교착 상태(DeadLock)
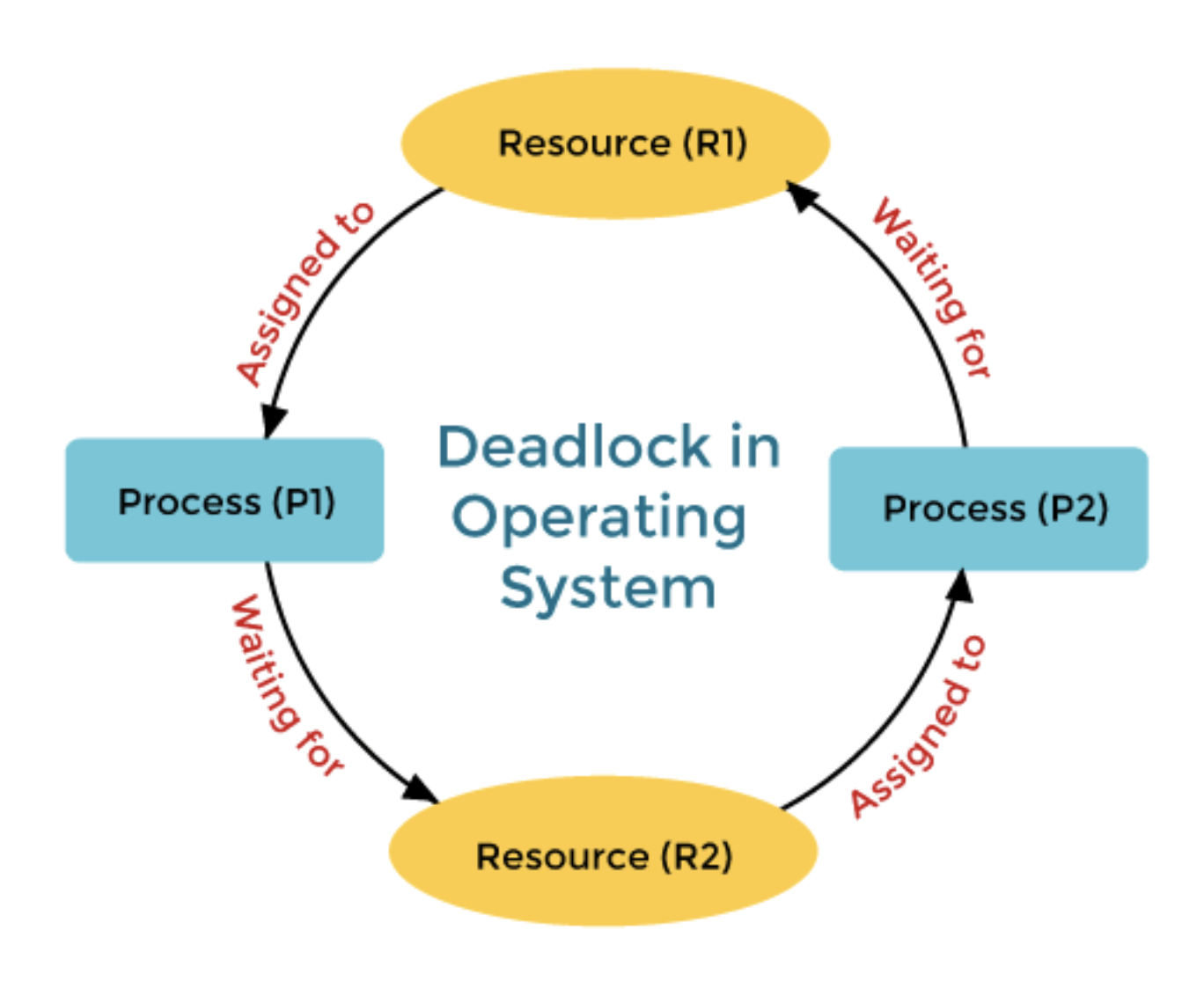
- 둘 이상의 프로세스나 스레드가 서로가 가진 자원을 기다리며 무한히 대기하는 상태를 말함
- 이로 인해 시스템이 멈추고 자원을 사용할 수 없게 됨
- 교착상태는 분산 시스템, 운영 체제, DB 관리 시슽ㅁ 등 여러 검퓨터 과학 분야에서 중요한 문제로 다루어짐
교착상태의 조건(Coffman의 조건)
- 상호 배제(Mutal Exculsion)
- 자원은 한 번에 하나의 프로세스만 사용할 수 있음, 한 프로세스가 자원을 점유하고 있는 동안 다른 프로세스는 그 자원을 사용할 수 없음
- 점유 대기(Hold and Wait)
- 최소한 하나의 프로세스가 자원을 점유한 상태에서 다른 자원을 추가로 요청하며 그 자원이 할당되지 않아 대기하고 있음
- 비선점(No Preemption)
- 프로세스가 점유한 자원을 강제로 빼앗을 수 없음, 자원을 점유한 프로세스는 자원의 사용을 끝낸 후 자원을 해제해야 함
- 순환 대기(Circular Wait)
- 두 개 이상의 프로세스가 자원을 순환 형태로 대기하고 있음
- 예를 들어 프로세스 A는 프로세스 B가 점유한 자원을 기다리고 프로세스 B는 프로세스 C가 점유한 자원을 기다리고 프로세스 C는 프로세스 A가 점유한 자원을 기다리는 상황
교착상태의 해결 방법
- 예방(Prevention)
- 교착상태 발생 조건 중 하나를 제거하여 교착상태가 발생하지 않도록 함
- 상호 배제 조건 제거 : 자원을 공유해서 사용할 수 있도록 함
- 점유 대기 조건 제거 : 프로세스가 자원을 요청할 때 다른 자원을 점유하고 있지 않도록 함
- 비선점 조건 제거 : 자원을 점유하고 있는 프로세스가 다른 자원을 요청할 때, 현재 점유한 자원을 강제로 해제하도록 함
- 순환 대기 조건 제거 : 자원에 대한 요청 순서를 정하여 순환 대기가 발생하지 않도록 함
- 회피(Avoidance)
- 시스템의 상태를 미리 검사하여 교착상태가 발생하지 않도록 함
- 은행가 알고리즘(Banker's Algorithm)을 사용하여 교착상태를 회피할 수 있음
- 검출(Detection)
- 시스템에서 교착상태가 발생했는지 주기적으로 검사
- 자원 할당 그래프(Resource Allocation Graph) 등을 사용하여 교착상태를 검출할 수 있음
- 복구(Recovery)
- 교착상태가 발생하면 이를 복구하는 방법
- 교착상태에 있는 프로세스를 종료하거나 교착상태를 발생시킨 자원을 강제로 해제하여 교착상태를 해결
은행가 알고리즘(Banker’s Algorithm)
- 교착상태를 회피하기 위한 방법 중 하나로 시스템이 항상 안전 상태에 있도록 자원 할당을 관리하는 알고리즘
- 운영 체제가 자원 요청을 수락하기 전에 요청이 시스템을 안정 상태로 유지할 수 있는지 확인
import java.util.Arrays;
public class BankersAlgorithm {
private int numberOfProcesses;
private int numberOfResources;
private int[] available;
private int[][] maximum;
private int[][] allocation;
private int[][] need;
public BankersAlgorithm(int numberOfProcesses, int numberOfResources, int[] available, int[][] maximum, int[][] allocation) {
this.numberOfProcesses = numberOfProcesses;
this.numberOfResources = numberOfResources;
this.available = available;
this.maximum = maximum;
this.allocation = allocation;
this.need = new int[numberOfProcesses][numberOfResources];
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfProcesses; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < numberOfResources; j++) {
need[i][j] = maximum[i][j] - allocation[i][j];
}
}
}
private int[] isSafe() {
int[] work = available.clone();
boolean[] finish = new boolean[numberOfProcesses];
int[] safeSequence = new int[numberOfProcesses];
int index = 0;
while (index < numberOfProcesses) {
boolean found = false;
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfProcesses; i++) {
if (!finish[i] && canAllocate(i, work)) {
for (int j = 0; j < numberOfResources; j++) {
work[j] += allocation[i][j];
}
safeSequence[index++] = i;
finish[i] = true;
found = true;
}
}
if (!found) break;
}
for (boolean f : finish) {
if (!f) return null;
}
return safeSequence;
}
private boolean canAllocate(int process, int[] work) {
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfResources; i++) {
if (need[process][i] > work[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean requestResources(int process, int[] request) {
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfResources; i++) {
if (request[i] > need[process][i]) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Requested more resources than needed");
}
if (request[i] > available[i]) {
return false;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfResources; i++) {
available[i] -= request[i];
allocation[process][i] += request[i];
need[process][i] -= request[i];
}
int[] safeSequence = isSafe();
if (safeSequence == null) {
for (int i = 0; i < numberOfResources; i++) {
available[i] += request[i];
allocation[process][i] -= request[i];
need[process][i] += request[i];
}
return false;
} else {
System.out.println("Safe sequence: " + Arrays.toString(safeSequence));
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int numberOfProcesses = 5;
int numberOfResources = 3;
int[] available = {3, 3, 2};
int[][] maximum = {
{7, 5, 3},
{3, 2, 2},
{9, 0, 2},
{2, 2, 2},
{4, 3, 3}
};
int[][] allocation = {
{0, 1, 0},
{2, 0, 0},
{3, 0, 2},
{2, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 2}
};
BankersAlgorithm ba = new BankersAlgorithm(numberOfProcesses, numberOfResources, available, maximum, allocation);
int[] request1 = {1, 0, 2};
System.out.println("Requesting resources for P1: " + ba.requestResources(1, request1));
int[] request2 = {3, 3, 0};
System.out.println("Requesting resources for P4: " + ba.requestResources(4, request2));
}
}

