📌제네릭(Generic)
- 프로그램에서 변수를 선언할 때 보든 변수는 자료형이 있다. 메서드에서 매개변수를 사용할 때도 자료형을 가지고 있다. 대부분은 하나의 자료형으로 구현하지만, 변수나 메서드의 자료형을 필요에 따라 여러 자료형으로 바꿀 수 있다면 프로그램이 훨씬 유연할 것이다.
이와 같이 어떤 값이 하나의 참조 자료형이 아닌 여러 참조 자료형을 사용할 수 있도록 프로그래밍 하는 것을제네릭(Generic)프로그래밍이라고 한다.
제네릭(Generic)의 장점
- 제네릭을 사용하면 잘못된 타입이 들어올 수 있는 것을 컴파일 단계에서 방지
- 클래스 외부에서 타입을 지정해주기 때문에 따로 타입을 체크하고 변환해줄 필요가 없다. 즉, 관리가 편리하다
- 비슷한 기능을 지원하는 경우 코드의 재사용성이 높아진다.
제네릭 사용법
프로그래머들 사이 일종의 관습 (Convention)
| 타입 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| < T > | Type |
| < E > | Element |
| < K > | Key |
| < V > | Value |
| < N > | Number |
List numbers = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5,6);
int sum = 0;
for(Object number : numbers){
sum += (int) number;
}
}List에 타입 지정을 안 했기 때문에 Object로 타입이 지정되고 더하는(sum)부분에서 형 변환을 직접 해줘야 하는 번거로움이 있다.
제네릭을 사용한 List
- 불필요한 형 변환을 안해도 되고 클린 코드가 된다. (타입 안정성)
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5,6);
int sum = 0;
for(Integer number : numbers){
sum += numbers;
}
} ❗
List<Integer>← Integer은 무엇일까???
📌래퍼 클래스란(Wrapper Class)?
- Java의 자료형은 크게 기본 타입(Primitive type)과 참조 타입(Reference type)으로 나누어진다. 대표적으로 기본 타입은 char, int, float, double, boolean 등이 있고 참조 타입은 class, interface 등이 있는데 프로그래밍을 하다 보면 기본 타입의 데이터를 객체로 표현해야 하는 경우가 종종있다.
기본 자료타입(Primitive type)을 객체로 다루기 위해서 사용하는 클래스들의 집합을 래퍼 클래스(Wrapper Class)라고 한다
| 기본타입(Primitive type) | 래퍼클래스(Wrapper Class) |
|---|---|
| byte | Byte |
| cahr | Character |
| int | Integer |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
| boolean | Boolean |
| long | Long |
| short | Short |
package j18_제네릭;
// Commit Message Response Data Transfer Object
// 클라이언트가 서버에게 요청을 날리면 동일한 형식으로 응답해주는 응답인터페이스
public class CMRespDto<T> {
private int code;
private String message;
private T data;
public CMRespDto(int code, String message, T data) {
super();
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
this.data = data;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CMRespDto [code=" + code + ", message=" + message + ", data=" + data + "]";
}package j18_제네릭;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* <?,?> // 필살기???
*/
TestData<String, Integer> td = new TestData<String, Integer>("가나다", 30);
TestData<String,Double> td2 = new TestData<String, Double>("junil", 100.05);
System.out.println(td);
System.out.println(td2);
CMRespDto<TestData<String,Integer>> cm =
new CMRespDto<TestData<String,Integer>>(200, "성공", td);
System.out.println(cm);
}
}제한된 제네릭(Generic)과 와일드카드(Wildcard)
- CMRespDto< T >
- Commit Message Response Data Transfer Ojbect
- 클라이언트가 서버에게 요청을 날리면 동일한 형식으로 응답해주는 응답인터페이스
package j18_제네릭;
public class Main2 { //class = 틀
/*
*
* ? 와일드카드 제약
* extends 대상 객체 하위
* super 대상 객체 상위
*
*/
public CMRespDto<?> reponse(CMRespDto<?>cmRespDto){ //확장성을 생각 했을때 wildCard [와일드 카드]
// ? -> Object(최상위 클래스)로 쓸수있음
//<? extends Person> Person을 상속받은 객체만 리턴 가능
//<? super Student> // Student를 기준으로 상위 객체 (나 , Person 객체만 리턴 가능)
System.out.println("[응답데이터]");
System.out.println(cmRespDto);
return cmRespDto;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main2 main = new Main2();////
CMRespDto<String> hello
= new CMRespDto<String>(200, "성공", "안녕하세요");
CMRespDto<Integer> score
= new CMRespDto<Integer>(200, "성공", 85);
System.out.println("hello");
System.out.println(main.reponse(hello));
System.out.println("score");
System.out.println(main.reponse(score));
/*
* 왜 안될까?? static method 안에는 멤버변수 사용 X
* reponse 메서드는 주소가 생성되야 사용할 수 있는 메서드이기때문
*/
}
}📌ArrayList
- 특징
- 표준 배열보다는 느리지만 배열에서 많은 조작이 필요한 경우 유용하게 사용할 수 있음
- List 인터페이스에서 상속받아 사용됨
- ArrayList는 객체가 추가되어 용량을 초과하면 자동으로 부족한 크기만큼 용량이 늘어남
예시
ArrayList<String> strList = new ArrayList<>();
strList.add("Java");
strList.add("Python");
//strList.add(" "); 계속 배열 늘어남
//strList.remove(" "); 삭제
//strList.add(1,"java");
//strList.remove(1);
for(int i = 0; i<strList.size();i++){
System.out.println(strList.get(i));
//======< 같은 구조 >======
for(String str : strList){
System.out.println(str);
📌자바 컬렉션 프레임워크(Collection Framework)
- 다수의 데이터를 쉽게 효과적으로 처리할 수 있는 표준화된 방법을 제공하는 클래스의 집합
- 데이터를 저장하는 자료 구조와 데이터를 처리하는 알고리즘을 구조화하여 클래스로 구현해 놓은 것
컬렉션 프레임워크는 JAVA의 인터페이스(interface)로 구현
| 인터페이스 | 설명 | 구현클래스 |
|---|---|---|
| List< E > | 순서가 있는 데이터의 집합, 데이터의 중복 허용 | Vector,ArrayList,LinkedList,Stack,Queue |
| Set< E > | 순서가 없는 데이터의 집합, 데이터의 중복 허용 X | HashSet,TreeSet |
| Map<K,V > | 키와 벨류가 한 쌍으로 이루어지는 데이터의 집합, 순서가 없음, 이때 키는 중복을 허용하지 않지만, 값은 중복 가능 | HashMap,TreeMap,Hashtable,Properies |
Set (주머니) : 순서X, 중복 X => Value값을 알고 싶으면 값을 하나씩 다 확인해야함 (전체 반복)
Map < Key, Value > : 순서X, 중복 O
List, Set 상위에 Collection.add method가 정의돼있음
Map은 put을 쓴다.
Collection 인터페이스
| 메소드 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| boolean add(E e) | 해당 컬렉션에 전달된 요소를 추가함.(선택적 기능) |
| void claer() | 해당 컬렉션의 모든 요소를 제거(선택적) |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 해당 컬렉션이 전달된 객체를 포함하고 있는지 확인 |
| boolean equals(Object o) | 해당 컬렉션과 전달된 객체가 같은지 확인 |
| boolean isEmpty() | 해당 컬렉션이 비어있는지 확인 |
| Iterator< E >iterator() | 해당 컬렉션의 반복자를 반환 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 해당 컬렉션에서 전달된 객체를 제거함(선택적) |
| int size() | 해당 컬렉션의 요소 총 개수를 반환 |
| Object[] toArray() | 해당 컬렉션의 모든 요소를 Object타입의 배열로 반환 |
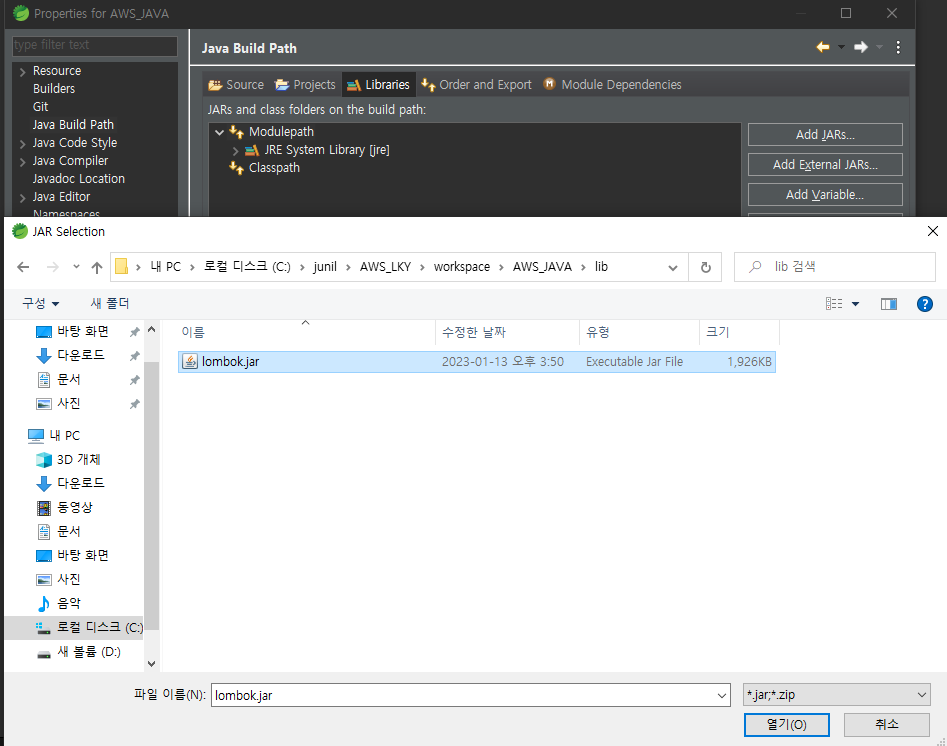
⚡lombok 설치
C:\junil\AWS_LKY\program\sts-4.17.0.RELEASE
sts 설치된 곳에 롬복 붙여넣기
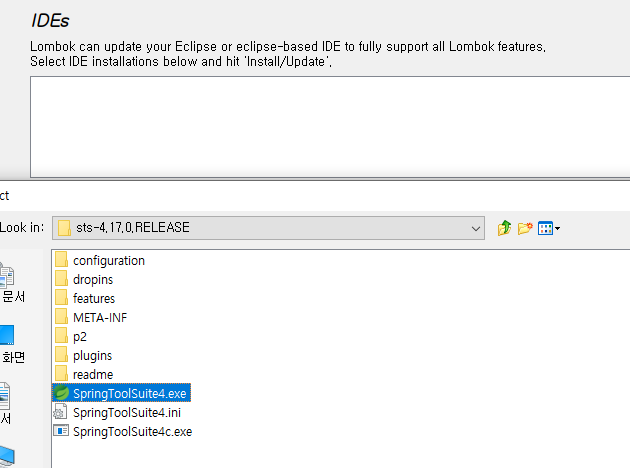
설치
lombok.jar ctrl + c
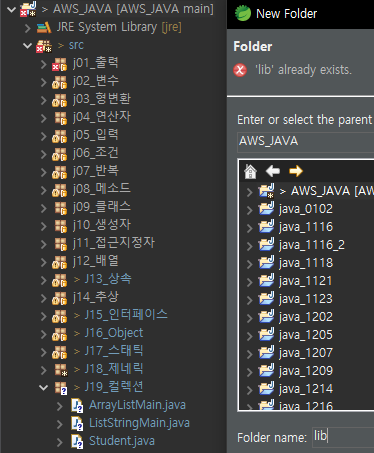
lib 폴더 생성
ctrl + v