1. 실행 컨텍스트란? 🎯
JavaScript에서 코드가 실행되는 환경을 정의하는 핵심 개념입니다.
🔍 실행 컨텍스트의 정의
실행 컨텍스트(Execution Context)는 자바스크립트가 코드를 실행할 때 필요한 모든 정보를 담고 있는 박스라고 생각하면 됩니다.
- 동일한 환경에 있는 코드들을 실행할 때 필요한 환경 정보들을 모아 구성된 객체
- 코드가 실행될 때 필요한 변수, 객체, 함수 등을 정의
- 콜 스택에 쌓아올려지며, 가장 위에 있는 컨텍스트의 코드가 실행됨
💡 왜 중요한가?
실행 컨텍스트를 이해하면 다음을 알 수 있습니다:
- 스코프(Scope): 변수의 유효 범위
- 호이스팅(Hoisting): 변수와 함수 선언의 끌어올림
- 클로저(Closure): 함수와 렉시컬 환경의 조합
- this 바인딩: this 키워드의 동작 원리
💡 자바스크립트의 동적 언어 특성
실행 컨텍스트는 자바스크립트의 동적 언어로서의 성격을 가장 잘 보여주는 개념입니다!
2. 실행 컨텍스트의 생성과 실행 🔄
📋 실행 컨텍스트의 단계
1️⃣ 생성 단계 (Creation Phase)
- 변수 환경 생성 (호이스팅 발생)
- 렉시컬 환경 생성
- this 바인딩 결정
2️⃣ 실행 단계 (Execution Phase)
- 코드 실행
- 변수 할당
- 함수 호출🎯 생성 단계 상세
1️⃣ 변수 환경 생성
// 코드 작성
console.log(name); // undefined (호이스팅!)
var name = "Alice";
console.log(name); // "Alice"생성 단계에서 일어나는 일:
var변수는undefined로 초기화- 함수 선언문은 전체가 메모리에 저장
2️⃣ 렉시컬 환경 생성
function outer() {
let x = 10; // 렉시컬 환경에 저장
function inner() {
console.log(x); // 외부 환경 참조로 접근
}
inner();
}
outer(); // 10렉시컬 환경의 구성:
- 환경 레코드: 변수와 함수 저장
- 외부 환경 참조: 상위 스코프 연결
3️⃣ this 바인딩
const obj = {
name: "JavaScript",
greet() {
console.log(this.name);
}
};
obj.greet(); // "JavaScript"3. 실행 컨텍스트의 종류 📦
🌐 전역 실행 컨텍스트
프로그램이 시작될 때 생성되는 기본 컨텍스트입니다.
var globalVar = "전역 변수";
function globalFunction() {
console.log("전역 함수! 🌍");
}
// 전역 컨텍스트에서 실행
globalFunction(); // "전역 함수! 🌍"특징:
- 프로그램 실행 시 가장 먼저 생성
- 단 하나만 존재
- 브라우저에서는
window, Node.js에서는global객체와 연결 - 프로그램 종료까지 유지
// 브라우저 환경
var a = 5;
console.log(window.a); // 5
window.globalFunction(); // "전역 함수! 🌍"🔧 함수 실행 컨텍스트
함수가 호출될 때마다 생성됩니다.
function first() {
console.log("First! 1️⃣");
second();
}
function second() {
console.log("Second! 2️⃣");
third();
}
function third() {
console.log("Third! 3️⃣");
}
first();
/* 출력:
First! 1️⃣
Second! 2️⃣
Third! 3️⃣
*/특징:
- 함수 호출 시마다 생성
- 함수마다 고유한 컨텍스트 보유
- 실행 종료 후 콜 스택에서 제거
4. 실행 컨텍스트의 구성 요소 🧩
📊 구성 요소 개요
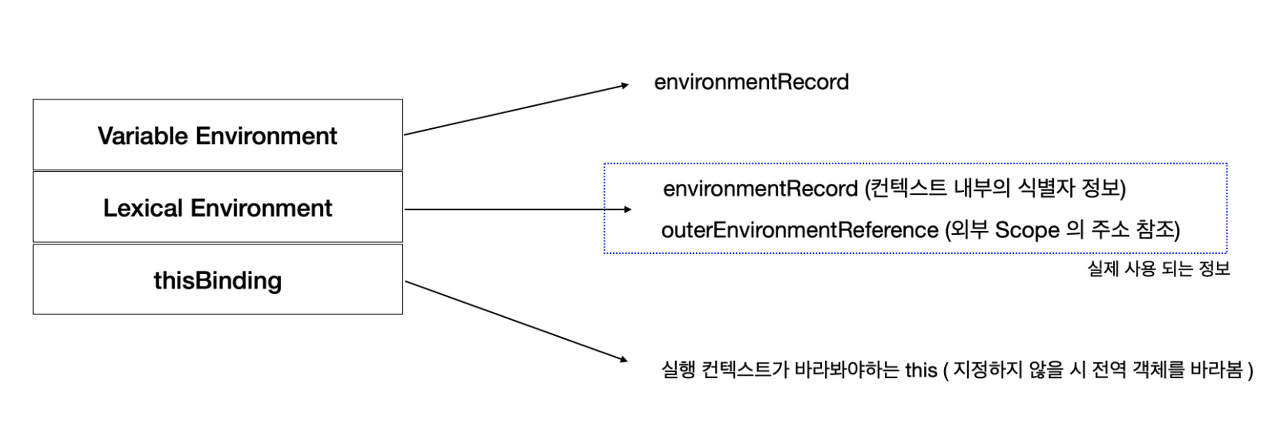
실행 컨텍스트
├── Lexical Environment (렉시컬 환경)
│ ├── Environment Record (환경 레코드)
│ └── Outer Environment Reference (외부 환경 참조)
│
├── Variable Environment (변수 환경)
│ └── Environment Record (환경 레코드)
│
└── This Binding (this 바인딩)1️⃣ Lexical Environment (렉시컬 환경)
정의: 코드의 스코프와 관련된 정보를 관리하는 구조
function outer() {
let x = 10; // outer의 환경 레코드
function inner() {
let y = 20; // inner의 환경 레코드
console.log(x + y); // 외부 환경 참조로 x 접근
}
inner(); // 30
}
outer();구성 요소:
📝 환경 레코드 (Environment Record)
현재 스코프의 변수와 함수를 저장합니다.
function example() {
let a = 1;
const b = 2;
function helper() {}
// 환경 레코드: { a: 1, b: 2, helper: function }
}🔗 외부 환경 참조 (Outer Environment Reference)
상위 스코프를 참조하여 스코프 체인을 만듭니다.
let global = "전역";
function level1() {
let x = 10;
function level2() {
let y = 20;
function level3() {
let z = 30;
// 스코프 체인: level3 → level2 → level1 → global
console.log(global + x + y + z);
}
level3();
}
level2();
}
level1(); // "전역102030"2️⃣ Variable Environment (변수 환경)
정의: var로 선언된 변수와 함수 선언을 관리
function test() {
console.log(x); // undefined (호이스팅)
var x = 10;
console.log(x); // 10
}
test();변수 환경 vs 렉시컬 환경:
| 특징 | Variable Environment | Lexical Environment |
|---|---|---|
| 관리 대상 | var, 함수 선언 | let, const, 함수 |
| 외부 참조 | 없음 | 있음 (스코프 체인) |
| 값 추적 | 초기값만 기억 | 실행 중 값 변경 반영 |
function outer() {
var x = 10; // 변수 환경에 저장
function inner() {
console.log(x); // 렉시컬 환경의 외부 참조로 접근
}
x = 20; // 값 변경
inner(); // 20 (렉시컬 환경은 변경된 값 참조)
}
outer();3️⃣ This Binding
정의: 현재 실행 컨텍스트의 this 값 결정
// 1. 전역 컨텍스트
console.log(this); // window (브라우저)
// 2. 함수 호출
function showThis() {
console.log(this);
}
showThis(); // window (또는 undefined in strict mode)
// 3. 메서드 호출
const obj = {
name: "객체",
method() {
console.log(this.name);
}
};
obj.method(); // "객체"
// 4. 생성자 함수
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
const person = new Person("Alice");
console.log(person.name); // "Alice"
// 5. 화살표 함수
const obj2 = {
name: "화살표",
method: () => {
console.log(this.name);
}
};
obj2.method(); // undefined (상위 스코프의 this)5. 콜 스택과 실행 컨텍스트 📚
🔄 콜 스택의 동작
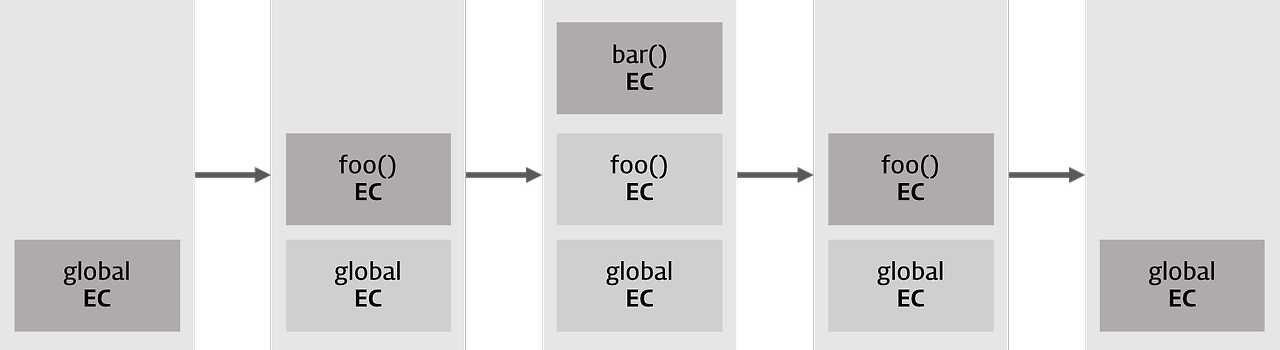
var x = 'xxx';
function foo() {
var y = 'yyy';
function bar() {
var z = 'zzz';
console.log(x + y + z);
}
bar();
}
foo(); // "xxxyyyzzz"실행 순서:
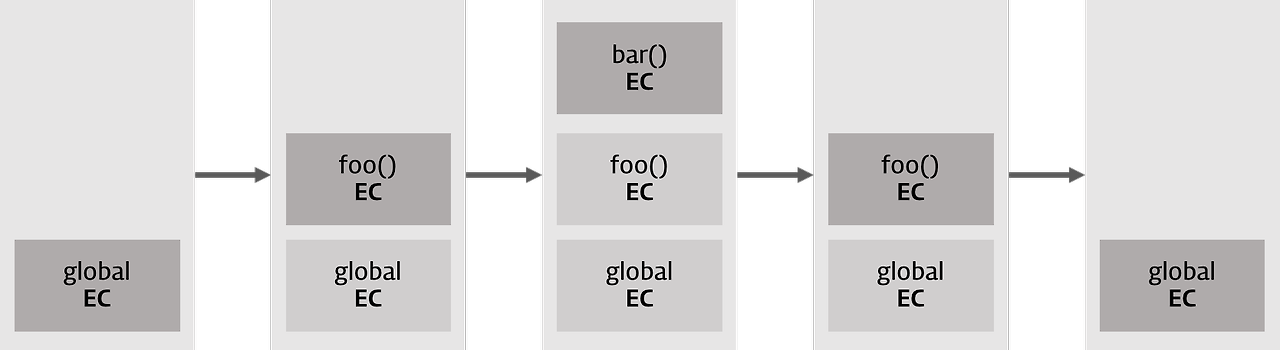
1️⃣ 전역 실행 컨텍스트 생성
└── 콜 스택: [전역]
2️⃣ foo() 호출
└── 콜 스택: [전역, foo]
3️⃣ bar() 호출
└── 콜 스택: [전역, foo, bar]
4️⃣ bar() 종료
└── 콜 스택: [전역, foo]
5️⃣ foo() 종료
└── 콜 스택: [전역]💡 상세 예시
function first() {
console.log("1️⃣ First function start");
second();
console.log("1️⃣ First function end");
}
function second() {
console.log(" 2️⃣ Second function start");
third();
console.log(" 2️⃣ Second function end");
}
function third() {
console.log(" 3️⃣ Third function");
}
console.log("🌐 Global start");
first();
console.log("🌐 Global end");
/* 출력:
🌐 Global start
1️⃣ First function start
2️⃣ Second function start
3️⃣ Third function
2️⃣ Second function end
1️⃣ First function end
🌐 Global end
*/6. 스코프 체인 🔗
🎯 스코프 체인이란?
변수를 찾을 때 현재 스코프에서 시작하여 상위 스코프로 이어지는 연결 고리입니다.
let level1 = "L1";
function outer() {
let level2 = "L2";
function middle() {
let level3 = "L3";
function inner() {
let level4 = "L4";
// 스코프 체인을 통한 변수 검색
console.log(level4); // 현재 스코프
console.log(level3); // 상위 스코프 (middle)
console.log(level2); // 상위 스코프 (outer)
console.log(level1); // 전역 스코프
}
inner();
}
middle();
}
outer();
/* 출력:
L4
L3
L2
L1
*/📊 스코프 체인 시각화
let x = 10;
function foo() {
let y = 20;
function bar() {
let z = 30;
console.log(x + y + z); // 10 + 20 + 30
}
bar();
}
foo(); // 60스코프 체인 구조:
bar의 렉시컬 환경
├── 환경 레코드: { z: 30 }
└── 외부 환경 참조 → foo의 렉시컬 환경
├── 환경 레코드: { y: 20 }
└── 외부 환경 참조 → 전역 환경
└── 환경 레코드: { x: 10 }⚠️ 스코프 체인의 한계
function outer() {
let x = 10;
}
function other() {
console.log(x); // ReferenceError: x is not defined
}
outer();
other();스코프 체인은 선언된 위치(렉시컬)를 기준으로 형성됩니다!
7. 클로저와 실행 컨텍스트 🔐
🎯 클로저란?
클로저(Closure): 반환된 내부 함수와 내부 함수가 선언되었던 렉시컬 환경의 조합
function makeCounter() {
let count = 0; // 외부 함수의 변수
return function() {
count++; // 클로저: 외부 함수 종료 후에도 접근 가능
return count;
};
}
const counter1 = makeCounter();
console.log(counter1()); // 1
console.log(counter1()); // 2
console.log(counter1()); // 3
const counter2 = makeCounter();
console.log(counter2()); // 1 (독립적인 클로저)💡 클로저의 동작 원리
function outer() {
let privateVar = "비밀 변수 🔒";
return {
getPrivate() {
return privateVar;
},
setPrivate(value) {
privateVar = value;
}
};
}
const instance1 = outer();
console.log(instance1.getPrivate()); // "비밀 변수 🔒"
instance1.setPrivate("변경된 값 ✨");
console.log(instance1.getPrivate()); // "변경된 값 ✨"
const instance2 = outer();
console.log(instance2.getPrivate()); // "비밀 변수 🔒" (독립적)🌟 실용적인 클로저 예시
// 1. 데이터 은닉
function createBankAccount(initialBalance) {
let balance = initialBalance;
return {
deposit(amount) {
balance += amount;
return `입금 완료! 잔액: ${balance}원 💰`;
},
withdraw(amount) {
if (balance >= amount) {
balance -= amount;
return `출금 완료! 잔액: ${balance}원 💸`;
}
return "잔액 부족! ⚠️";
},
getBalance() {
return `현재 잔액: ${balance}원 💵`;
}
};
}
const myAccount = createBankAccount(10000);
console.log(myAccount.deposit(5000)); // "입금 완료! 잔액: 15000원 💰"
console.log(myAccount.withdraw(3000)); // "출금 완료! 잔액: 12000원 💸"
console.log(myAccount.getBalance()); // "현재 잔액: 12000원 💵"
// console.log(balance); // ReferenceError (외부에서 접근 불가)// 2. 함수 팩토리
function createMultiplier(multiplier) {
return function(num) {
return num * multiplier;
};
}
const double = createMultiplier(2);
const triple = createMultiplier(3);
const quadruple = createMultiplier(4);
console.log(double(5)); // 10
console.log(triple(5)); // 15
console.log(quadruple(5)); // 208. this 바인딩 상세 가이드 🎭
📌 바인딩이란?
바인딩: 식별자와 값을 연결하는 과정
🎯 this 바인딩 규칙
1️⃣ 전역 컨텍스트
console.log(this); // window (브라우저) / global (Node.js)
function showGlobalThis() {
console.log(this);
}
showGlobalThis(); // window (non-strict) / undefined (strict)2️⃣ 암시적 바인딩 (메서드 호출)
const person = {
name: "Alice",
greet() {
console.log(`안녕하세요, ${this.name}입니다! 👋`);
}
};
person.greet(); // "안녕하세요, Alice입니다! 👋"
// ⚠️ 주의: 메서드를 변수에 할당하면?
const greetFunc = person.greet;
greetFunc(); // "안녕하세요, undefined입니다! 👋" (this가 전역 객체)3️⃣ 명시적 바인딩 (call, apply, bind)
const person1 = { name: "Alice" };
const person2 = { name: "Bob" };
function introduce(greeting, punctuation) {
console.log(`${greeting}, 저는 ${this.name}입니다${punctuation}`);
}
// call: 인자를 개별적으로 전달
introduce.call(person1, "안녕하세요", "!");
// "안녕하세요, 저는 Alice입니다!"
// apply: 인자를 배열로 전달
introduce.apply(person2, ["Hello", "."]);
// "Hello, 저는 Bob입니다."
// bind: 새로운 함수 생성
const aliceIntroduce = introduce.bind(person1);
aliceIntroduce("Hi", "~");
// "Hi, 저는 Alice입니다~"4️⃣ new 바인딩 (생성자 함수)
function User(name, age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.greet = function() {
console.log(`${this.name} (${this.age}세) 👤`);
};
}
const user1 = new User("Alice", 25);
const user2 = new User("Bob", 30);
user1.greet(); // "Alice (25세) 👤"
user2.greet(); // "Bob (30세) 👤"5️⃣ 화살표 함수
// ❌ 일반 함수: this가 호출 방식에 따라 달라짐
const obj1 = {
name: "일반 함수",
regularFunc: function() {
setTimeout(function() {
console.log(this.name); // undefined (this가 전역)
}, 100);
}
};
// ✅ 화살표 함수: 상위 스코프의 this 사용
const obj2 = {
name: "화살표 함수",
arrowFunc: function() {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(this.name); // "화살표 함수"
}, 100);
}
};
obj1.regularFunc(); // undefined
obj2.arrowFunc(); // "화살표 함수"9. 호이스팅 완벽 이해 🎈
🔍 호이스팅이란?
변수와 함수 선언이 코드 실행 전에 메모리에 저장되어 마치 코드의 최상단으로 끌어올려진 것처럼 동작하는 현상
📝 var 호이스팅
console.log(x); // undefined (선언은 호이스팅, 할당은 X)
var x = 10;
console.log(x); // 10
// 위 코드는 실제로 이렇게 동작:
// var x; // 선언 호이스팅
// console.log(x); // undefined
// x = 10; // 할당은 원래 위치
// console.log(x); // 10🚫 let, const 호이스팅
// ❌ TDZ (Temporal Dead Zone) 에러
console.log(y); // ReferenceError: Cannot access 'y' before initialization
let y = 20;
console.log(z); // ReferenceError: Cannot access 'z' before initialization
const z = 30;TDZ (일시적 사각지대):
let x = 10;
function example() {
// TDZ 시작
console.log(x); // ReferenceError (외부 x가 아닌 내부 x 참조 시도)
let x = 20; // TDZ 종료
// x 사용 가능
}🔧 함수 호이스팅
// ✅ 함수 선언문: 전체 호이스팅
hello(); // "Hello! 👋" (호출 가능)
function hello() {
console.log("Hello! 👋");
}
// ❌ 함수 표현식: 변수만 호이스팅
greet(); // TypeError: greet is not a function
var greet = function() {
console.log("Greet! 🎉");
};
// ❌ 화살표 함수: 변수만 호이스팅
wave(); // TypeError: wave is not a function
const wave = () => {
console.log("Wave! 🌊");
};10. 실전 활용 패턴 ⚡
🎯 즉시 실행 함수 (IIFE)
// 전역 스코프 오염 방지
(function() {
var private = "비공개 변수";
console.log("IIFE 실행! 🚀");
})();
// console.log(private); // ReferenceError
// 매개변수 전달
(function(name) {
console.log(`Hello, ${name}! 👋`);
})("Alice");🔒 모듈 패턴
const calculator = (function() {
// Private 변수
let result = 0;
// Private 함수
function log(message) {
console.log(`[Calculator] ${message}`);
}
// Public API 반환
return {
add(num) {
result += num;
log(`Added ${num}, result: ${result}`);
return this;
},
subtract(num) {
result -= num;
log(`Subtracted ${num}, result: ${result}`);
return this;
},
multiply(num) {
result *= num;
log(`Multiplied by ${num}, result: ${result}`);
return this;
},
getResult() {
return result;
},
reset() {
result = 0;
log("Reset!");
return this;
}
};
})();
// 메서드 체이닝
calculator
.add(10) // [Calculator] Added 10, result: 10
.multiply(2) // [Calculator] Multiplied by 2, result: 20
.subtract(5); // [Calculator] Subtracted 5, result: 15
console.log(calculator.getResult()); // 15🏭 팩토리 패턴
function createUser(name, role) {
// Private 변수
let isAuthenticated = false;
return {
// Public 메서드
getName() {
return name;
},
getRole() {
return role;
},
login() {
isAuthenticated = true;
console.log(`${name} logged in as ${role} ✅`);
},
logout() {
isAuthenticated = false;
console.log(`${name} logged out ❌`);
},
isLoggedIn() {
return isAuthenticated;
}
};
}
const admin = createUser("Alice", "admin");
const user = createUser("Bob", "user");
admin.login(); // Alice logged in as admin ✅
console.log(admin.isLoggedIn()); // true
user.login(); // Bob logged in as user ✅
console.log(user.isLoggedIn()); // true