특징
특징1
- fundamental building block in the program
- subprogram can be used multiplie times
- performs a task or calculate a value
first-class function
- functions are treated like any other variable
- can be assigned as a value to variable
: 변수의 값에 할당될 수 있다.
- can be passed as an argument to other funtions
: 다른 함수의 인자(파라미터)로 보낼 수 있다.
- can be returned by another function
: 다른 함수의 리턴 값이 될 수 있다.
Function declaration
function name(param1, param2){
body ....
return ;
}
- one function === one thing
- naming : doSomething, command, verb
-> 무언가를 한다 이런거
- function is object in JS
function printHello() {
console.log("Hello");
}
printHello();
function log(message) {
console.log(message);
}
log("hellooooo");
log(123);
console.log("-----------------------------");

Parameters
- primitive parameters : passed by value
- object parameters : passed by reference
-> 참조 형태로
function changeName(obj) {
obj.name = "coder";
}
const ellie2 = {
name: "ellie",
};
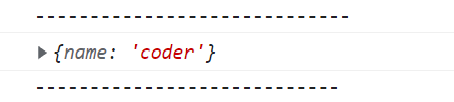
changeName(ellie2);
console.log(ellie2);
console.log("----------------------------");
Default parameters (added in ES6)
parameter = 'unknown'
function showMessage(message, from = "unknown") {
console.log(`${message} by ${from}`);
}
showMessage("hihihi nicoco");
console.log("---------------------------");

Rest parameters (added in ES6)
parameter = ...args
- 배열 형태로
function printAll(...args) {
for (let i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
console.log(args[i]);
}
for (const arg of args) {
console.log(arg);
}
args.forEach((arg) => console.log(arg));
}
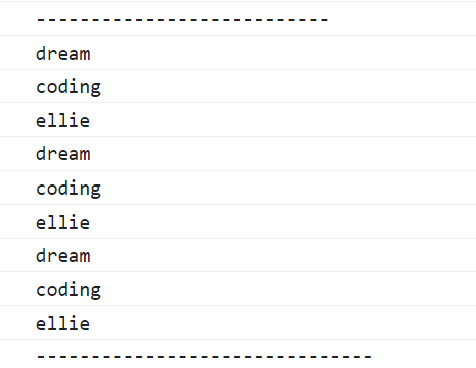
printAll("dream", "coding", "ellie");
console.log("-------------------------------");
Local scope
let globalMessage = "global";
function printMessage() {
let message = "hello";
console.log(message);
console.log(globalMessage);
function printAnother() {
console.log(message);
let childMessage = "hello";
}
return undefined;
}
printMessage();
console.log("-------------------------------");

Return a value
function sum(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
const result = sum(1, 2);
console.log(`result: ${result}`);
console.log(`sum: ${sum(1, 2)}`);
console.log("-------------------------------");

✨Early return, early exit
bad
function badUpgradUser(user) {
if (user.point > 10) {
}
}
good
- ✨✨✨조건이 맞지 않을 때 빨리 리턴하도록
-> 조건이 맞지 않은 경우/ 값이 -1이거나 undefined 인 경우
function goodUpgradeUser(user) {
if (user.point <= 10) {
return;
}
}
Function expression
- a function declaration can be called earlier than it is defined. (hoisted)
: 선언보다 호출을 먼저 해도 된다.
- a function expression is created when the excution reaches it.
할당된 변수에 ()를 붙이면 함수처럼 사용할 수 있다.
- 재할당 시 재할당된 ✨✨변수의 값엔
()를 붙이지 않기
const print = function () {
console.log("print");
};
print();
const printAgain = print;
printAgain();
const sumAgain = sum;
sumAgain();
console.log(sumAgain(1, 3));
console.log("----------------------------------");

Callback function
- Callback function using function expression
- 다른 코드의 인수로서 넘겨주는 실행 가능한 코드를 말한다. 콜백을 넘겨받는 코드는 이 콜백을 필요에 따라 즉시 실행할 수도 있고, 아니면 나중에 실행할 수도 있다.
function randomQuiz(answer, printYes, printNo) {
if (answer === "love you") {
printYes();
} else {
printNo();
}
}
const printYes = function () {
console.log("yes!");
};
const printNo = function prints() {
console.log("no!");
};
randomQuiz("wrong", printYes, printNo);
randomQuiz("love you", printYes, printNo);

Arrow function
const simplePrint = () => {
console.log("simplerPrint!");
};
const add = (a, b) => a + b;
const simpleMultiply = (a, b) => {
return a * b;
};
IIFE
- IIFE : Immediately Invoked Function Expression
- 선언과 동시에 호출
(function hello() {
console.log("IIFE");
})();










