Ⅰ. Virtual 환경에서 하드디스크 추가
- VMware 시작 윈도우에서 Edit virtual machine settings 클릭
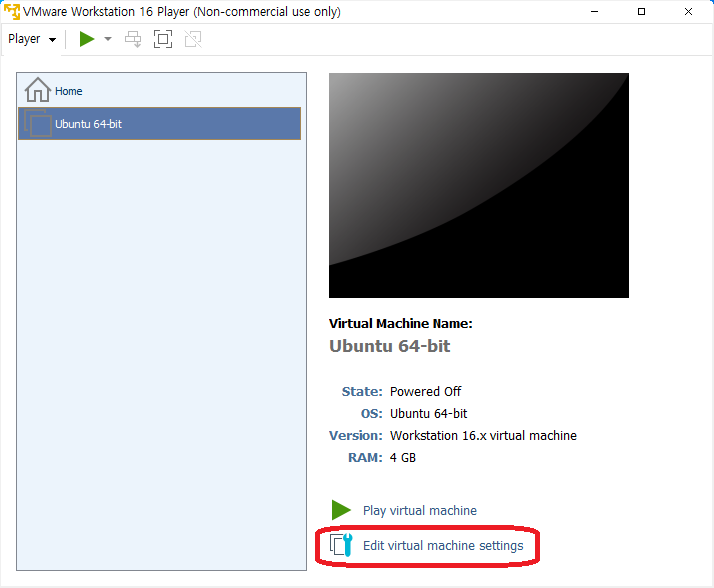
- Add.. 클릭 -> Hard Disk 선택 -> Next 클릭
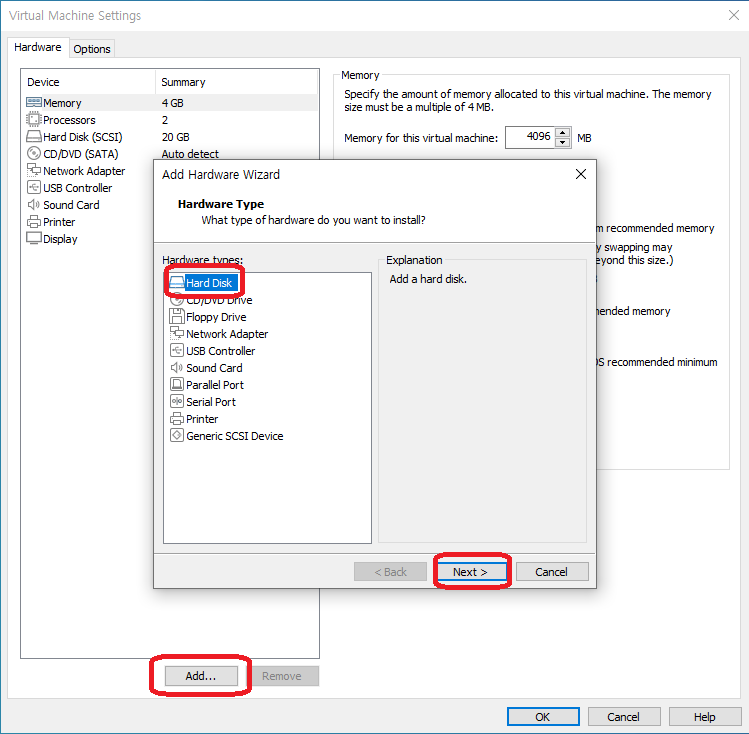
- SCSI 선택 후 Next
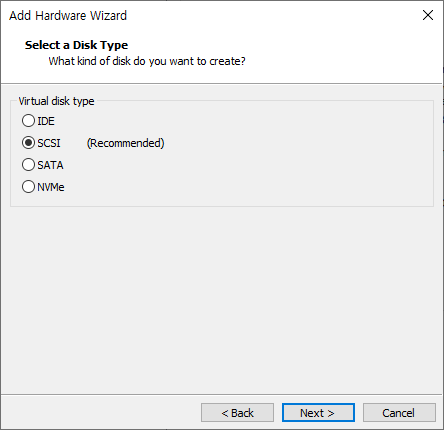
- Create a new virtual disk 선택 후 Next
- 용량 지정 후 Next
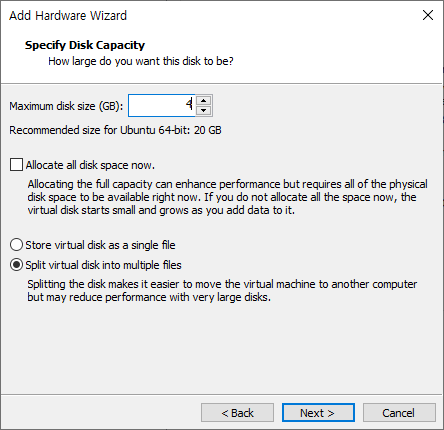
- Finish를 눌러 완료
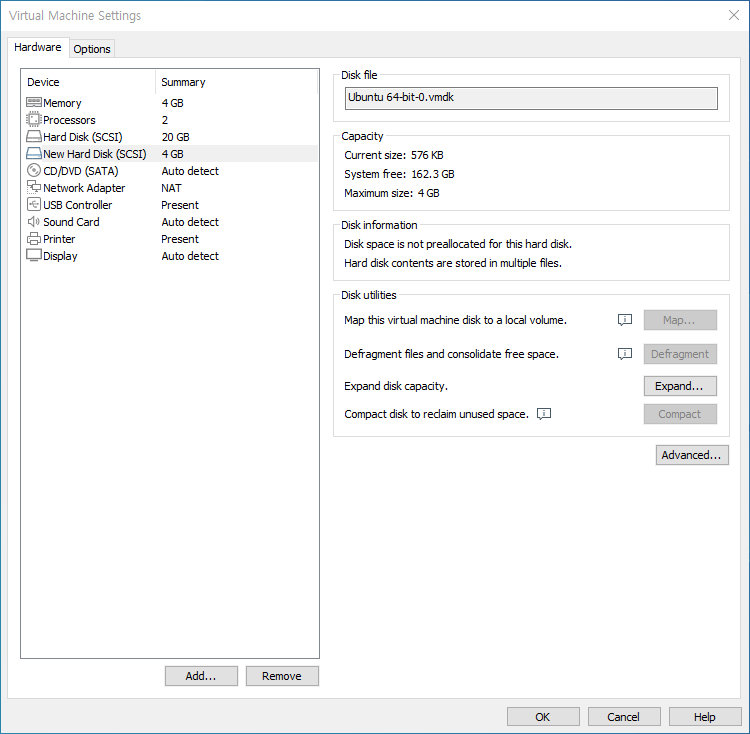
- New Hard Disk 가 생겼으면 성공
Ⅱ. Partitioning
-
Physical / Logical 로 나뉨 : 작은 시스템에는 Physical partition으로 충분
-
Physical partioning은 label타입에 따라 DOS방식, GTP 방식이로 나뉨
- DOS : 최대 2T, fdisk 사용
- GPT : 용량 제한 없음, parted 사용
1. DOS labeled disk
- 최대 4 개의 primary partition을 만들 수 있음
- 그 이상을 쓰고 싶을 경우 하나의 primary partition을 extened partition로 대체 할 수 있음
- extended partition을 여러 개의 logical drive로 나눌 수 있음
a. 디스크 목록
# fdisk -lor# lsblk
root@jsg-ubuntu:~# fdisk -l Disk /dev/sda: 20 GiB, 21474836480 bytes, 41943040 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disklabel type: dos Disk identifier: 0x2658b87a Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type /dev/sda1 * 2048 39942143 39940096 19G 83 Linux /dev/sda2 39944190 41940991 1996802 975M 5 Extended /dev/sda5 39944192 41940991 1996800 975M 82 Linux swap / Solaris Disk /dev/sdb: 4 GiB, 4294967296 bytes, 8388608 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
- /dev/sd[abcd..:몇 번째 디스크인지][123...:몇 번째 파티션인지]
b. 특정 디스크 조작
# fdisk /dev/...- m 을 입력하면 가능한 커맨드를 볼 수 있음
root@jsg-ubuntu:~# fdisk /dev/sdb Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.27.1). Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them. Be careful before using the write command. Device does not contain a recognized partition table. Created a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x059ba759. Command (m for help): m Help: ... Generic d delete a partition # 파티션 삭제 F list free unpartitioned space l list known partition types # 파티션 타입 목록 n add a new partition # 새로운 파티션 생성 p print the partition table # 현재 파티션 상태 출력 t change a partition type # 파티션 타입 변경 v verify the partition table i print information about a partition ... Save & Exit w write table to disk and exit # 변경된 사항 저장하고 종료 q quit without saving changes # 변경된 사항 저장하지 않고 종료 ...
- 새로운 파티션 생성 : n
Command (m for help): n Partition type p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free) e extended (container for logical partitions) Select (default p): p # primary partion으로 생성 Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1 # 1번 파티션 (/dev/sdb1) First sector (2048-8388607, default 2048): # 시작점 Last sector, +size{K,M,G,T,P} (2048-8388607, default 8388607): +2G # 끝점(+크기) Created a new partition 1 of type 'Linux' and of size 2 GiB. Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/sdb: 4 GiB, 4294967296 bytes, 8388608 sectors Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disklabel type: dos Disk identifier: 0x059ba759 Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type /dev/sdb1 2048 4196351 4194304 2G 83 Linux
- 파티션 삭제 : d
Command (m for help): d Selected partition 1 Partition 1 has been deleted.
Ⅲ. make file system
- 포맷이라고도 함
1. File System 종류
- ext4 : 리눅스 고유 파일 시스템, 작은 기기에 유리
- xfs : RHEL계열(7 이후부터) 기본 시스템, 고성능 기기에 유리
- zfs : CoW가 지원되어 좋지만 아직 실험적인 단계인 파일 시스템
- ntfs : 윈도우NT 계열 파일 시스템
- fat32/exfat : 카메라에서 많이 쓰이는 파일 시스템
2. mkfs
- file system 생성
# mkfs -t fs_type device or # mkfs.fs_type device
root@jsg-ubuntu:~# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1 mke2fs 1.42.13 (17-May-2015) Creating filesystem with 524288 4k blocks and 131072 inodes Filesystem UUID: 2dcf43d4-819c-40b2-9bd3-bf3c415c4a35 Superblock backups stored on blocks: 32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912 Allocating group tables: done Writing inode tables: done Creating journal (16384 blocks): done Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
3. fsck
-
file system의 무결성을 확인
-
offline(unmount) 상태에서하는게 안전함
-
# fsck -t fs_type deviceor# fsck.file_type device
root@jsg-ubuntu:~# fsck.ext4 /dev/sdb1 e2fsck 1.42.13 (17-May-2015) /dev/sdb1: clean, 11/131072 files, 25388/524288 blocks root@jsg-ubuntu:~# echo $? 0 # 0이면 정상
4. mkswap
-
메모리 부족할 때 디스크의 도움 받을 수 있음
-
# mkswap -L label_name device: 스왑 공간 생성
root@jsg-ubuntu:~# mkswap -L swapfs2 /dev/sdb2 mkswap: /dev/sdb2: warning: don't erase bootbits sectors (dos partition table detected). Use -f to force. Setting up swapspace version 1, size = 1024 MiB (1073737728 bytes) LABEL=swapfs2, UUID=c44f5b14-9bcc-4eca-89f9-13dff591f124
-
# swapon device: 스왑 활성화 -
# swapoff device: 스왑 비활성화 -
# cat /proc/swaps: 스왑 공간 확인
root@jsg-ubuntu:~# cat /proc/swaps Filename Type Size Used Priority /dev/sda5 partition 998396 0 -2 /dev/sdb2 partition 1048572 0 -3
Ⅳ. mount
1. mount table 보기
# findmnt
root@jsg-ubuntu:~# findmnt TARGET SOURCE FSTYPE OPTIONS / /dev/sda1 ext4 rw,relatime,errors=remo ├─/sys sysfs sysfs rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec, │ ├─/sys/kernel/security securityfs securit rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec, │ ├─/sys/fs/cgroup tmpfs tmpfs ro,nosuid,nodev,noexec, │ │ ├─/sys/fs/cgroup/systemd cgroup cgroup rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec, │ │ ├─/sys/fs/cgroup/memory cgroup cgroup rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec, │ │ ├─/sys/fs/cgroup/freezer cgroup cgroup ... ... └─/run/user/1000 tmpfs tmpfs rw,nosuid,nodev,relatim └─/run/user/1000/gvfs gvfsd-fuse fuse.gv rw,nosuid,nodev,relatim
2. mount 하기
# mount -t fs_type [-o option] device directory
root@jsg-ubuntu:~# mkdir /media/backup root@jsg-ubuntu:~# mount -t ext4 /dev/sdb1 /media/backup root@jsg-ubuntu:~# lsblk NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT sdb 8:16 0 4G 0 disk ├─sdb2 8:18 0 1G 0 part [SWAP] └─sdb1 8:17 0 2G 0 part /media/backup # mount 됨 확인 sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom sda 8:0 0 20G 0 disk ├─sda2 8:2 0 1K 0 part ├─sda5 8:5 0 975M 0 part [SWAP] └─sda1 8:1 0 19G 0 part /
- 기존 mount할 directory에 있던 파일들은 보이지 않게 됨. unmount하면 다시 보임!
3. unmount 하기
# umount deviceor# umount directory
root@jsg-ubuntu:~# umount /media/backup root@jsg-ubuntu:~# lsblk NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT sdb 8:16 0 4G 0 disk ├─sdb2 8:18 0 1G 0 part [SWAP] └─sdb1 8:17 0 2G 0 part sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom sda 8:0 0 20G 0 disk ├─sda2 8:2 0 1K 0 part ├─sda5 8:5 0 975M 0 part [SWAP] └─sda1 8:1 0 19G 0 part /
- "target is busy"가 뜨는 경우
fuser -c[k] dir로 PID 찾은후 kill 명령
root@jsg-ubuntu:/media/backup# umount /media/backup umount: /media/backup: target is busy (In some cases useful info about processes that use the device is found by lsof(8) or fuser(1).) root@jsg-ubuntu:/media/backup# fuser -c /media/backup /media/backup: 2657c
4. remount
-
mount된 파티션의 옵션을 변경할 때
-
# mount -o remount,option device
root@jsg-ubuntu:~# mount -o remount,ro /dev/sdb1 root@jsg-ubuntu:~# findmnt TARGET SOURCE FSTYPE OPTIONS / /dev/sda1 ext4 rw,relatime,errors=remo ├─/sys sysfs sysfs rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec, │ ├─/sys/kernel/security securityfs securit rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec, ... └─/media/backup /dev/sdb1 ext4 ro,relatime,data=ordere
5. bind
# mount --bind old_dir new_dir: 하나의 디렉토리를 다른 디렉토리에 연결시킴
Ⅴ. fstab
-
부팅시 파일 시스템을 자동 마운트하기 위한 정보
- device : 아래 중 하나
- /dev/sd... : 실제 디바이스로 설정하는 방식
- Label=name : 레이블 이름으로 검색해서 설정하는 방식
- UUID=uuid : UUID 값으로 검색해서 설정하는 가장 최신 방식
- mount point : mount 할 directory
- fstype : file type
- options :
- defaults : 기본값, 부팅시 자동으로 마운트
- noauto : 부팅시 자동으로 마운트 X
- rw : 읽기/ 쓰기 가능
- ro : 읽기만 가능
- user : 일반 유저도 마운트 가능
- nouser : 루트 유저만 마운트 가능
- noexec : 실행파일의 사용 금지
- dump: 백업 가능(0) / 불가능 (1)
- fsck: fsck 우선순위, 안함(0), 루트와 같은 우선 순위(1), 후순위(2)
- device : 아래 중 하나
| device | mount point | fstype | options | dump | fsck |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UUID=e65ee1... | / | ext4 | errors=remount-ro | 0 | 1 |
| UUID=84970b... | none | swap | sw | 0 | 0 |
1. Label, UUID 값 생성
a. 레이블 생성
e2label device [new-label]
root@jsg-ubuntu:~# blkid /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdb1: LABEL="Study" UUID="2dcf43d4-819c-40b2-9bd3-bf3c415c4a35" TYPE="ext4" PARTUUID="059ba759-01"
b. UUID 생성
tune2fs -U <clear|random|time|uuid_value> device
- -L 을 옵션으로 주면 Label도 설정 가능
- uuid 입력 방법:
- clear : 값 클리어
- random : 랜덤으로 지정
- time : 시간을 토대로 지정
- uuid_value : uuid_value를 직접 입력해 지정 (uuidgen을 많이 사용)
root@jsg-ubuntu:~# tune2fs -U $(uuidgen) /dev/sdb1 tune2fs 1.42.13 (17-May-2015) root@jsg-ubuntu:~# blkid /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdb1: LABEL="Study" UUID="9c4daae1-21b2-4619-8d02-db881a6fd4b3" TYPE="ext4" PARTUUID="059ba759-01"
c. 레이블, UUID 로 디바이스 검색
findfs LABEL=label or findfs UUID=uuid
root@jsg-ubuntu:~# findfs LABEL=Study /dev/sdb1 root@jsg-ubuntu:~# findfs UUID=9c4daae1-21b2-4619-8d02-db881a6fd4b3 /dev/sdb1
d. 레이블/UUID 등 디바이스 정보 보기
# blkid [device]
root@jsg-ubuntu:~# blkid /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdb1: LABEL="Study" UUID="9c4daae1-21b2-4619-8d02-db881a6fd4b3" TYPE="ext4" PARTUUID="059ba759-01"
2. /etc/fstab 수정
root@jsg-ubuntu:~# cat /etc/fstab # /etc/fstab: static file system information. # # Use 'blkid' to print the universally unique identifier for a # device; this may be used with UUID= as a more robust way to name devices # that works even if disks are added and removed. See fstab(5). # # file_system mount_point type options dump pass UUID=e65ee146-aea7-418b-8946-8993e297d5a6 / ext4 errors=remount-ro 0 1 UUID=84970be2-9cd1-49c0-9f99-eec452cfccaa none swap sw 0 0 UUID=9c4daae1-21b2-4619-8d02-db881a6fd4b3 /media/backup ext4 defaults 0 1 root@jsg-ubuntu:~# lsblk # 컴퓨터 재실행시 자동 마운트 됨 NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT sdb 8:16 0 4G 0 disk ├─sdb2 8:18 0 1G 0 part └─sdb1 8:17 0 2G 0 part /media/backup sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom sda 8:0 0 20G 0 disk ├─sda2 8:2 0 1K 0 part ├─sda5 8:5 0 975M 0 part [SWAP] └─sda1 8:1 0 19G 0 part /
Ⅵ. udisksctl
-
수동 mount 대신 자주 쓰임
-
일반 유저로 명령을 실행해야하고, 디렉토리를 자동 생성/삭제 해줌
-
$ udisksctl mount -b device: 마운트 -
$ udisksctl unmount -b device: 언마운트 -
$ udisksctl loop-setup --file XXX.iso: 파일을 디바이스처럼 마운트 -
$ udisksctl status: 장착된 장치 정보 -
$ udisksctl dumpor$ udisksctl info -d device: 개별 장치 정보
