문제
풀이
라이브러리 사용 ❌
이모티콘의 할인율은 10%, 20%, 30%, 40% 네 개로 제한되어 있다. 각각의 이모티콘에 대해 4개의 할인율을 전부 적용한 중복 순열을 만드는 함수 find_product와 그렇게 설정된 각각의 할인율 조합에 대해 가능한 모든 가입자수와 판매액을 계산하는 price_calc 함수를 통해 최종적으로 가장 큰 가입자수와 판매액을 갖는 경우를 찾아 답 반환.
def solution(users, emoticons):
# 변수 선언
m = len(emoticons)
answer = [-1, -1]
products = []
def find_product(lst, m):
nonlocal products
if len(lst) == m:
products.append(lst)
return
for i in (40, 30, 20, 10):
find_product(lst+[i], m)
def price_calc(user, product):
nonlocal signup, sales
price = 0
for i in range(m):
if user[0] <= product[i]: # 유저의 할인율보다 높아야 계산
price += emoticons[i] * (1-0.01*product[i])
if price >= user[1]: # 유저의 가격 한계치보다 높으면 가입함
signup += 1
return
sales += price
find_product([], m)
for product in products:
signup = sales = 0 # 각 할인율에 따른 가입자수와 판매액
for user in users:
price_calc(user, product)
answer = max(answer, [signup, sales]) # 가입자수의 우선순위가 더 높음
return answer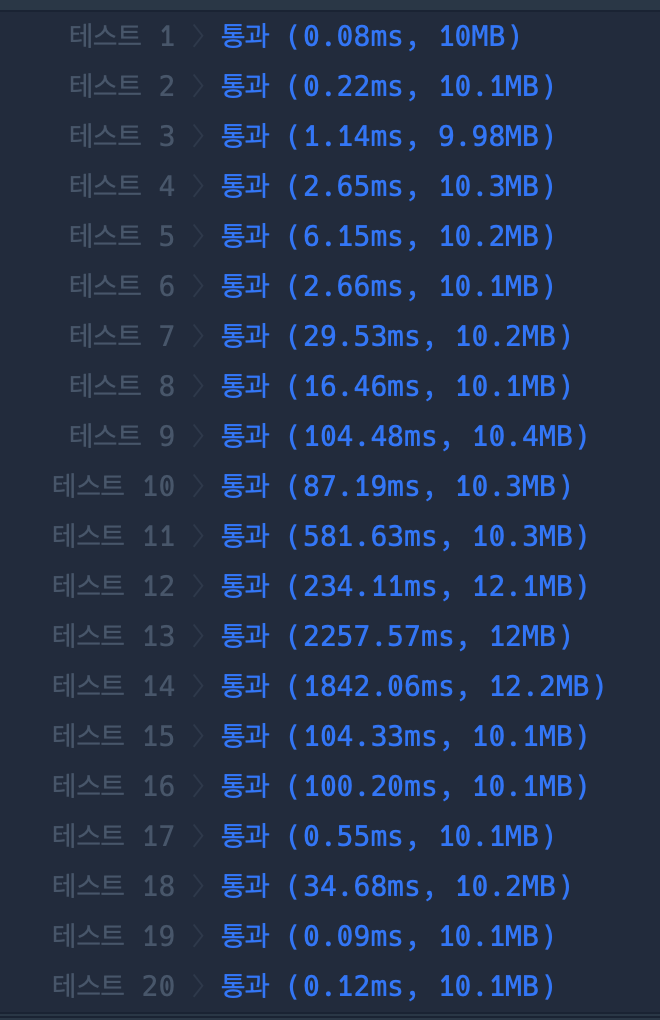
product 라이브러리 사용 ⭕️
파이썬의 itertools 라이브러리에 순열과 조합을 구하는 combinations와 permutations가 있는데 중복 순열을 구하는 products도 있다. 위의 코드에서의 find_product와 같은 역할.
시간은 라이브러리를 사용하는 경우가 좀 더 빠르다.
def solution(users, emoticons):
answer = []
lst = [40, 30, 20, 10]
emoticons.sort(reverse=1)
for sale in product(lst, repeat=len(emoticons)):
signin = total_price = 0
for percent, price in users:
user_price = 0
for i in range(len(sale)):
if sale[i] < percent:
continue
user_price += emoticons[i] * (1-0.01*sale[i])
if user_price >= price:
signin += 1
break
else:
total_price += user_price
answer = max(answer, [signin, total_price])
return answer
from itertools import product
