1. 스트림 생성하기
- Collection -> Stream
Collection의 경우 .stream() 을 사용해 스트림을 만들 수 있다.
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c");
Stream<String> listStream = list.stream();- 배열 -> Stream
배열의 경우 Stream.of(), Arrays.stream() 을 사용해 스트림을 만들 수 있다.
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("a", "b", "c");
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of(new String[] {"a", "b", "c"});
Stream<String> stream = Arrays.stream(new String[] {"a", "b", "c"});2. 스트림 가공하기
2-1. 필터링
- filter
Filter는 Stream에서 조건에 맞는 데이터만을 뽑아내는 연산입니다.
함수의 인자로 함수형 인터페이스 Predicate를 받고 있기 때문에
boolean을 반환하는 람다식을 작성하여 filter 함수를 구현할 수 있습니다.
return votes.stream()
.filter(Region -> Region.getUserDto().getUserId().equals(user.getUserId()) ||Region.getRegionRestriction().getDisplayValue().equals(region) || Region.getRegionRestriction().equals(RegionRestriction.All) )
.filter(Gender -> Gender.getUserDto().getUserId().equals(user.getUserId()) ||Gender.getGenderRestriction().getDisplayValue().equals(gender) || Gender.getGenderRestriction().equals(GenderRestriction.All))
.filter(Friends -> Friends.getUserDto().getUserId().equals(user.getUserId()) || Friends.getDisplayRange().equals(DisplayRange.PUBLIC) || followRepository.findByFromUserAndToUser(user, Friends.getUserDto().toEntity()) !=null && followRepository.findByFromUserAndToUser(user, Friends.getUserDto().toEntity()).isFriend() )
.filter(Age -> Age.getUserDto().getUserId().equals(user.getUserId()) || Age.getAgeRestriction().getDisplayValue().equals(age_range) || Age.getAgeRestriction().equals(AgeRestriction.All))
.collect(Collectors.toList());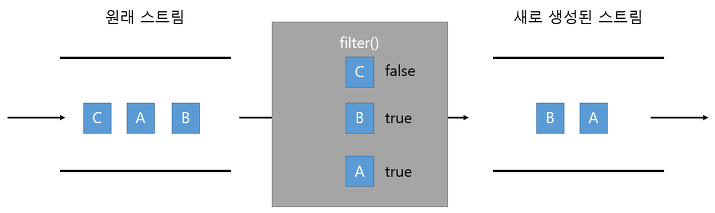
- distinct
distinct() 메소드는 중복을 제거해 줍니다.
.equals(Object) 가 true 이면 동일한 객체로 판단하고 중복을 제거합니다.
따라서 우리는 equals와 hashCode를 오버라이드 해야합니다.
또한, IntStream, LongStream, DoubleStream은 동일값일 경우 중복을 제거합니다.
return list.stream()
.distinct()
.기타 연산~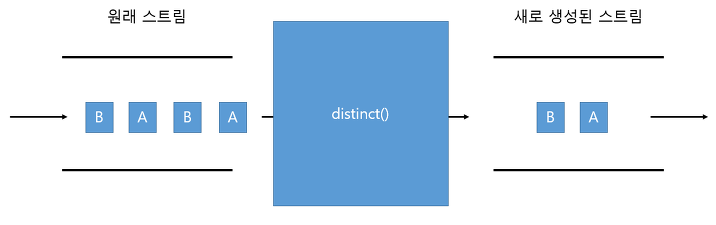
2-2. 매핑
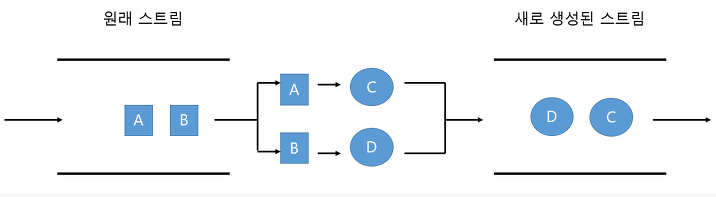
- map
Map은 기존의 Stream 요소들을 변환하여 새로운 Stream을 만드는 연산입니다.
값을 특정한 형태로 변환하는데 주로 사용되며,
함수의 인자로 함수형 인터페이스 function을 받고 있습니다.
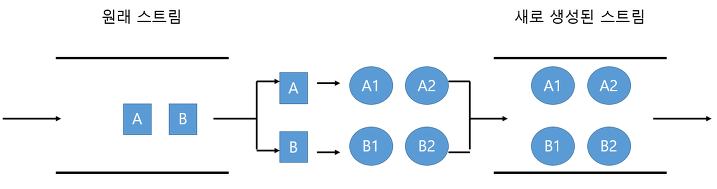
- flatmap
2중 배열 또는 2중 리스트 -> 1차원으로 바꾸는 연산입니다.
.stream()을 통해 껍데기를 한번 벗기고
.flatMap()을 통해 한번 더 벗겨서 사용하게 됩니다.
flatMap은 Function 함수형 인터페이스를 매개 변수로 받고 있습니다.
List<Vote> votes = voteRepository.findAll(); // 1차원 리스트
List<VoteDto> map = votes.stream() // .stream()을 통해 껍데기를 한번 벗기면 Vote가 나옴
.map(VoteDto::from) // 여기서 Vote -> VoteDto 로 변환
.peek(System.out::println)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
List<List<Vote>> votesList = Arrays.asList(votes); // 2차원 리스트
List<VoteDto> flatmap = votesList.stream() // .stream()을 통해 껍데기를 한번 벗기면 List<Vote>가 나옴
.flatMap(flat -> flat.stream()) // .flatMap()을 통해 List<Vote> -> Vote 로 변환
.map(VoteDto::from) // 여기서 Vote -> VoteDto 로 변환
.peek(System.out::println)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
- 결과

2-3. 정렬
- sort
스트림은 요소가 최종 처리되기 전에 중간 단계에서 요소를 정렬해서 최종 처리 순서를 변경할 수 있습니다.
Stream의 요소들을 정렬하기 위해서는 sorted를 사용해야 하며, 파라미터로 Comparator를 넘길 수도 있습니다.
Comparator 인자 없이 호출할 경우에는 오름차순으로 정렬이 되며
내림차순으로 정렬하기 위해서는 Comparator의 reverseOrder를 이용하면 됩니다.
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f");
Stream<String> stream = list.stream().sorted()
// a, b, c, d, e, f
Stream<String> stream = list.stream()
.sorted(Comparator.reverseOrder())
// f, e, d, c, b, a2-4. 중간결과 확인
- peek
'확인해본다'라는 뜻을 지닌 peek 함수는 Stream의 요소들에 대해 확인만 할 뿐 결과에 영향을 주지 않습니다.
파라미터로 함수형 인터페이스 Consumer를 인자로 받습니다. 예시는 위쪽에 있습니다.
3. 스트림 결과 만들기
3-1. 출력
- foreach
요소들을 출력하기를 원할 때 forEach를 사용할 수 있습니다.
비슷한 함수로 peek()가 있습니다.
파라미터로 함수형 인터페이스 Consumer를 인자로 받습니다.
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("a", "b", "c", "d");
stream.forEach(System.out::println);3-2. 소모
- reduce
reduce 함수는 Stream의 요소들을 소모해 하나의 데이터로 만드는 작업을 수행합니다.
첫번째 인자와 두번째 인자를 더해 하나의 값을 만들고 그 값을 3번째 인자와 더하고......
이런방식으로 끝까지 인자를 소모해 하나의 데이터를 만듭니다.
따라서 인자값을 2개 넘겨줘야 합니다.
IntStream range = IntStream.range(1, 11);
int result = range.reduce((x, y) -> x + y).getAsInt(); // 55 초기값이 없는 형태
int result = range.reduce(10,(x, y) -> x + y); // 65 초기값이 있는 형태
3-3. 검색
- findAny() & findFirst()
Stream에서 어떤 조건에 일치하는 요소(element) 1개를 찾을 때
findAny()와 findFirst() 를 사용할 수 있습니다.
IntStream stream1 = IntStream.rnage(1,10);
IntStream stream2 = IntStream.rnage(1,10);
OptionalInt result1 = stream1.sorted().findFirst();
System.out.println(result1.getAsInt()); // 직렬: return 1
OptionalInt result2 = stream2.sorted().findAny();
System.out.println(result2.getAsInt()); // 직렬: return 1
OptionalInt result1 = stream1.parallel().sorted().findFirst();
System.out.println(result1.getAsInt()); // 병렬: return 1
OptionalInt result2 = stream2.parallel().sorted().findAny();
System.out.println(result2.getAsInt()); // 병렬: return 5 (5가 될 수 있음)- findAny() & findFirst() 차이점
Stream을 직렬로 처리할 때 findFirst()와 findAny()는 동일한 요소를 리턴하며, 차이점이 없습니다.
하지만 Stream을 병렬로 처리할 때는 차이가 있습니다.
findFirst()는 Stream의 순서를 고려하여 가장 앞에 있는 요소를 리턴합니다.
반면에 findAny()는 Multi thread에서 Stream을 처리할 때 가장 먼저 찾은 요소를 리턴합니다.
따라서 Stream의 뒤쪽에 있는 element가 리턴될 수 있습니다.
3-4. 검사
- anyMatch(), allMatch(), noneMatch()
anyMatch() : 해당 스트림의 일부 요소가 특정 조건을 만족할 경우에 true를 반환함.
allMatch() : 해당 스트림의 모든 요소가 특정 조건을 만족할 경우에 true를 반환함.
noneMatch() : 해당 스트림의 모든 요소가 특정 조건을 만족하지 않을 경우에 true를 반환함.
모두 파라미터로 함수형 인터페이스 Predicate를 인자로 받습니다.
IntStream stream1 = IntStream.of(30, 90, 70, 10);
IntStream stream2 = IntStream.of(30, 90, 70, 10);
IntStream stream3 = IntStream.of(30, 90, 70, 10);
System.out.println(stream1.anyMatch(n -> n > 80)); // true
System.out.println(stream2.allMatch(n -> n > 80)); // false
System.out.println(stream3.noneMatch(n -> n > 80)); // false3-5. 통계 및 연산
- count(), min(), max(), sum(), average()
IntStream stream1 = IntStream.of(30, 90, 70, 10);
IntStream stream2 = IntStream.of(30, 90, 70, 10);
IntStream stream3 = IntStream.of(30, 90, 70, 10);
IntStream stream4 = IntStream.of(30, 90, 70, 10);
DoubleStream stream5 = DoubleStream.of(30.3, 90.9, 70.7, 10.1);
System.out.println(stream1.count()); // 4
System.out.println(stream2.max().getAsInt()); // 90
System.out.println(stream3.min().getAsInt()); // 90
System.out.println(stream4.sum()); // 200
System.out.println(stream5.average().getAsDouble()); // 50.53-6. 수집
- collect()
스트림을 배열이나 컬렉션으로 변환 : toArray(), toCollection(), toList(), toSet(), toMap()
요소의 통계 및 연산 메소드와 같은 동작을 수행 : counting(), maxBy(), minBy(), summingInt(), averagingInt(), summarizingInt()
요소의 소모와 같은 동작을 수행 : reducing(), joining()
요소의 그룹화와 분할 : groupingBy(), partitioningBy()
모두 collect( Collectors.메서드이름() ) 형태로 사용합니다.
4. 마무리
이번 스트림 시리즈를 통해 스트림을 좀더 알아볼 수 있었습니다.
완벽히 안다고 할 수 없지만 앞으로 간결하고 가독성 좋은 코드를 짤때 조금이나마 도움이 되지 않을까요??
일단은 제가 나중에 보려고 쓴 글이지만 누군가 보고 도움이 됐으면 좋겠습니다
