제네릭(generic)
- 데이터의 타입(data type)을 일반화하는 것(generalize)
- 오직
"참조타입"만 Generic 처리해서 사용할 수 있음
public class MainWrapper {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Box<String> box1 = new Box<String>();
box1.setItem("Hello World");
System.out.println(box1.getItem());
Box<Integer> box2 = new Box<Integer>();
box2.setItem(10);
System.out.println(box2.getItem());
Box<Person> box3 = new Box<Person>();
box3.setItem(new Person("홍길동"));
System.out.println(box3.getItem());
}
}

리스트(List)
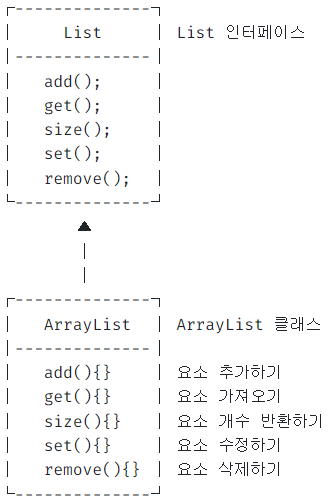
- ArrayList의 인터페이스 List 타입 선언
List<String> season;
season = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> hobbies = new ArrayList<String>();
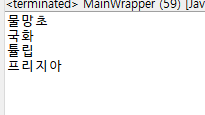
season.add("여름");
season.add("가을");
season.add("겨울");
season.add(0, "봄");
System.out.println(season.get(0));
System.out.println(season.get(1));
System.out.println(season.get(2));
System.out.println(season.get(3));
System.out.println(season.size());
System.out.println(season.get(season.size() - 1));
for (int i = 0; i < season.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(season.get(i));
}
for (int i = 0, length = season.size(); i < length; i++) {
System.out.println(season.get(i));
Integer[] a = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(a);
for (int i = 0, length = numbers.size(); i < length; i++) {
System.out.println(numbers.get(i));
Set
- 인덱스가 없다. 저장 순서가 없다
- 중복 저장이 되지 않는다
Set<String> hobbies = new HashSet<String>();
hobbies.add("독서");
hobbies.add("요리");
hobbies.add("운동");
hobbies.add("체스");
- for문 활용하기 (
인덱스가 없으므로 향상 for문)
for (String hobby : hobbies) {
System.out.println(hobby);
}
Iterator<String> arm = hobbies.iterator();
while (arm.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(arm.next());
}