
목차
- 데드락이란
- 데드락의 발생조건
- 데드락을 방지하기
1. 데드락(DeadLock)이란
- 운영체제(OS)에서
데드락(DeadLock)은 시스템 자원에 대한 요구가 뒤엉킨 상태이다. - 아래 그림처럼 둘 이상의 프로세스가 다른 프로세스가 점유하고 있는 리소스를 서로 기다릴 때 무한 대기에 빠지는 상황이다.
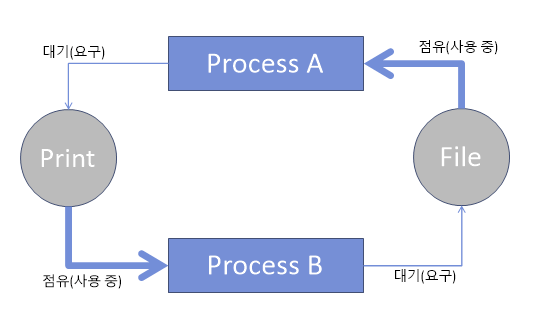
2. 데드락의 발생조건
데드락이 발생하기 위해서는 아래 4가지 조건이 모두 만족되어야 한다. 이 조건들은
Coffman의 조건으로도 알려져 있다.
1.상호 배제
2.점유 및 대기
3.비선점
4.순환 대기
상호 배제(Mutual Exclusion)
상호 배제는 특정 자원이 한 번에 하나의 프로세스만 사용할 수 있도록 하는 메커니즘이다.
- 상호 배제의 조건을 만족한다는 것은, 특정 자원이 오직 한 프로세스에 의해서만 점유될 수 있다는 것을 의미
- 자원에 대한 접근을 관리하는 보호 메커니즘(세마포어, 뮤텍스, 모니터)이 필요하다.
- 이 메커니즘은 자원에 대한 동시 접근을 방지하여 데이터 무결성과 시스템 안정성을 유지한다.
- 상호 배제는
자원의 일관성과무결성을 유지하기 위해 필수적이다.- 데이터 일관성 보장 : 한 번에 하나의 프로세스만 파일에 접근하기 때문에 데이터 일관성을 보장한다.
- 자원 충돌 방지 : 프린터를 예를 들면 동시에 사용한다면 출력이 혼란스럽게 섞인다. 상호 배제를 통해 한 번에 하나의 프로세스만 프린터를 사용하기 때문에 자원 충돌을 방지한다.
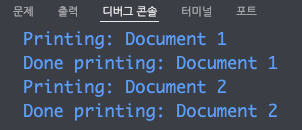
- 아래 예시 코드는 두 개의 스레드가 동시에 동일한 자원(프린터)를 사용할 때 상호 배제를 구현하는 방식이다.
public class PrintingTask implements Runnable{
private final Printer printer;
private final String message;
public PrintingTask(Printer printer, String message) {
this.printer = printer;
this.message = message;
}
@Override
public void run() {
printer.print(message);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Printer printer = new Printer();
Thread t1 = new Thread(new PrintingTask(printer, "Document 1"));
Thread t2 = new Thread(new PrintingTask(printer, "Document 2"));
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
class Printer {
private final Object lock = new Object();
public void print(String message) {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println("Printing: " + message);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000); // Simulate the time taken to print
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
System.out.println("Done printing: " + message);
}
}
}- 아래 출력 결과를 보면 자원의 점유가 끝나면 다음 프로세스가 점유된다.
점유 및 대기(Hold and Wait)
데드락이 발생하기 위한 조건 중 하나인 점유 및 대기는 자원을 점유한 상태에서 추가 자원을 기다리는 상황을 의미한다.
점유(Hold): 프로세스가 하나 이상의 자원을 점유하고 있는 상태대기(Wait): 이미 점유한 자원을 해제하지 않은 상태에서, 추가적인 자원을 요청하고 대기하는 상태
- 점유 및 대기 조건을 보다 명확히 이해하기 위해서 다음 구성요소를 알아햐 한다.
자원의 점유: 프로세스가 현재 특정 자원을 접유하고 있어야 한다. -> 점유 자원은 다른 프로세스가 접근불가추가 자원의 요청: 프로세스가 추가적인 자원을 요청한다. -> 이미 점유하고 있는 자원은 해제하지 않은상태대기 상태: 요청한 자원이 사용 중이기 때문에, 프로세스는 해당 자원이 해제될 때가지 대기한다.
- 점유 및 대기 조건을 예방하기 위해서는 다음과 같은 방법이 있다.
- 자원 요청 시점에 모든 자원을 할당
- 비선점 자원의 최소화
- 자원 할당 그래프 사용
- 아래 예시 코드는 점유 및 대기 조건을 구현한 코드이다.
public class DeadlockExample {
private static final Object resource1 = new Object();
private static final Object resource2 = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (resource1) {
System.out.println("Thread 1: Holding resource 1...");
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Thread 1: Waiting for resource 2...");
synchronized (resource2) {
System.out.println("Thread 1: Acquired resource 2.");
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (resource2) {
System.out.println("Thread 2: Holding resource 2...");
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Thread 2: Waiting for resource 1...");
synchronized (resource1) {
System.out.println("Thread 2: Acquired resource 1.");
}
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}- 아래 출력결과가 나오고 계속 프로그램이 돌아간다.

비선점(Non -preemptive)
비선점은 OS와 리소스 관리에서 사용하는 개념으로, 자원을 한 번 할당받은 프로세스는 그 자원을 스스로 해제할 때까지 다른 프로세스가 강제로 뺴앗을 수 없음을 의미한다.
- 자원을 점유하고 있는 프로세스가 해당 자원을 자발적으로 해제할 때까지 다른 프로세스가 해당 자원을 사용할 수 없는 상태
- 비선점 조건은 데드락을 일으키는 다른 조건(상호배제, 점유 및 대기, 순환대기)과 결합하여 데드락을 유발할 수 있다.
- 아래 코드는 비선점 조건을 설명하는 코드이다. 두 개의 스레드가 두 개의 자원을 점유하고 있으며, 각 스레드가 다른 자원을 기다리는 동안 데드락 상태에 빠진다.
public class NonPreemptiveDeadlockExample {
private static final Object resource1 = new Object();
private static final Object resource2 = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (resource1) {
System.out.println("Thread 1: Holding resource 1...");
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Thread 1: Waiting for resource 2...");
synchronized (resource2) {
System.out.println("Thread 1: Acquired resource 2.");
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (resource2) {
System.out.println("Thread 2: Holding resource 2...");
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Thread 2: Waiting for resource 1...");
synchronized (resource1) {
System.out.println("Thread 2: Acquired resource 1.");
}
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}- 아래 그림처럼 계속 데드락 상태에 빠져 애플리케이션이 구동된다.

순환 대기(Circular Wait)
프로세스들이 순환 형태로 자원을 기다리는 상태를 말한다.
- 순환 대기는 특정 자원을 점유하고 있는 프로세스가 다음 자원을 기다리고, 그 자원을 점유한 프로세스가 또 다른 자원을 기다리는 형태가 순환적으로 이어져 있는 경우이다.
- 예시로 들면 프로세스 집합 P1,P2,...Pn 이 존재하고, P1은 P2가 점유한 자원을 기다리고,..., Pn은 P1이 점유한 자원을 기다리는 순환적인 대기 상태이다.
- 아래 코드는 두 개의 스레드가 두 개의 자원을 점유하고 있고, 각 스레드가 다른 자원을 기다리는 동안 데드락 상태에 빠지는 예시이다.
public class CircularWaitExample {
private static final Object resource1 = new Object();
private static final Object resource2 = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (resource1) {
System.out.println("Thread 1: Holding resource 1...");
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Thread 1: Waiting for resource 2...");
synchronized (resource2) {
System.out.println("Thread 1: Acquired resource 2.");
}
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (resource2) {
System.out.println("Thread 2: Holding resource 2...");
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("Thread 2: Waiting for resource 1...");
synchronized (resource1) {
System.out.println("Thread 2: Acquired resource 1.");
}
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}- 실행결과를 보면 데드락 상태에 빠져있는 것을 알 수 있다.

3. 데드락을 방지하기
데드락을 예방하거나 회피하는 방법은 시스템의 안정성을 유지하고 자원 관리를 효율적으로 수행하기 위해 매우 중요하다.
데드락을 방지하기 위한 전략은예방(Prevention),회피(Avoidance),탐지 및 복구(Detection and Recovery)가 있다.
데드락 예방(Deadlock Prevention)
- 데드락의 4가지 필요조건(상호배제, 점유 및 대기, 비선점, 순환대기) 중 하나 이상을 무력화 하여 발생하지 않도록 해야 한다.
상호배제 조건 제거- 대부분의 자원은 본질적으로 상호배제이기 때문에 이 조건을 완전히 제거하는 것은 불가능하다.
- 가능한 한 상호 배제적인 자원의 사용을 줄여야 한다.
점유 및 대기 조건 제거- 모든 자원 선할당(All-at-Once Allocation) : 프로세스가 실행되기 전에 모든 자원을 한꺼번에 할당받는다.
- 자원 요청 시 자원 해제(Request and Release) : 자원을 요청할 때 점유자원을 모두 해제한 후 다시 요청하도록 한다.(자원낭비와 기아현상 발생할 수 있다)
비선점 조건 제거- 프로세스가 자원을 점유하고 있을 때, 추가 자원을 요청하면 현재 점유하고 있는 자원을 해제하도록 한다.
순환대기 조건 제거- 모든 자원에 순서 번호를 부여하고, 프로세스가 자원을 요청할 때 항상 순서 번호가 증가하는 방향으로만 요청하도록 한다.
데드락 회피(Deadlock Avoidance)
- 데드락 회피는 시스템이 안전 상태를 유지할 수 있도록 자원 할당을 동적으로 조정하는 방법이다.
- 대표적인 알고리즘은
은행가 알고리즘(Banker's Algorithm)이 있다. - 은행가 알고리즘은 프로세스가 자원을 요청할 때 시스템이 안전한 상태인지 검사하여, 안전한 상태일 때만 자원을 할당한다.
안전 상태(Safe State): 시스템이 모든 프로세스에 대해 자원을 할당할 수 있는 순서가 존재하는 상태안전 순서(Safe Sequence): 프로세스들이 데드락 없이 자원을 할당받아 실행될 수 있는 순서
- 알고리즘 단계는 아래와 같다.
- 초기화
- 시스템의 자원총량, 현재 할당된 자원, 프로세스의 최대 자원 요청량을 초기화
- 자원요청
- 프로세스가 자원을 요청하면, 시스템은 요청을 일시적으로 할당해본 후 안전 상태를 검사
- 안전 상태면 자원을 실제로 할당, 그렇지 않으면 프로세스는 대기 상태로 유지
- 안전검사
- 현재 시스템 상태에서 모든 프로세스가 자원을 할당받아 완료될 수 있는지 검사
- 모든 프로세스가 완료될 수 있으면 안전상태, 그렇지 않으면 불완전 상태이다.
- 초기화
데드락 탐지(Detection) 및 복구(Recovery)
- 데드락 탐지기법은 시스템의 상태를 모니터링하여 데드락이 발생했는지 여부를 판단하는 방법이다.
- 탐지 방법에는 대표적으로
자원 할당 그래프와웨이트-포 그래프를 사용한다.
- 자원 할당 그래프(Resource Allocation Graph)
- 자원가 프로세스의 관계를 그래플로 표현
- 그래프에서 사이클이 발생하면 데드락이 존재
- 웨이트-포 그래프(Wait-For Graph)
- 자원 할당 그래프를 단순화하여 프로세스 간의 대기 관계만을 나타낸다.
- 그래프에서 사이클이 발생하면 데드락 발생
- 데드락 복구는 데드락이 탐지됐을 때 이를 해결한다. 대표적인 방법은
프로세스 종료와자원 선점이다.
- 프로세스 종료(Process Termination)
- 모든 데드락 프로세스 종료
- 한 번에 한 프로세스 종료
- 자원 선점(Resource Preemption)
- 점유된 자원을 강제로 회수하여 데드락 최소화
- 자원을 선점할 프로세스를 선택