
📌UI 기본 구조
액티비티 - 사용자 화면을 제공하는 컴포넌트
뷰 - 액티비티 자체에는 빈 화면만 보임, 이 화면의 요소들이 View의 하위 클래스들임
🔑뷰 그룹
뷰 컨테이너의 기본 클래스
종류
- 뷰 컨테이너
- 뷰 페이저
- 툴바
- 기본 레이아웃 클래스
- linearlayout
- relative layout 등
🔑뷰의 속성
- color, dimension, positioning
- 포커스 있을 수 있음
- 인터렉티브 기능(클릭에 응답)
- visible
- 다른 뷰와의 관계
+lambda 활용한 button setOnClickListener
SAM (single Abstract Method)
- 메서드가 하나만 있는 클래스나 인터페이스로 setonclicklistener(onclick을 override)가 이러하다.
자바식으로 작성된 코드이다.
val btn1 = findViewById<Button>(R.id.button1)
btn1.setOnClickListener( object : View.OnClickListener { // object : anonymous nested class를 만든다
override fun onClick(v: View) {
Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "Hello World", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
})람다식으로 표현하여 작성하는 방법이다.
btn1.setOnClickListener( { view -> //parameter를 명시적 변수로 받을 경우
Toast.makeText(this, "Hello World", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
})
btn1.setOnClickListener( { _ -> // parameter를 사용하지 않을 경우
Toast.makeText(this, "Hello World", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
})
한개인 변수명은 it으로 자동선언 된다.
btn1.setOnClickListener {
Toast.makeText(this, "Hello World", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
btn1.setOnClickListener {
Log.d(TAG, "onCreate: ${it.javaClass.name}")
Toast.makeText(this, "Hello World" + it.javaClass.name, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}📌FrameLayout
안의 뷰들을 자유롭게 겹쳐서 배치할 수 있는 레이아웃이다.
여기서 framelayout의 레이아웃 width, height을 주면 가장 큰 파란 박스 안에서 요소들을 배치할 수 있다.
📌gravity, layout_gravity
사진에서 layout_gravity는 텍스트뷰가 차지하는 상자의 위치를 지정해준다. 즉, 부모 레이아웃 내에서 정렬되는 위치를 결정한다.
end|center_vertical이란 수평적으로는 가장 오른쪽에, 수직적으로는 가운데에 배치시킨다는 것이다.
그냥 gravity를 쓰면 그 textview의 텍스트의 위치를 지정해준다.
center이라고 하면 상하좌우 모두의 가운데를 뜻한다.
📌ConstraintLayout
어떠한 뷰에 종속적으로 배치
constraintLayout에서 높이, 너비를 0dp라고 쓰는 것은 match_constraint 라는 의미
🔑 체인
서로 연결되어 그룹으로 동작하는 뷰의 묶음
체인으로 연결된 뷰 끼리도 체인이 연결된 방향으로만 그룹으로 동작함
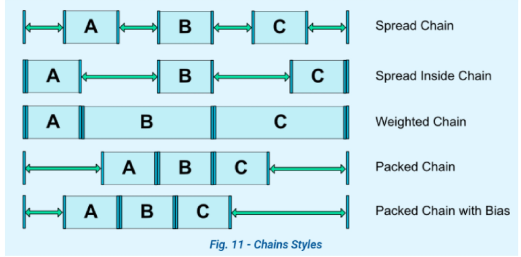
gone 기준 constraint
View.GONE 인 뷰를 기준으로 constraint를 잡을 때, margin값을 아래와 같은 방식으로 준다.
layout_goneMarginStart
layout_goneMarginTop 등등
각을 기준으로 constraint
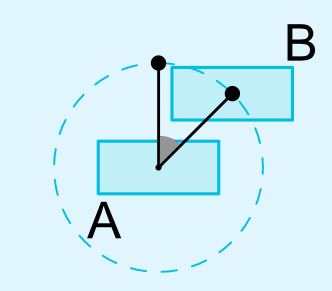
layout_constraintCircle : references another widget id
layout_constraintCircleRadius : the distance to the other widget center
layout_constraintCircleAngle : which angle the widget should be at (in degrees, from 0 to 360)
🔑ImageView 둥글게
<androidx.cardview.widget.CardView
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
app:cardCornerRadius="75dp"
app:cardElevation="0dp"
>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/userImageView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:src="@drawable/user_basic"
android:scaleType="centerCrop"
/>
</androidx.cardview.widget.CardView>카드 뷰 안에 이미지 넣고 카드뷰 속성에 CornerRadius주면 됨
🔑 AppcompatButton 없이 button에 색 주기
android:background="@color/my_red"
android:backgroundTint="@null"위처럼 하면 되지 않을것이다
android:backgroundTint가 아니라
app:backgroundTint이다!! 명심하자
android:background="@color/colorPrimary"
app:backgroundTint="@null"🔑 화면에 이미지 높이/너비 맞추기
android:adjustViewBounds="true"📌Menu
Options Menu
- 디바이스의 Menu키(점3개 버튼)를 누르면 나타나는 메뉴
Context Menu
- 뷰를 길게 눌렀을때 나타나는 floating 메뉴
Popup Menu
- 뷰를 짧게 눌렀을 때 나타나는 floating 메뉴
sub Menu
- Options Menu나 Context Menu안의 item에 의해 나타나는 메뉴
위 메뉴를 xml 파일로 정의하고 파일내에서 onCreateOptionsMenu등을 오버라이딩하여 뷰를 넣고 onOptionsItemSelected 를 오버라이딩하여 선택에 따른 분기를 제어한다.
contextMenuBtn = findViewById(R.id.context_menu_btn)
// long click 시 context 메뉴를 연결할 view 등록
registerForContextMenu(contextMenuBtn)
override fun onCreateContextMenu(
menu: ContextMenu?,
v: View?,
menuInfo: ContextMenu.ContextMenuInfo?
) {
super.onCreateContextMenu(menu, v, menuInfo)
menuInflater.inflate(R.menu.contextmenu, menu)
}
override fun onContextItemSelected(item: MenuItem): Boolean {
when (item.itemId) {
R.id.context_menu_blue -> contextMenuBtn.setTextColor(Color.BLUE)
R.id.context_menu_red -> contextMenuBtn.setTextColor(Color.RED)
R.id.context_menu_green -> contextMenuBtn.setTextColor(Color.GREEN)
}
return super.onContextItemSelected(item)
}
override fun onCreateOptionsMenu(menu: Menu?): Boolean {
val inflater = menuInflater
inflater.inflate(R.menu.menutest, menu)
return super.onCreateOptionsMenu(menu)
}
override fun onOptionsItemSelected(item: MenuItem): Boolean {
if (item.itemId == R.id.item_exit) {
finish()
} else {
if (item.itemId == R.id.example_item) {
Toast.makeText(this, "Example.... ${item.title}", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
} else
Toast.makeText(this, "Hello Menu, ${item.title}", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item)
}
}길게 눌렀을 때 띄우는 contextMenu는
registerForContextMenu로 메뉴를 버튼 등 뷰에 연결해주고
onCreateContextMenu로 contextmenu에 원하는 메뉴 아이템을 넣어주고(inflate 처리)
onContextItemSelected로 선택된 아이템에 대한 분기 처리를 한다.
findViewById<Button>(R.id.popup_menu_btn).setOnClickListener {
val popupMenu = PopupMenu(applicationContext, it)
menuInflater.inflate(R.menu.pupupmenu, popupMenu.menu)
popupMenu.setOnMenuItemClickListener { menuItem ->
if (menuItem.itemId == R.id.popup_menu1) {
Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "메뉴 1 클릭", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
} else if (menuItem.itemId == R.id.popup_menu2) {
Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "메뉴 2 클릭", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
} else {
Toast.makeText(this@MainActivity, "메뉴 3 클릭", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
false//물려있는 다른 이벤트 처리를 수행할지 안할지를 return
}
popupMenu.show();
}밑에 메뉴를 달아주는 팝업메뉴를 달기 위해 위와 같이 작성할 수 있는데, 여기서 this@MainActivity는 mainActivity를 가져오기 위한 코드다.
그냥 this를 사용하면 메서드를 부른 것을 불러와서 위 코드는 this가 액티비티라 상관이 없지만 this가 뷰인 경우에는 this@MainActivity로 액티비티를 가져올 수 있다.
🔑res 와 assets
assets는 앱 안이 아닌 바깥에 들어가는 의미로 컴파일되지 않고 빌드시에 그대로 들어감
