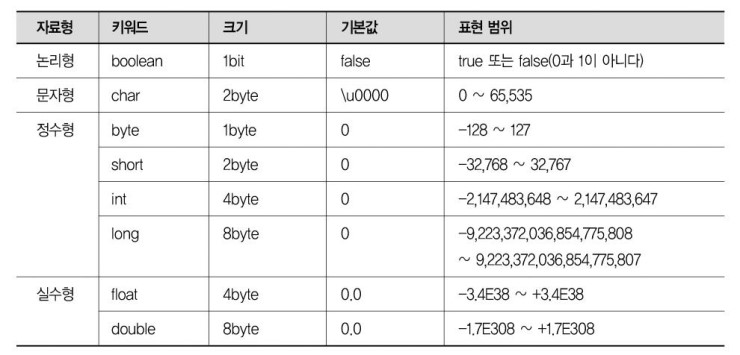
불 차 / 바 숏 인 롱 / 플 더
1 2 / 1 2 4 8 / 4 8 바이트
8 16 32 64 비트
리터럴 접미사
정수long 타입
- ✨✨
리터럴숫자+L - 없으면 int
- 👀👀 자료형이
byte,short인데도int라고??
-> 변수와 리터럴의 자료형이 일치하는 것이 기본이지만 불일치해도 OK인 경우가 있다. 단-128~127,-32768~32767라는 범위에 해당하는 수가 들어가야 한다.
-> 뒤에 변수와 리터럴의 불일치에서- 💖💖💖주의
(X) 리터럴 타입이 int이기 때문에
long l = 10_000_000_000; //백억, 에러->
(O) 리터럴 타입이 long이므로 해당 범위가 백억을 포함함
long l = 10_000_000_000L;실수 float 타입
- ✨✨
(소수점)리터럴+f d또는 생략 -> 실수double타입
리터럴 접두사
2진수(binary)
- ✨
0b+리터럴숫자
8진수(oct)
- ✨
0+리터럴숫자
16진수(hex)
- ✨
0x+리터럴숫자
1e3=1000.0, 아무것도 안붙었으니 double타입
e = 10의 n승
변수와 리터럴의 불일치
(O) 범위가 변수 > 리터럴
int i = 'A'; // int > char, -20억~20억 > 65
int l = 123; // long > int
double d = 3.14f; // double > float(X) 범위가 변수 < 리터럴
int i = 30억; // -20억~20억 < 30억
long l = 3.14f; // ✨long < float
float f = 3.14; // float < doublebyte, short변수에 int리터럴 저장가능
- 단 변수의 타입의 범위 이내에
char 과 for
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (char i = 'a'; i <= 'z'; i++)
{
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
}a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z
👀 작은따옴표와 큰따옴표를 저런 방식으로 쓰면 틀리게 나오거나 오류가 뜬다 !!
궁금해서 찾아보니,
- 큰따옴표" " : 문자열로 인식. 연산자 사용 시 붙기만 함. -> 문자열 결합 뒤에!
- 작은따옴표' ' : 아스키코드?로 인식. 연산자 사용 시 해당 아스키코드로 처리하여 각종 연산(+ - * / %) 등 사용 가능
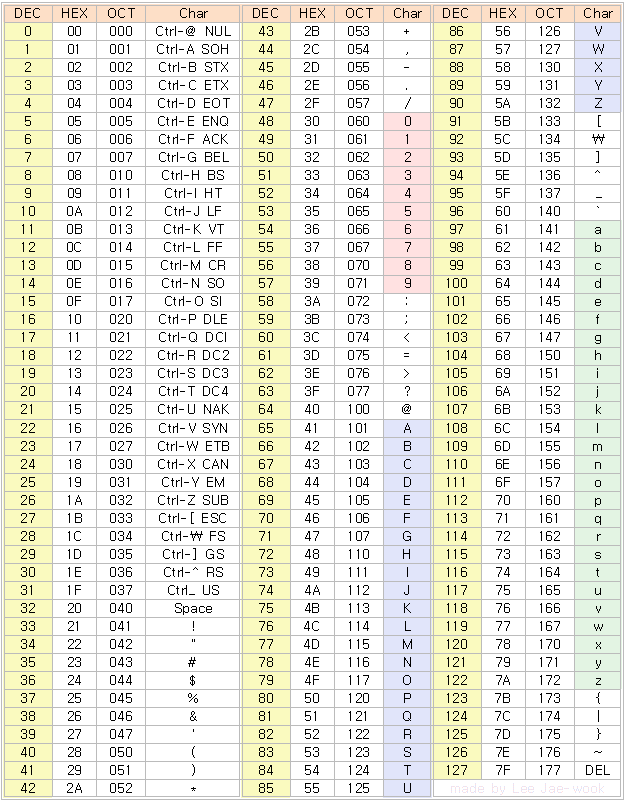
- a ~ z = 97 ~ 122, ' ' = 32
따라서
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (char i = 'a'; i <= 'z'; i++)
{
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println("\n");
for (char k = 'a'; k <= 'z'; k++)
{
System.out.print(k + ' ' + " ");
}
System.out.println("\n");
// 참고로 "a" 는 String 이기 때문에 안된다!
// String k = "a"; 요런식으로 해야함. 그러나 i++가 안되기 때문에 애초에 불가능
for (int j = 'a'; j <= 'z'; j++)
{
System.out.print(j + " ");
}
}
}
// 애초에 정수로 인식했기에 아스키코드로 처리
// 만약 " " 대신 ' '로 한다면 두번째와 같은 결과가 나옴
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z
129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154
∵ 129 (= 97 + 32) ... 154 (= 122 + 32)
97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122
아스키코드
문자열과 '+'
문자열 결합
"문자열"과+가 만날 때 붙기만 한다!!
String s = "A" + "B"; -> "AB"
anytype + "" // "" + anytype -> ""
- 어떤 타입이든 문자열과 결합(+)하면 문자열이 된다.
✨✨숫자를 문자열로 변환하는 방법
"" + 7 -> "7" : 숫자를 빈 문자열과 결합하기
순서는 왼쪽에서 오른쪽으로
"" + 7 + 7 -> ✨"7" + 7 -> ✨"7" + "7" -> "77"
7 + 7 + "" -> 14 + "" -> "14"
진수 변환
system.out.format("String format", Object... args);
- 해당 포맷으로 변환
- ✨큰따옴표 " "
- 개행 없음
- %o : 8진수
%x : 16진수
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 200;
System.out.println("10진수 : " + a);
System.out.format("8진수 : %o\n", a);
System.out.format("16진수 : %x\n", a);
}
}
10진수 : 200
8진수 : 310
16진수 : c8String, substring
System.out.println("String".substring(int beginindex, int endindex));
- beginindex : 0, 1, 2 ... n 번째에서 시작하여
- endindex : endindex-1 까지 출력
- endindex가 없으면 끝까지 출력
- return된 문자열의 길이 = endindex - beginindex
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "Jone Doe";
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(name.substring(0, 1));
System.out.println(name.substring(3, 6));
System.out.println(name.substring(5, 8));
System.out.println(name.substring(0, 4));
}
}Jone Doe
J
e D
Doe
Jone