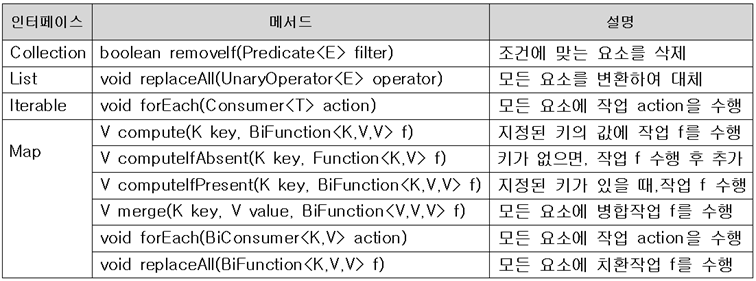
컬렉션 프레임워크와 함수형 인터페이스
- 함수형 인터페이스를 사용하는 컬렉션 프레임워크의 메소드.
- 여기선 와일드카드를 생략했다.
- ✨✨
forEach가 가장 많이 쓰임
list.forEach(i -> System.out.print(i + ", ")); //list의 모든요소 출력
list.removeIf(x -> x%2 == 0 || x%3 == 0); //2 또는 3의 배수인 list의 요소들 제거
list.replaceAll(i -> i*10); //list의 모든 요소에 10을 곱한다.
//***map의 모든 요소를 {k,v}, {k,v} ...의 형식으로 출력
map.forEach( (k,v) -> System.out.print("{"+k+","+v+"},");- CF를 사용하면서 불편한 게 많았는데, 이젠 간단해졌다!!!!😍😍
ex14_4
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
public class Ex14_04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
list.add(i);
//***list의 모든 요소를 출력하는 방법
//1.
list.forEach(i -> System.out.print(i+", "));
System.out.println();
//2.
System.out.println(list);
//3.
Iterator it = list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext())
System.out.print(it.next()+", ");
System.out.println();
//list의 요소 중 2 또는 3의 배수인 요소를 제거한다.
list.removeIf(x -> x%2==0 || x%3==0);
// list.forEach(i -> System.out.print(i+", "));
System.out.println(list);
//list의 각 요소에 10을 곱한다.
list.replaceAll(i -> i*10);
System.out.println(list);
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("1", "10");
map.put("2", "20");
map.put("3", "30");
map.put("4", "40");
//***map의 모든 요소를 {k,v}, {k,v}, ... 의 형식으로 출력한다.
//1.
map.forEach((k,v) -> System.out.print("{"+k+","+v+"}, "));
System.out.println();
//2.
System.out.println(map);
//3.
Iterator it2 = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(it2.hasNext())
System.out.print(it2.next()+", ");
System.out.println();
}
}0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
[1, 5, 7]
[10, 50, 70]
{1,10}, {2,20}, {3,30}, {4,40},
{1=10, 2=20, 3=30, 4=40}
1=10, 2=20, 3=30, 4=40, 