CORS(Cross-Origin Resource Sharing)을 설명하기 위해서는 먼저 오리진(Origin)과 동일 출처 정책(SOP,Same-Origin Policy)에 대한 이해가 필요함
오리진(Origin)
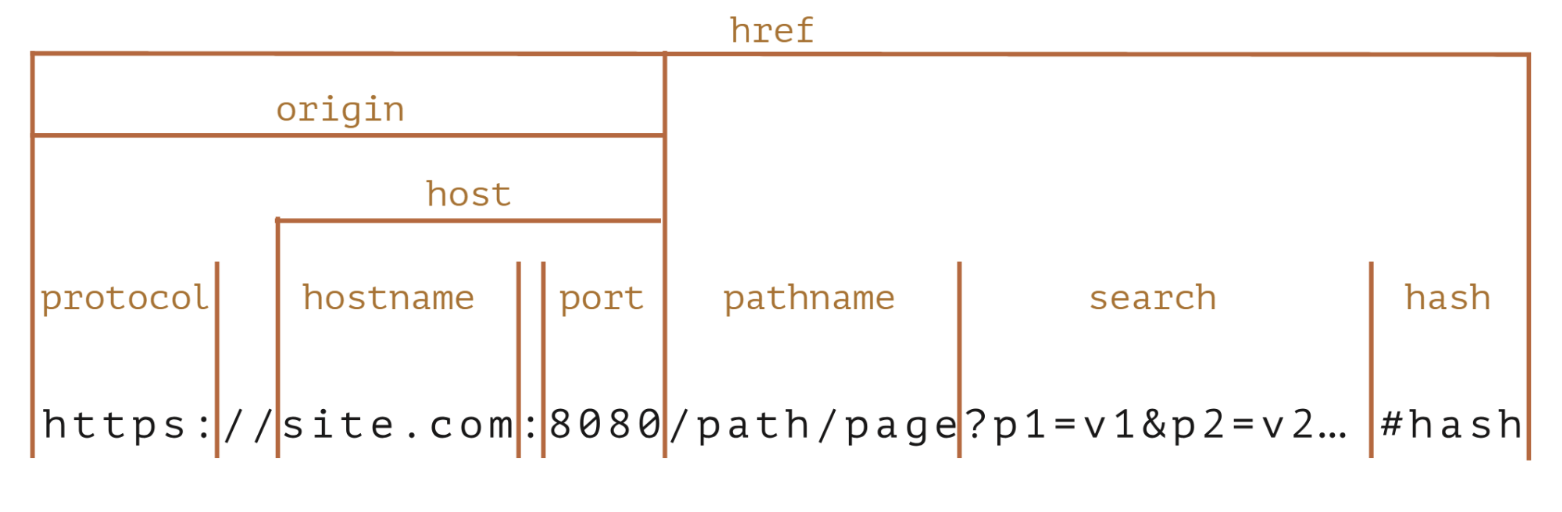
- 웹에서 오리진(Origin)은 URL의 스키마, 호스트, 포트 세 부분으로 구성
https://www.example.com:8080/path/page.html
여기서 오리진은 다음과 같음
- 스키마 : https
- 호스트 : www.example.com
- 포트 : 8080
따라서 오리진은https://www.example.com:8080이 됨
동일 출처 정책(SOP, Same-Origin Policy)
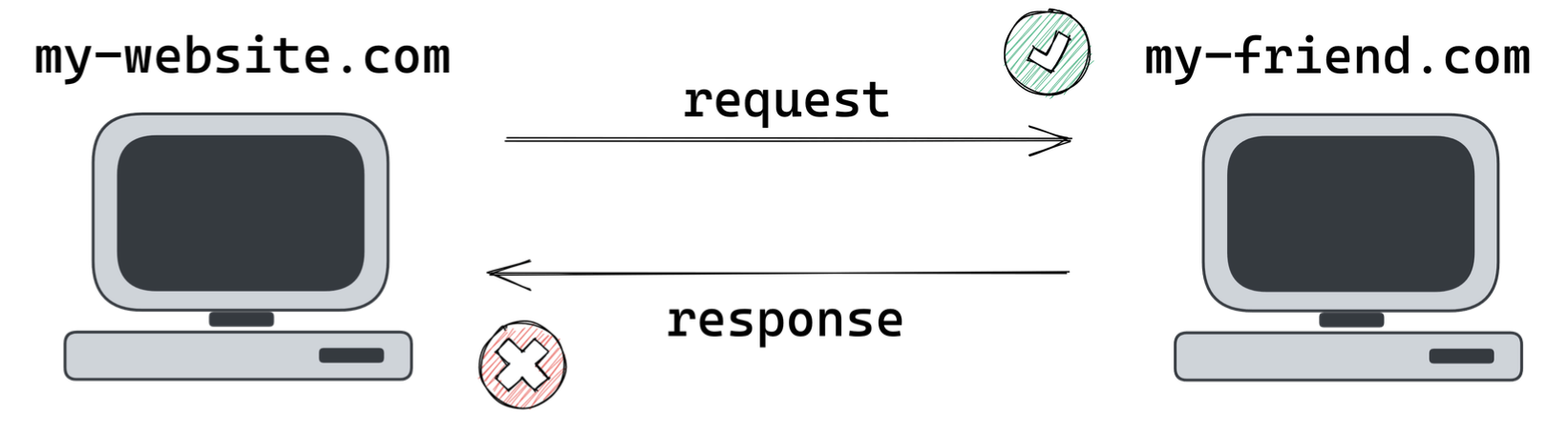
- 웹 브라우저 보안 모델의 중요한 부분으로 한 오리진에서 로드된 문서 또는 스크립트가 다른 ㅗ오리진의 리소스에 접근하는 것을 제한함
- 이 정책은 잠재적인 악의적 사이트로부터 사용자의 데이터를 보호하기 위해 존재
예를 들어, 오리진 https://www.example.com에서 로드된 스크립트는 기본적으로 https://api.example.com에서 제공하는 데이터에 접근할 수 없음 (두 오리진이 다르기 때문(포트번호, 서브도메인이 다른 경우도 포함))
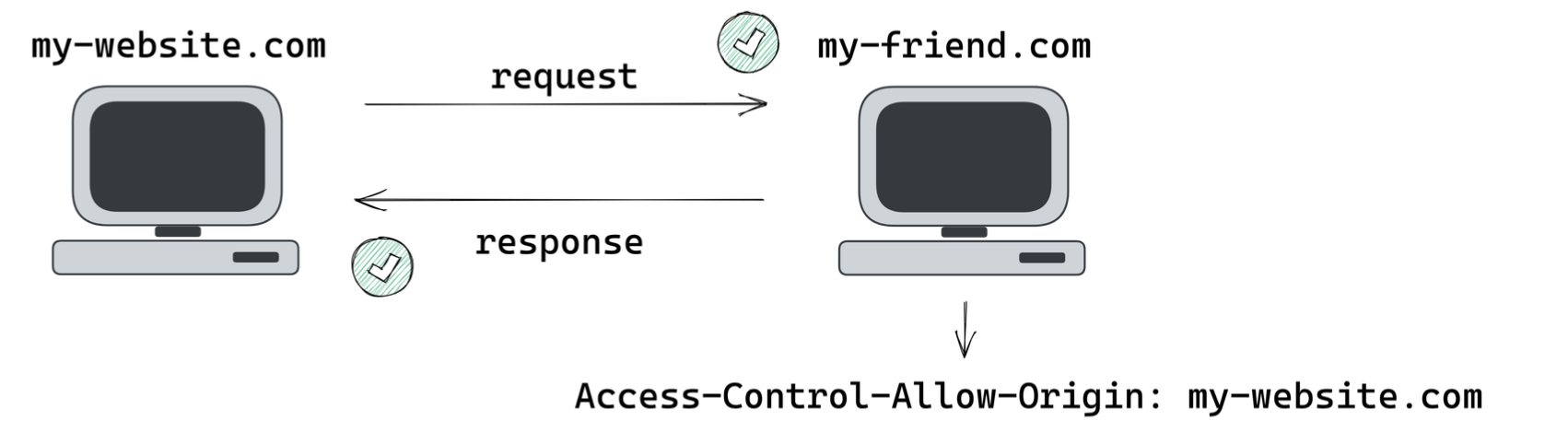
CORS(Cross-Origin Resource Sharing)
-
교차 출처 리소스 공유의 약자로, SOP의 제한을 우회하여 한 오리진에서 로드된 웹 애플리케이션이 다른 오리진의 리소스에 접근할 수 있도록 허용하는 메커니즘
-
CORS는 서버 측에서 특정 오리진을 허용하도록 설정하여 작동
-
CORS에서 브라우저는 두 가지 유형의 요청을 사용할 수 있음
Simple Request(간단한 요청)
간단한 요청은 특정 조건을 충족하는 요청- 브라우저는 사전 검사 없이 바로 서버에 요청을 보냄
- HTTP 메서드
- GET
- HEAD
- POST
- HTTP 헤더
- Accept
- Accept-Language
- Content-Language
- content-Type
- Content-Type 헤더의 값이 다음 중 하나일 경우
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- multipart/form-data
- text/plain
실습
npm install express cors
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width,
initial-scale=1.0"
/>
<title>최고의 CS강의!</title>
<script>
const req = () => {
fetch("http://127.0.0.1:3001/api", {
method: "GET",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
//"Content-Type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
},
})
.then((req) => req.json())
.then((e) => {
document.getElementById("love").innerText = e.data;
});
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1 id="love">별점 5점은 사랑입니다.</h1>
<button onclick="req()">다른 오리진으로 요청</button>
</body>
</html>
a.js
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
const path = require("path");
const pt = path.join(__dirname, "index.html");
app.use(express.static(pt));
app.get("/", (req, res) => res.sendFile(pt));
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log("Server listening on port 3000");
});
b.js
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
const cors = require("cors");
const corsOptions = {
origin: "http://127.0.0.1:3000", //origin: 'http://127.0.0.1:3004',
};
app.use(cors(corsOptions));
app.get("/api", (req, res) => res.json({ data: "수강생 여러분 감사합니다." }));
app.listen(3001, () => {
console.log("Server listening on port 3001");
});
