ref 사용방법
클래스형 컴포넌트
React.createRef() API를 이용하는 방법
(React 16.3에 추가. 사용 권장)
import React, { Component } from "react";
class MyComponent extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.myRef = React.createRef();
}
render() {
return (
<>
<input ref={this.myRef} />
<button onClick={this.handler}>포커스전달</button>
</>
);
}
handler =() => {
const node = this.myRef.current; // current 속성 붙여줘야 한다.
node.focus();
}
}
function App() {
return <MyComponent />;
}
export default App;
포커스전달을 클릭하면 input에 포커싱된다.
콜백 ref를 이용하는 방법 ❌
ref 어트리뷰트에 React.createRef()를 통해 생성된 ref를 전달하는 대신, 함수를 전달
전달된 함수는 다른 곳에 저장되고 접근될 수 있는 React 컴포넌트의 인스턴스나 DOM 엘리먼트를 인자로 받음
<input ref={ x => this.myInput = x} />
~~~~~~~~~~~~
이 변수를 이용해서 <input> 요소를 직접 제어하는 것이 가능
ex) this.myInput.focus();import { Component } from "react";
class MyComponent extends Component {
state = {
message: ""
};
handler = () => {
const node = this.myRef;
node.focus();
}
render() {
return (
<>
<input ref={x => { this.myRef = x; console.log(x); }}
onChange={e => this.setState({ message: e.target.value })} />
<button onClick={this.handler}>포커스전달</button>
</>
);
}
}
function App() {
return <MyComponent />;
}
export default App;
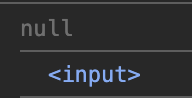
처음에 null 을 전달해서 초기화 시키고 요소를 넣어서 값을 설정해준다.
그래서 콜백함수가 두 번 호출된다. -> side effect 를 낼 수 있다 😭
가급적이면 React.createRef() API를 이용하자.
패스워드를 검증하는 컴포넌트를 작성
패스워드 검증 버튼을 클릭하면, 패스워드 입력창의 내용이 0000이면 배경색을 파란색으로, 아니면 붉은색으로 설정
PasswordChecker.js 파일을 생성
import { Component } from "react";
class PasswordChecker extends Component {
state = {
password: "",
};
changePassword = e => this.setState({ password: e.target.value });
render() {
return (
<>
<input type="password" value={this.state.password} onChange={this.changePassword} />
<button>패스워드 검증</button>
</>
);
}
}
export default PasswordChecker;PasswordChecker 컴포넌트에 패스워드 검증 버튼을 클릭했을 때 동작을 추가
어떤 요소가 있는 값을 이용하거나 스타일을 적용할 때는 상태 변수를 활용하면 충분하다.
import { Component } from "react";
class PasswordChecker extends Component {
state = {
password: "",
isValid: false
};
changePassword = e => this.setState({ password: e.target.value });
clickButton = () => {
if (this.state.password === "0000") {
this.setState({isValid: true});
} else {
this.setState({isValid: false});
}
};
render() {
return (
<>
<input type="password"
value={this.state.password}
onChange={this.changePassword}
style={this.state.isValid ? { backgroundColor: "blue" } : { backgroundColor: "red" }}
/>
<button onClick={this.clickButton}>패스워드 검증</button>
</>
);
}
}
export default PasswordChecker;0000 누르면

그 외

패스워드가 잘못되었을 때 패스워드 입력창에 포커스가 전달되도록 수정
콜백 함수를 이용하는 방법
ref 변수 추가 및 틀렸을 때 this.myInput.focus(); 추가
import { Component } from "react";
class PasswordChecker extends Component {
state = {
password: "",
isValid: false
};
changePassword = e => this.setState({ password: e.target.value });
clickButton = () => {
if (this.state.password === "0000") {
this.setState({isValid: true});
} else {
this.setState({isValid: false});
this.myInput.focus();
}
};
render() {
return (
<>
<input type="password"
value={this.state.password}
onChange={this.changePassword}
style={this.state.isValid ? { backgroundColor: "blue" } : { backgroundColor: "red" }}
ref={x => this.myInput = x}
/>
<button onClick={this.clickButton}>패스워드 검증</button>
</>
);
}
}
export default PasswordChecker;
틀리게 입력하고 검증을 누르면 focus가 깜빡인다.
createRef()를 이용하는 방법
import React, { Component } from "react";
class PasswordChecker extends Component {
state = {
password: "",
isValid: false
};
myInput = React.createRef();
changePassword = e => this.setState({ password: e.target.value });
clickButton = () => {
if (this.state.password === "0000") {
this.setState({isValid: true});
} else {
this.setState({isValid: false});
this.myInput.focus();
}
};
render() {
return (
<>
<input type="password"
value={this.state.password}
onChange={this.changePassword}
style={this.state.isValid ? { backgroundColor: "blue" } : { backgroundColor: "red" }}
ref={this.myInput}
/>
<button onClick={this.clickButton}>패스워드 검증</button>
</>
);
}
}
export default PasswordChecker;스크롤 박스 구현!
ref 디렉토리를 생성하고, 생성한 디렉토리에 ScrollBox.js 파일을 추가
import { Component } from "react";
class ScrollBox extends Component {
render() {
const styles = {
outer: {
marginTop: 300,
border: "1px solid black",
height: 300,
width: 300,
overflow: "auto",
},
inner: {
width: "100%",
height: 650,
background: "linear-gradient(white, black)"
}
}
return (
<div style={styles.outer}>
<div style={styles.inner}></div>
</div>
);
}
}
export default ScrollBox;
ScrollBox 컴포넌트에 맨 위로 이동, 맨 아래로 이동 버튼 추가
<div>
<button>맨 위로 이동</button>
<button>맨 아래로 이동</button>
</div>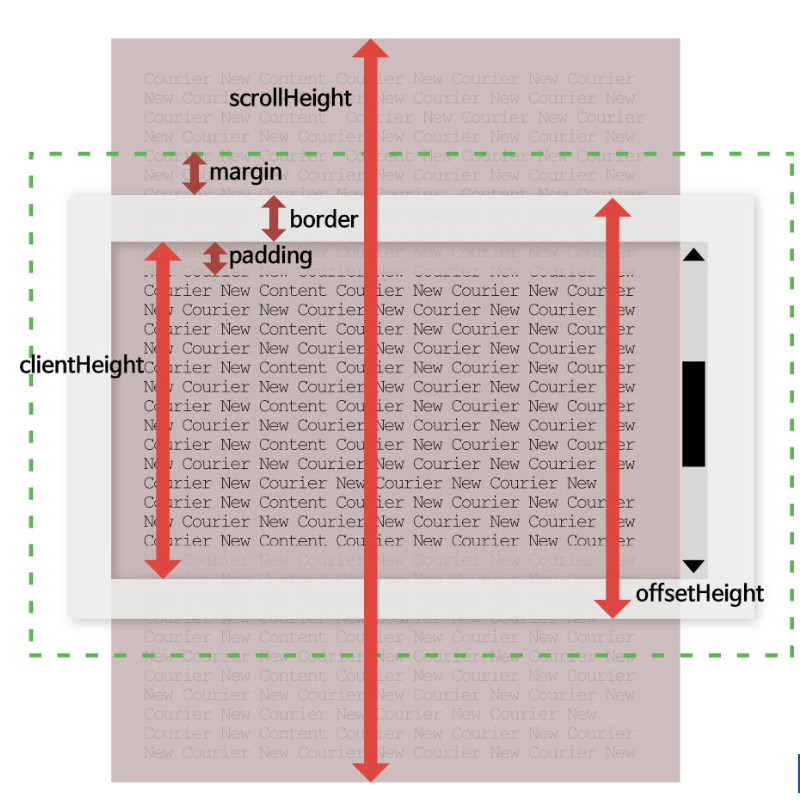
맨 아래쪽 : 전체(scrollHeight) - 보이는 영역(clientHeight)
ScrollBox 컴포넌트에 바닥 또는 위로 스크롤하는 함수를 추가
import { Component } from "react";
class ScrollBox extends Component {
scrollBottom = () => {
/*
const scrollHeight = this.myDiv.scrollHeight;
const clientHeight = this.myDiv.clientHeight;
*/
const { scrollHeight, clientHeight } = this.myDiv;
this.myDiv.scrollTop = scrollHeight - clientHeight;
};
scrollTop = () => {
this.myDiv.scrollTop = 0;
};
render() {
const styles = {
outer: {
marginTop: 300,
border: "1px solid black",
height: 300,
width: 300,
overflow: "auto",
},
inner: {
width: "100%",
height: 650,
background: "linear-gradient(white, black)"
}
};
return (
<>
<div style={styles.outer} ref={ x => this.myDiv = x}>
<div style={styles.inner}></div>
</div>
<div>
<button onClick={this.scrollTop}>맨 위로 이동</button>
<button onClick={this.scrollBottom}>맨 아래로 이동</button>
</div>
</>
);
}
}
export default ScrollBox;맨 위로 이동을 누르면 ⬇️

맨 아래로 이동을 누르면 ⬇️

이런 건 상태변수로 할 수가 없다 !! ref를 사용해야만 가능하다
createRef() 사용하는 것으로 변경
- myDiv = React.createRef(); 선언
- current를 붙이기
- ref={this.myDiv}를 사용
import React, { Component } from "react";
class ScrollBox extends Component {
myDiv = React.createRef();
scrollBottom = () => {
/*
const scrollHeight = this.myDiv.scrollHeight;
const clientHeight = this.myDiv.clientHeight;
*/
const { scrollHeight, clientHeight } = this.myDiv.current;
this.myDiv.current.scrollTop = scrollHeight - clientHeight;
};
scrollTop = () => {
this.myDiv.current.scrollTop = 0;
};
render() {
const styles = {
outer: {
marginTop: 300,
border: "1px solid black",
height: 300,
width: 300,
overflow: "auto",
},
inner: {
width: "100%",
height: 650,
background: "linear-gradient(white, black)"
}
};
return (
<>
<div style={styles.outer} ref={this.myDiv}>
<div style={styles.inner}></div>
</div>
<div>
<button onClick={this.scrollTop}>맨 위로 이동</button>
<button onClick={this.scrollBottom}>맨 아래로 이동</button>
</div>
</>
);
}
}
export default ScrollBox;[실습] ID, PW 검증

등록 버튼을 클릭하면, ID, PW 입력창에 값 입력 여부와 PW 입력창에 값 일치 여부를 체크해서 적절한 메시지를 출력하고, 문제가 있는 입력창으로 포커스를 이동하도록 아래 코드를 완성해 보세요.
import { Component } from "react";
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
ID: <input type="text" /><br/>
PW: <input type="password" /><br/>
PW: <input type="password" /><br/>
<button type="submit">등록</button>
</div>
)
}
}
export default App;상태변수와 상태변수를 변경하는 핸들러 함수를 정의하고 설정
import { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
state = {
userId: '',
userPw1: '',
userrPw2: '',
};
changeUserId = (e) => this.setState({ userId: e.target.value });
changeUserPw1 = (e) => this.setState({ userPw1: e.target.value });
changeUserPw2 = (e) => this.setState({ userPw2: e.target.value });
render() {
const { userId, userPw1, userPw2 } = this.state;
return (
<div>
ID:
<input type="text" value={userId} onChange={this.changeUserId} />
<br />
PW:
<input type="password" value={userPw1} onChange={this.changeUserPw1} />
<br />
PW:
<input type="password" value={userPw2} onChange={this.changeUserPw2} />
<br />
<button type="submit">등록</button>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;계산된 속성명을 이용해서 이벤트 핸들러 함수를 하나의 함수로 변경
import { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
state = {
userId: '',
userPw1: '',
userrPw2: '',
};
/*
changeUserId = (e) => this.setState({ userId: e.target.value });
changeUserPw1 = (e) => this.setState({ userPw1: e.target.value });
changeUserPw2 = (e) => this.setState({ userPw2: e.target.value });
*/
changeUser = (e) => this.setState({ [e.target.name]: e.target.value });
render() {
const { userId, userPw1, userPw2 } = this.state;
return (
<div>
ID:
<input type="text" value={userId} name="userId" onChange={this.changeUser} />
<br />
PW:
<input type="password" value={userPw1} name="userPw1" onChange={this.changeUser} />
<br />
PW:
<input type="password" value={userPw2} name="userPw2" onChange={this.changeUser} />
<br />
<button type="submit">등록</button>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;입력창을 직접 제어하기 위한 ref를 추가 (콜백 함수 형태)
import { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
state = {
userId: '',
userPw1: '',
userrPw2: '',
};
/*
changeUserId = (e) => this.setState({ userId: e.target.value });
changeUserPw1 = (e) => this.setState({ userPw1: e.target.value });
changeUserPw2 = (e) => this.setState({ userPw2: e.target.value });
*/
changeUser = (e) => this.setState({ [e.target.name]: e.target.value });
render() {
const { userId, userPw1, userPw2 } = this.state;
return (
<div>
ID:
<input ref={x => this.refUserId = x} type="text" value={userId} name="userId" onChange={this.changeUser} />
<br />
PW:
<input ref={x => this.refUserPw1 = x} type="password" value={userPw1} name="userPw1" onChange={this.changeUser} />
<br />
PW:
<input ref={x => this.refUserPw2 = x} type="password" value={userPw2} name="userPw2" onChange={this.changeUser} />
<br />
<button type="submit">등록</button>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;등록 버튼을 클릭했을 때 동작을 추가
import { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
state = {
userId: '',
userPw1: '',
userrPw2: '',
};
changeUser = (e) => this.setState({ [e.target.name]: e.target.value });
clickButton = (e) => {
// Submit 버튼의 기본 동작을 중지
e.preventDefault();
// 객체 비구조화를 통해 상태변수를 지역변수로 변경
const { userId, userPw1, userPw2 } = this.state;
// 입력 여부 체크
if (userId.trim() === '') {
alert('ID를 입력하세요.');
this.refUserId.focus();
return;
}
if (userPw1.trim() === '') {
alert('PW1을 입력하세요.');
this.refUserPw1.focus();
return;
}
if (userPw2.trim() === '') {
alert('PW2를 입력하세요.');
this.refUserPw2.focus();
return;
}
// 패스워드 일치 여부를 확인
if (userPw1.trim() !== userPw2.trim()) {
alert('PW와 PW 확인이 일치하지 않습니다.');
this.setState({ userPw1: '', userPw2: '' });
this.refUserPw1.focus();
return;
}
// 입력 내용을 alert 창으로 출력
alert(`ID: ${userId}\nPW1: ${userPw1}\nPW2: ${userPw2}`);
};
render() {
const { userId, userPw1, userPw2 } = this.state;
return (
<div>
ID:
<input
ref={(x) => (this.refUserId = x)}
type="text"
value={userId}
name="userId"
onChange={this.changeUser}
/>
<br />
PW:
<input
ref={(x) => (this.refUserPw1 = x)}
type="password"
value={userPw1}
name="userPw1"
onChange={this.changeUser}
/>
<br />
PW:
<input
ref={(x) => (this.refUserPw2 = x)}
type="password"
value={userPw2}
name="userPw2"
onChange={this.changeUser}
/>
<br />
<button type="submit" onClick={this.clickButton}>
등록
</button>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;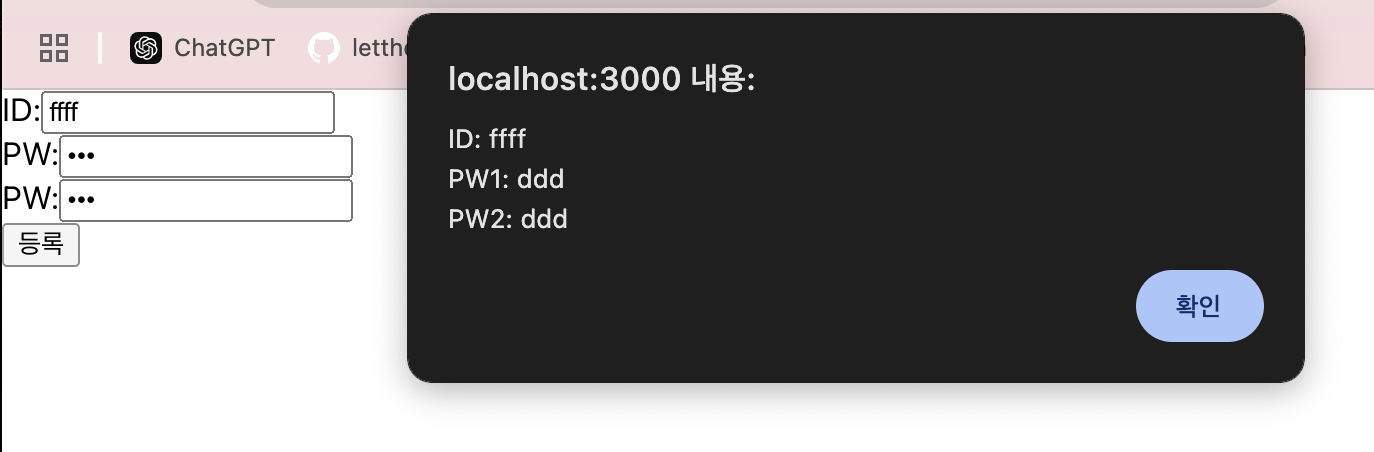
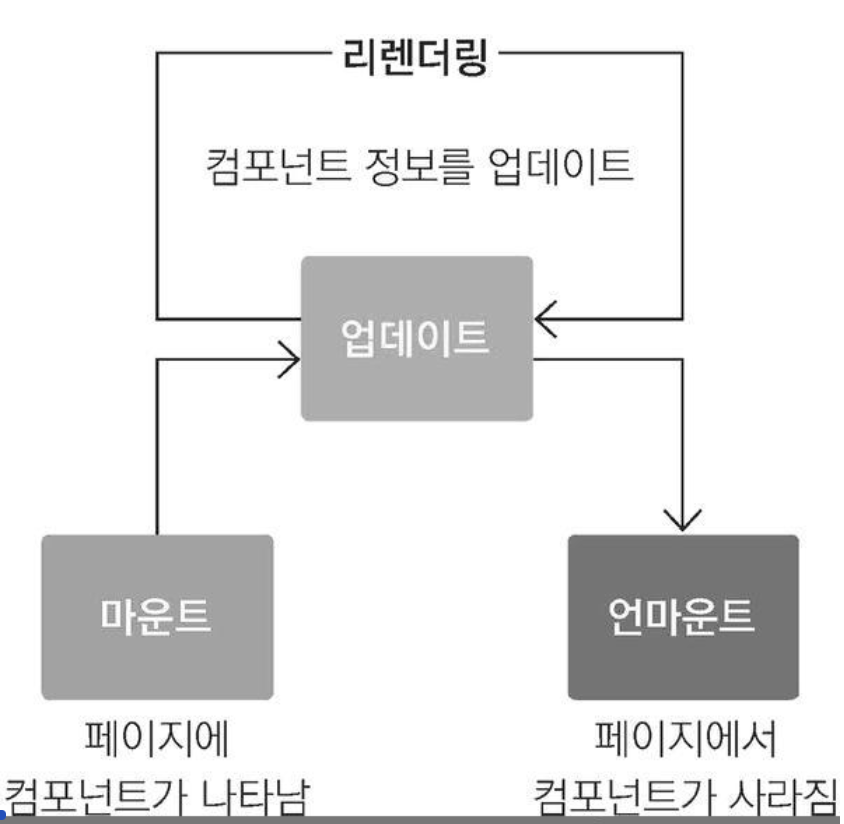
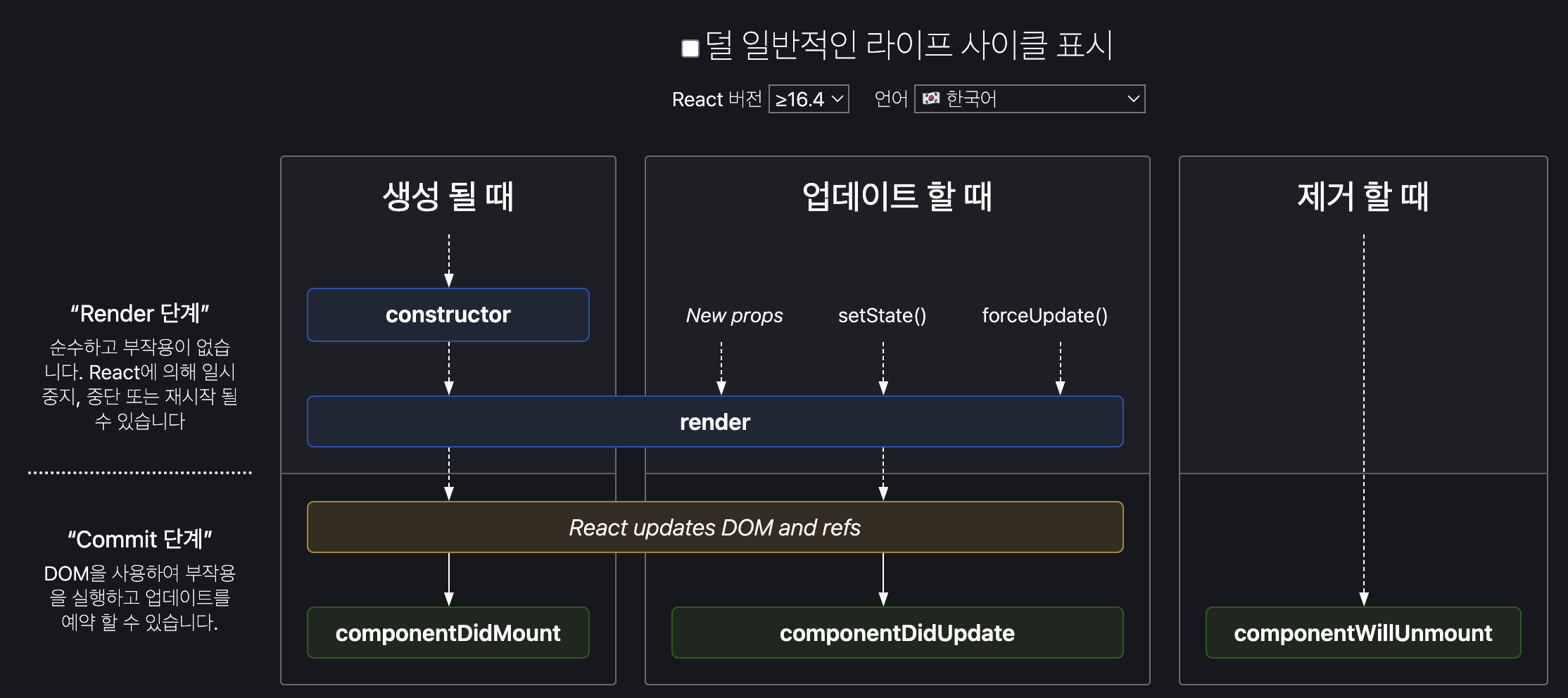
컴포넌트의 라이프사이클 메서드
개념
컴포넌트가 생성, 업데이트, 소멸되는 과정에서 특정 시점에 호출되는 메서드
- constructor : 생성자 (초기화)
- render : 화면에 출력되는 내용을 반환한다. 모든 컴포넌트마다 생성해줘야 한다
- 리액트는 render 를 바탕으로 DOM과 ref를 업데이트한다. - componentDidMount : 화면에 나타난 이후(로딩 페이지라도) componentDidMount에서 시간이 걸리는 작업(데이터를 가져온다든지)을 보여준다. 그 전에 가져오려고 하면 렌더링이 안 돼서 사용자 화면이 백지상태가 된다.
- componentDidUpdate : props나 state가 바뀌면 리렌더링 되고 componentDidUpdate 호출
- componentWillUnmount : 컴포넌트가 사라지기 바로 직전에 호출. clean up 함수(연결, 파일을 닫는 작업하는 함수들)
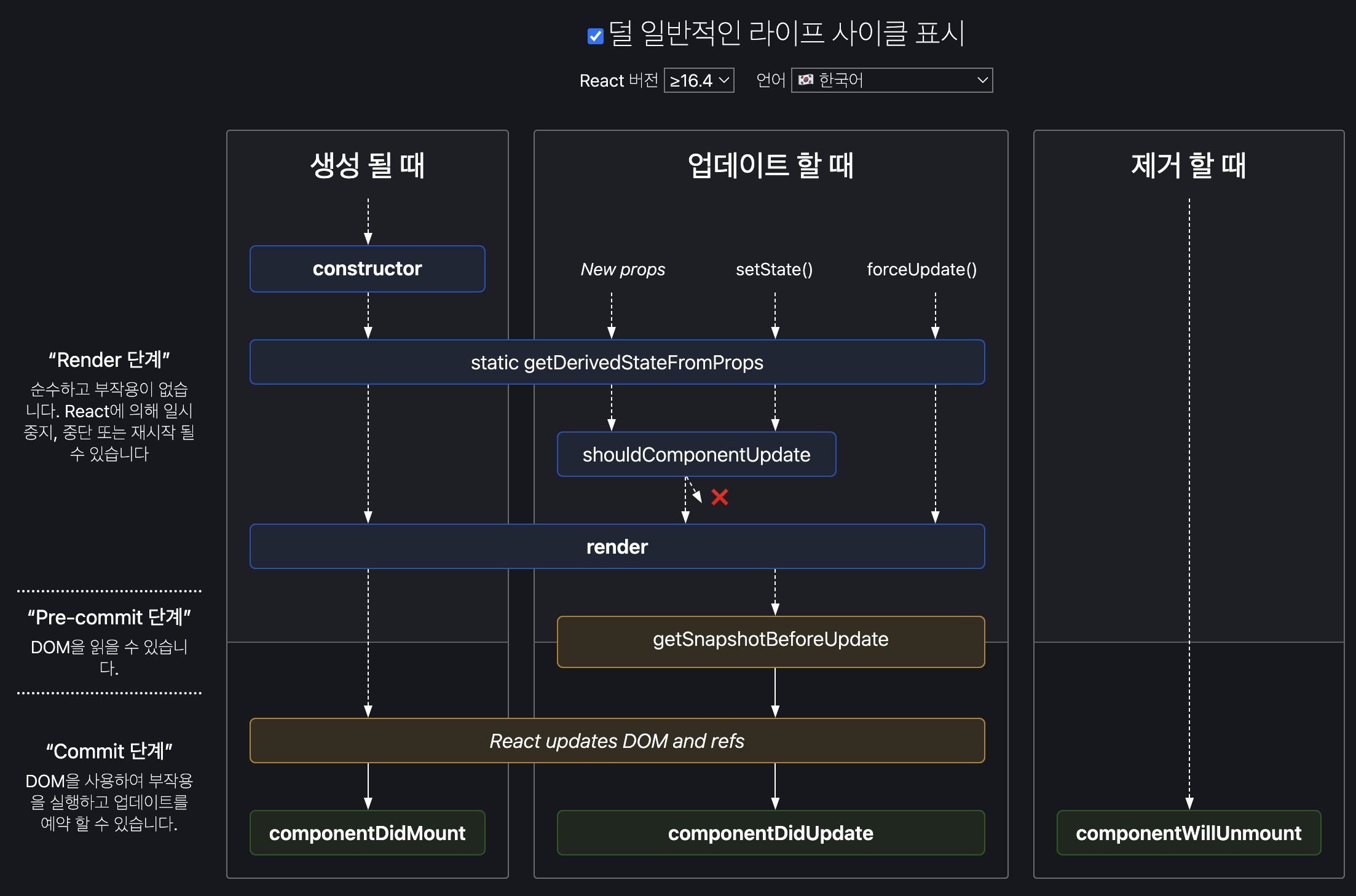
- static getDerigvedStateFromProps : props에 있는 값을 state에 넣어주려고 할 때
- shouldComponentUpdate : 업데이트 할 때 O, X
- O 면 업데이트 실행 -> render- X 면 업데이트 실행 X -> render X (빈번한 리렌더링을 막고자 할 때 사용)
라이프사이클 메서드 예제
부모 컴포넌트가 랜덤하게 생성한 글자색을 자식 컴포넌트에게 전달하고, 자식 컴포넌트는 글자색을 반영한 카운트를 제공
LifecycleSample.js 파일을 생성
import { Component } from 'react';
class LifecycleSample extends Component {
state = {
count: 0,
};
changeCount = (e) => {
console.log('하나 증가 버튼 클릭!!!');
this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });
};
render() {
console.log('render is called');
return (
<>
<h1>자식 컴포넌트</h1>
<h1 style={{ color: this.props.color }}>{this.state.count}</h1>
<button onClick={this.changeCount}>하나 증가</button>
</>
);
}
}
export default LifecycleSample;App.js 파일에 버튼을 하나 더 추가하고, 해당 버튼을 클릭하면 랜덤 컬러 버튼과 자식 컴포넌트를 토글링해서 보이는 기능을 추가
import { Component } from 'react';
import LifecycleSample from './LifecycleSample';
// 랜덤하게 색상(#0 ~ #ffffff)을 생성하는 함수
const getRandomColor = () => '#' + Math.floor(Math.random() * 16777215).toString(16);
class App extends Component {
state = {
color: '#000000',
isVisible: false,
};
changeColor = () => {
console.log('랜덤 컬러 버튼 클릭!!!');
this.setState({ color: getRandomColor() });
};
changeIsVisible = () => {
console.log(`자식 컴포넌트 ${this.state.isVisible ? '숨기기' : '보이기'} 버튼 클릭!!!`);
this.setState({ isVisible: !this.state.isVisible });
};
render() {
return (
<>
<button onClick={this.changeIsVisible}>
자식 컴포넌트 {this.state.isVisible ? '숨기기' : '보이기'}
</button>
{this.state.isVisible && (
<div style={{ border: '1px solid red', padding: 10, margin: 10, borderRadius: 10 }}>
<button onClick={this.changeColor}>랜덤 컬러</button>
<LifecycleSample color={this.state.color} />
</div>
)}
</>
);
}
}
export default App;
LifecycleSample 컴포넌트에 constructor, componentDidMount, componentDidUpdate, componentWillUnmount 메서드를 추가하고 해당 메서드에 로그를 추가
import { Component } from 'react';
class LifecycleSample extends Component {
state = {
count: 0,
};
changeCount = () => {
console.log('하나 증가 버튼 클릭!!!');
this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });
};
constructor(props) {
super(props);
console.log('constructor is called');
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('componentDidMount is called');
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {
console.log('componentDidUpdate is called');
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('componentWillUnmount is called');
}
render() {
console.log('render is called');
return (
<>
<h1>자식 컴포넌트</h1>
<h1 style={{ color: this.props.color }}>{this.state.count}</h1>
<button onClick={this.changeCount}>하나 증가</button>
</>
);
}
}
export default LifecycleSample;테스트
- 자식 컴포넌트 보이기 버튼 클릭 => 마운트 과정의 로그가 출력
- 랜덤 컬러 버튼 클릭 => props 변수가 변경 => 업데이트 과정의 로그가 출력
- 하나 증가 버튼 클릭 => state 변수가 변경 => 업데이트 과정의 로그가 출력
- 자식 컴포넌트 숨기기 버튼 클릭 => 언마운트 과정의 로그가 출력
부모 컴포넌트로부터 전달되는 글자색을 상태변수로 설정하고, 해당 상태변수의 값을 화면에 출력하도록 수정
import { Component } from 'react';
class LifecycleSample extends Component {
state = {
count: 0,
color: this.props.color
};
changeCount = () => {
console.log('하나 증가 버튼 클릭!!!');
this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });
};
constructor(props) {
super(props);
console.log('constructor is called');
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('componentDidMount is called');
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {
console.log('componentDidUpdate is called');
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('componentWillUnmount is called');
}
render() {
console.log('render is called');
return (
<>
<h1>자식 컴포넌트</h1>
<h1 style={{ color: this.props.color }}>{this.state.count}</h1>
<h1>color: {this.state.color}</h1>
<button onClick={this.changeCount}>하나 증가</button>
</>
);
}
}
export default LifecycleSample;color 상태 변수를 초기화 하고 출력하는 코드 추가 ! - 글자 실제 색은 바뀌는데 <h1>color: {this.state.color}</h1> 이 부분은 안 바뀜
상태 변수의 업데이트 로직이 없기 때문. 초기값만 설정되어 있고, 초기값 이후에 setter 함수가 없다!
상태변수 업데이트 로직이 없기 때문에 변경된 글자색 정보가 반영되지 않는다
=> getDerivedStateFromProps 메서드를 이용해서 props 변수로 전달된 글자색 정보를 상태변수에 반영해보자
...
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) {
console.log('getDerivedStateFromProps is called');
if (state.color !== props.color) {
return { color: props.color };
}
return null;
}
...
render() {
return (
<>
<h1>자식 컴포넌트</h1>
<h1 style={{ color: this.props.color }}>{this.state.count}</h1>
<h1>color: {this.state.color}</h1>
<button onClick={this.changeCount}>하나 증가</button>
</>
);
}
}
export default LifecycleSample;
클릭하는 대로 색이 바뀌어서 표시된다!!
카운트가 짝수인 경우에만 리렌더링되도록 수정
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
console.log('shouldComponentUpdate is called');
return nextState.count % 2 === 0;
}
짝수일 때만 바뀐다 (필요할 때만 리렌더링되도록 설정하고 싶을 때 유용)
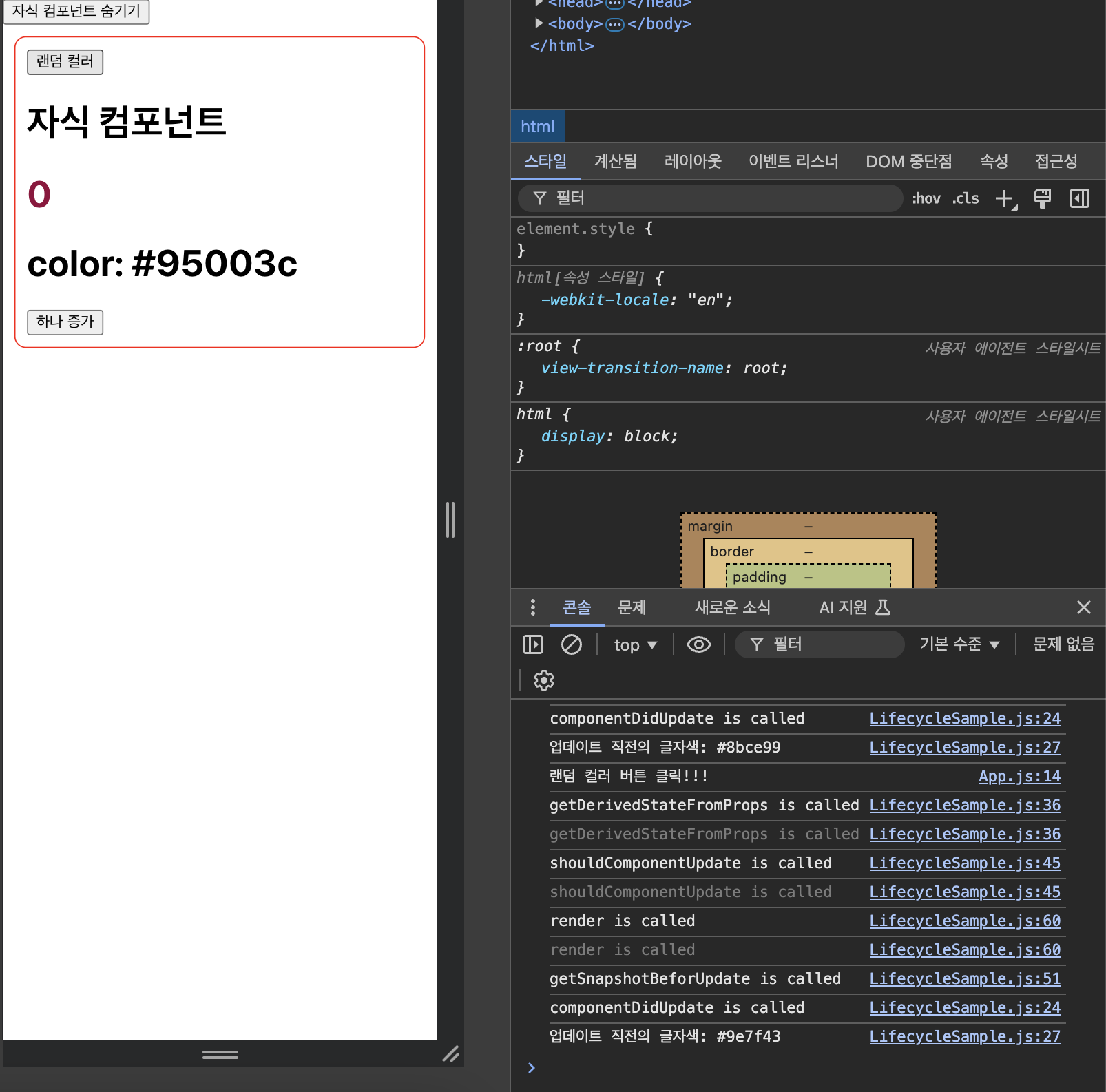
리렌더링 직전의 글자색을 로그로 출력하도록 수정 (snapshot)
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {
console.log('componentDidUpdate is called');
if (snapshot) {
console.log(`업데이트 직전의 글자색: ${snapshot}`)
}
}
...
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
console.log("getSnapshotBeforUpdate is called");
if (prevProps.color !== this.props.color) {
return prevProps.color;
}
return null;
}
최종 LifecycleSample
import { Component } from 'react';
class LifecycleSample extends Component {
state = {
count: 0,
color: this.props.color,
};
changeCount = () => {
console.log('하나 증가 버튼 클릭!!!');
this.setState({ count: this.state.count + 1 });
};
constructor(props) {
super(props);
console.log('constructor is called');
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('componentDidMount is called');
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {
console.log('componentDidUpdate is called');
if (snapshot) {
console.log(`업데이트 직전의 글자색: ${snapshot}`);
}
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('componentWillUnmount is called');
}
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state) {
console.log('getDerivedStateFromProps is called');
if (state.color !== props.color) {
return { color: props.color };
}
return null;
}
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
console.log('shouldComponentUpdate is called');
return nextState.count % 2 === 0;
}
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
console.log('getSnapshotBeforeUpdate is called');
if (prevProps.color !== this.props.color) {
return prevProps.color;
}
return null;
}
render() {
console.log('render is called');
return (
<>
<h1>자식 컴포넌트</h1>
<h1 style={{ color: this.props.color }}>{this.state.count}</h1>
<h1>color: {this.state.color}</h1>
<button onClick={this.changeCount}>하나 증가</button>
</>
);
}
}
export default LifecycleSample;
index.js 에 React.StrictMode로 감싸져 있어서 로그에 이렇게 두 번씩 호출되는 문제가 있다
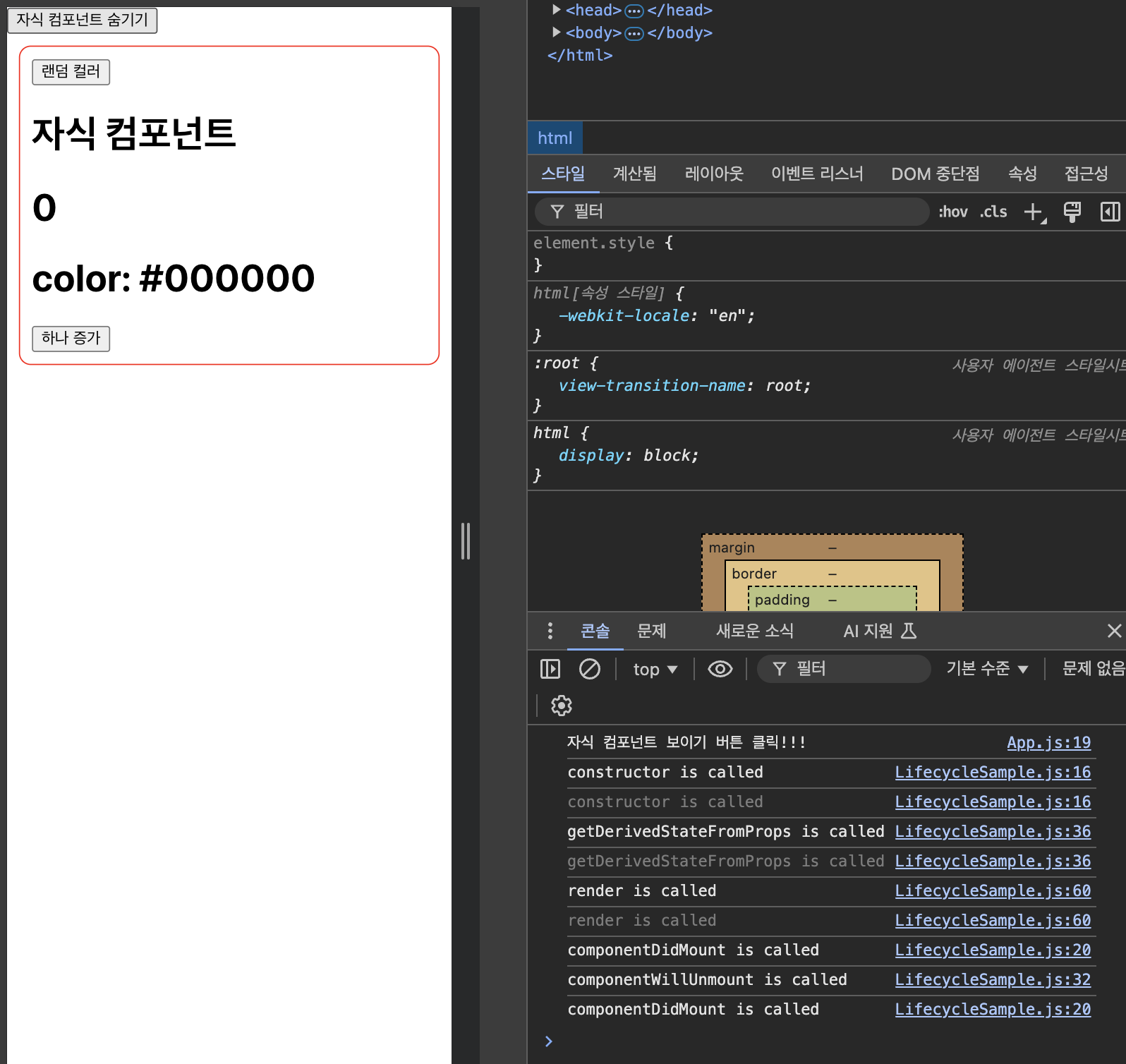
일단 주석 처리하자 !
render 함수에 에러를 발생시키는 코드를 추가
render() {
console.log('render is called');
return (
<>
{this.state.missing.value} {/* 정의되지 않은 state 변수를 참조 */}
<h1>자식 컴포넌트</h1>
<h1 style={{ color: this.props.color }}>{this.state.count}</h1>
<h1>color: {this.state.color}</h1>
<button onClick={this.changeCount}>하나 증가</button>
</>
);
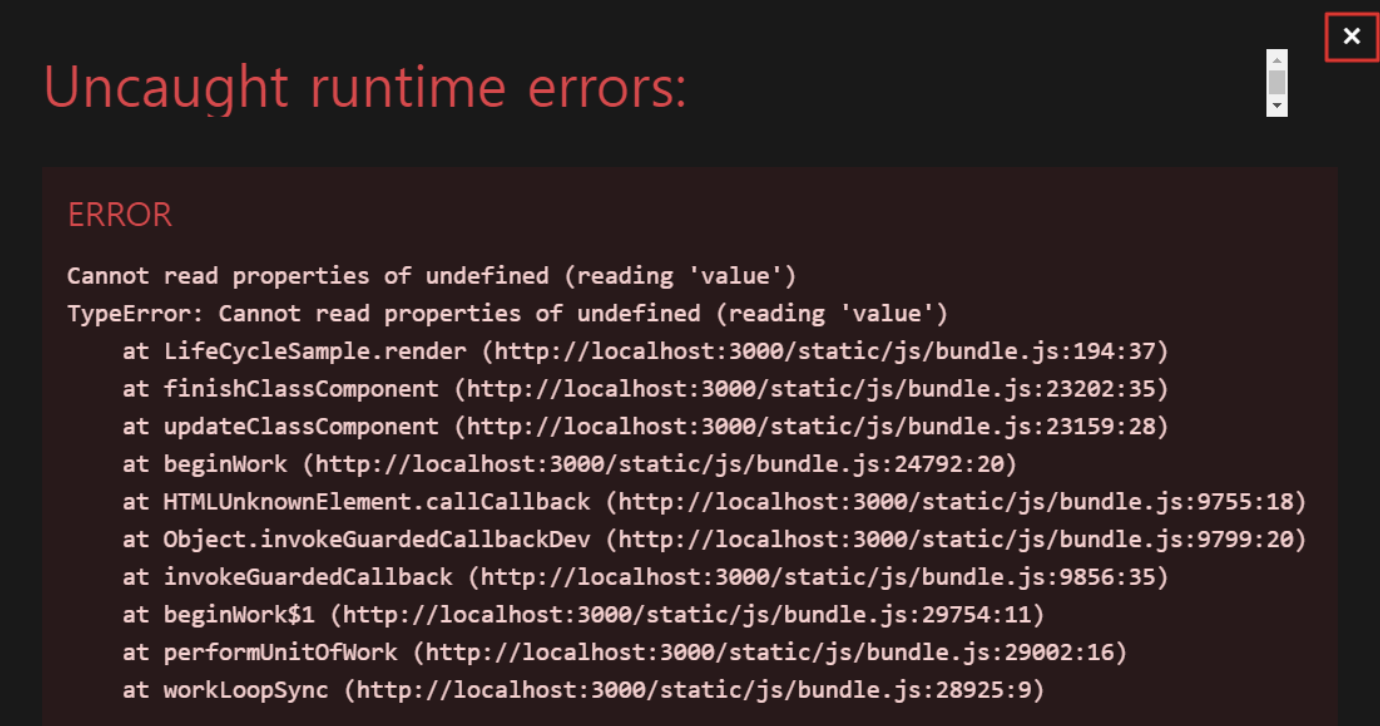
}{this.state.missing.value} <- 오류가 나는 코드 넣기 !
개발 서버를 통해서 제공되는 오류 내용이 출력 => x 버튼을 클릭하면 오류 내용이 사라지고 아무런 내용이 출력되지 않는 것을 확인
ErrorBoundary.js 파일을 생성하고, componentDidCatch 메서드를 추가
import { Component } from 'react';
class ErrorBoundary extends Component {
state = {
error: false,
message: '',
};
componentDidCatch(error, info) {
console.log('componentDidCatch is called');
console.log({ error, info });
this.setState({ error: true, message: error.message });
}
render() {
if (this.state.error) {
return (
<>
<h1>자식 컴포넌트에 에러가 발생했습니다.</h1>
<div>{this.state.message}</div>
</>
);
} else {
return this.props.children;
}
}
}
export default ErrorBoundary;App.js 파일에 ErrorBoundary 컴포넌트를 추가
import { Component } from 'react';
import LifecycleSample from './LifecycleSample';
import ErrorBoundary from './ErrorBoundary';
// 랜덤하게 색상(#0 ~ #ffffff)을 생성하는 함수
const getRandomColor = () => '#' + Math.floor(Math.random() * 16777215).toString(16);
class App extends Component {
state = {
color: '#000000',
isVisible: false,
};
changeColor = () => {
console.log('랜덤 컬러 버튼 클릭!!!');
this.setState({ color: getRandomColor() });
};
changeIsVisible = () => {
console.log(`자식 컴포넌트 ${this.state.isVisible ? '숨기기' : '보이기'} 버튼 클릭!!!`);
this.setState({ isVisible: !this.state.isVisible });
};
render() {
return (
<>
<button onClick={this.changeIsVisible}>
자식 컴포넌트 {this.state.isVisible ? '숨기기' : '보이기'}
</button>
{this.state.isVisible && (
<div style={{ border: '1px solid red', padding: 10, margin: 10, borderRadius: 10 }}>
<button onClick={this.changeColor}>랜덤 컬러</button>
<ErrorBoundary>
<LifecycleSample color={this.state.color} />
</ErrorBoundary>
</div>
)}
</>
);
}
}
export default App;개발 서버를 통해 제공되는 오류 메시지를 닫으면 ErrorBoundary에서 제공하는 오류 메시지가 출력되는 것을 확인

Hooks
훅 함수의 이름은 use 접두어를 사용
current 속성을 꼭 붙여줘야 한다
Info.js 파일을 생성
// 사용자 이름과 별명을 관리
import { useState } from 'react';
function Info() {
const [name, setName] = useState('');
const [nickname, setNickname] = useState('');
const changeName = (e) => setName(e.target.value);
const changeNickname = (e) => setNickname(e.target.value);
return (
<>
<div>
<p>이름: {name}</p>
<p>별명: {nickname}</p>
</div>
<div>
<p>
이름: <input type="text" name="name" value={name} onChange={changeName} />
별명: <input type="text" name="nickname" value={nickname} onChange={changeNickname} />
</p>
</div>
</>
);
}
export default Info;App.js 파일에 Info 컴포넌트를 추가
import Info from './Info';
const App = () => {
return <Info />;
};
export default App;=
import Info from "./Info";
export default function App() {
return <Info />;
};=
import Info from "./Info";
export default () => <Info />;useEffect ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️
시기적절하게 잘 사용해야 한다 !!!! useEffect 잘못쓰면 집에 못 간다 ㅜㅜ
클래스형 컴포넌트의 componentDidMount, componentDidUpdate, componentWillUnmount를 합친 형태
일반적인 라이프사이클 메서드의 대부분을 구현할 수 있다!
useEffect(이펙트 함수, 의존성 배열);
- 의존성 배열
- 이펙트 함수가 의존하고 있는 배열
- 배열 안에 있는 변수 중 하나라도 값이 변경되면 이펙트 함수를 실행
=> 이펙트 함수의 실행 여부를 결정하는 용도 !
Info 컴포넌트에 useEffect 훅을 추가
마운트, 업데이트 모두 이펙트 함수를 실행 => 의존성 배열을 생략
// 의존성 배열을 생략 => 마운트, 업데이트 모두 이펙트 함수를 실행
useEffect(() => {
console.log("렌더링이 완료되었습니다.");
console.log({ name, nickname });
});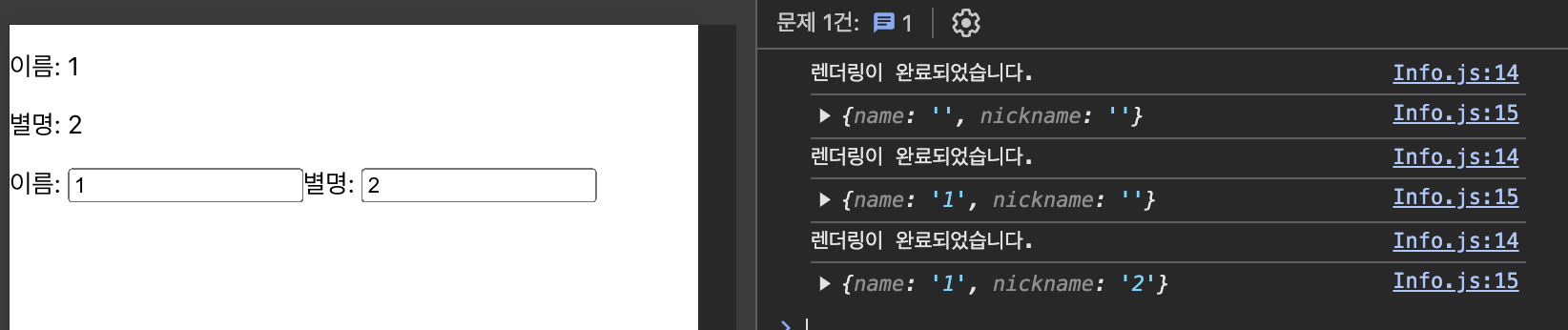

- mount
2, 3. update
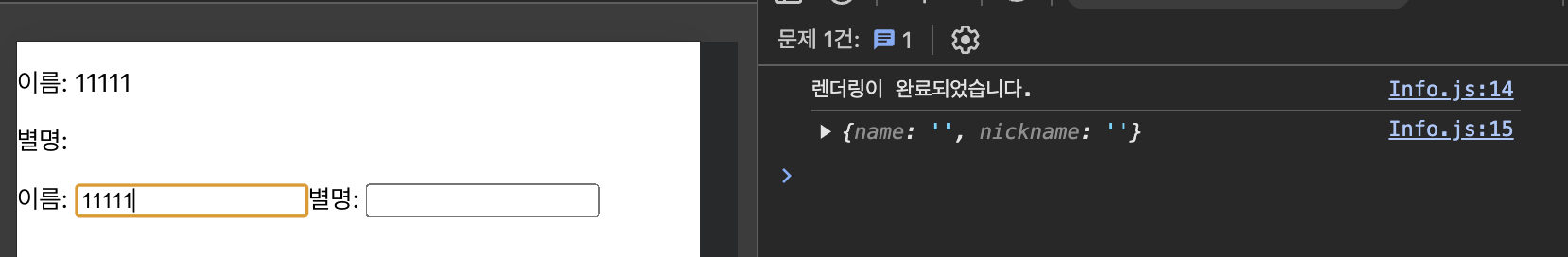
마운트될 때만 이펙트 함수를 실행하도록 수정 => 의존성 배열의 값으로 빈 배열([ ])을 설정
useEffect(() => {
console.log('렌더링이 완료되었습니다.');
console.log({ name, nickname });
}, []);
마운트될 때와 특정 상태변수가 변경될 때 이펙트 함수가 실행되도록 수정 ⇒ 의존성 배열에 변경을 검사할 상태변수를 추가
// 마운트될 때와 name 상태변수의 값이 변경될 때 이펙트 함수를 실행
useEffect(() => {
console.log('렌더링이 완료되었습니다.');
console.log({ name, nickname });
}, [name]);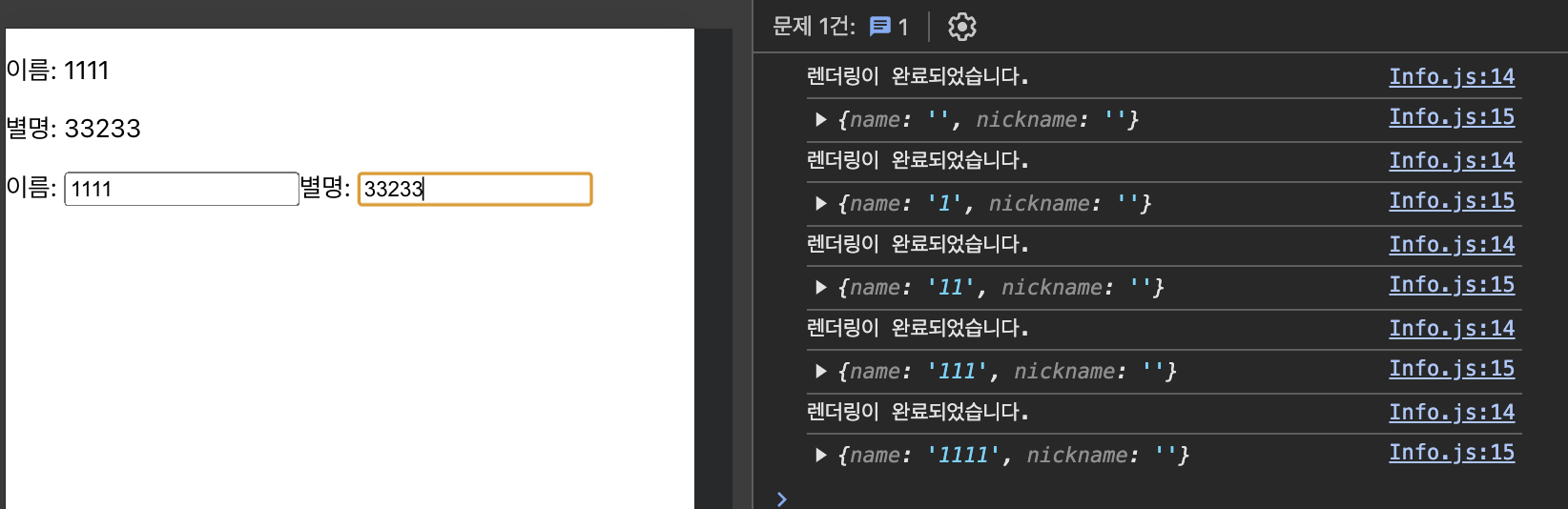
별명을 넣었을 땐 리렌더링 X, 이름을 넣으면 리렌더링 O
후처리(cleanup) 함수 추가
컴포넌트가 언마운트 또는 리렌더링되기 전에 어떤 작업을 수행하고 싶은 경우, 이펙트 함수에서 후처리 작업을 수행하는 함수를 반환
- 언마운트 또는 리렌더링되기 전에 후처리 함수가 실행된다 !
useEffect(() => {
console.log('렌더링이 완료되었습니다.');
console.log({ name, nickname });
return () => console.log('cleanup', name); // <= name 상태변수가 변경되거나 컴포넌트가 언마운트될 때 실행
}, [name]); [실습] cleanup 함수 동작을 테스트하기 위해 App 컴포넌트에 Info 컴포넌트 보이기/숨기기 기능을 추가
내 실습 코드 ⬇️
import { useState } from 'react';
import Info from './Info';
const App = () => {
const [isVisible, setIsVisible] = useState(false);
return (
<>
<button onClick={() => setIsVisible((prev) => !prev)}>
{isVisible ? '숨기기' : '보이기'}
</button>
{isVisible && <Info />}
</>
);
};
export default App;강사님 코드 ⬇️
import { useState } from 'react';
import Info from './Info';
const App = () => {
const [isVisible, setIsVisible] = useState(false);
const changeIsVisible = () => setIsVisible(!isVisible);
return (
<>
<button onClick={changeIsVisible}>{isVisible ? '숨기기' : '보이기'}</button>
<br/>
{isVisible && <Info />}
</>
);
};
export default App;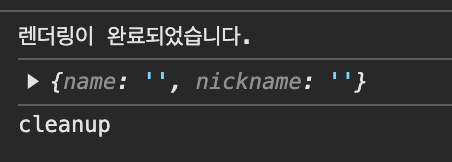
컴포넌트가 언마운트될 때만 cleanup 함수가 실행되도록 하고 싶으면 의존성 배열에 빈 배열을 설정
useEffect(() => {
console.log('렌더링이 완료되었습니다.');
console.log({ name, nickname });
// componentWillUnmount 메서드와 동일
return () => console.log('cleanup', name);
}, []);의존성 배열이 비어있기 때문에 컴포넌트가 언마운트될 때만 호출!
TODO. 참고: 컴포넌트가 언마운트될 때 cleanup 함수에서 현재 상태변수를 참조하기 위해서는 useRef 훅을 사용해야 함
DOM 요소 직접 제어
[실습] 문제
- 숫자를 입력할 수 있는 입력창과 입력한 숫자를 등록하는 버튼을 제공
- 숫자를 입력하면 입력한 숫자가 표시되고, 등록 버튼을 클릭하면 등록된 숫자들을 리스트로 출력하고 입력창에 내용을 지우고 포커스를 이동
Average.js 파일을 생성
import { useState } from "react"
export default function Average() {
const [number, setNumber] = useState("");
const [list, setList] = useState([]);
return (
<>
<div>
<input type="number" />
<button>등록</button>
</div>
<div>
<p>입력값: </p>
</div>
<div>
등록된 숫자
<ul>
</ul>
</div>
</>
)
}
- 화면에 뿌려줘야 하는 값을 useState로 상태 변수로 만들자
- 상태 변수가 변경될 수 있는 case : 이벤트가 발생했을 때 상태 변수를 바꾸는 이벤트 핸들러 함수를 만들자
- UI에 상태변수와 이벤트 핸들러 함수 붙여주기
1. 숫자를 입력하면 입력한 숫자가 표시되고, 등록 버튼을 클릭하면 등록된 숫자들을 리스트로 출력하기
import { useRef, useState } from 'react';
export default function Average() {
const [number, setNumber] = useState('');
const [list, setList] = useState([]);
const inputRef = useRef();
const changeNumber = e => setNumber(e.target.value);
const changeList = () => {
// 1. concat 활용
const newList = list.concat(number); // 2. 전개연산자 활용 [...list, number]
setList(newList);
}
return (
<>
<div>
<input
type="number"
value={number}
ref={inputRef}
onChange={changeNumber}
/>
<button onClick={changeList}>등록</button>
</div>
<div>
<p>입력값: {number}</p>
</div>
<div>
등록된 숫자
<ul>
{list.map((data, index) => (
<li key={index}>{data}</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
</>
);
}
2. 입력창에 내용을 지우고 포커스를 이동 (최종 코드)
import React, { useRef, useState } from 'react';
export default function Average() {
const [number, setNumber] = useState('');
const [list, setList] = useState([]);
// const refNumber = React.createRef();
const refNumber = useRef(); // useRef hook 사용
const changeNumber = e => setNumber(e.target.value);
const changeList = () => {
// 1. concat 활용
const newList = list.concat(number); // 2. 전개연산자 활용 [...list, number]
setList(newList);
setNumber(""); // number 지우기
refNumber.current.focus(); // focus 하기
};
return (
<>
<div>
<input
ref={refNumber}
type="number"
value={number}
onChange={changeNumber}
/>
<button onClick={changeList}>등록</button>
</div>
<div>
<p>입력값: {number}</p>
</div>
<div>
등록된 숫자
<ul>
{list.map((data, index) => (
<li key={index}>{data}</li>
))}
</ul>
</div>
</>
);
}컴포넌트의 로컬 변수로 사용
=> ref 변수는 상태변수처럼 컴포넌트의 생명주기 동안 값을 유지하지만 값이 변경되어도 리렌더링을 하지 않는다 !
ex1) 렌더링 횟수를 출력 => App.js
로컬 변수 사용
import { useEffect, useState } from 'react';
import Average from './Average';
const ChangeCountWithLocalVariable = () => {
const [message, setMessage] = useState('');
let count = 0;
console.log('#1', message);
// 의존성 배열을 정의하지 않았기 때문에 마운트될 때와 업데이트될 때 이펙트 함수가 실행
useEffect(() => {
console.log('렌더링 되었습니다.');
count++;
return (
<>
<h1>지역변수를 사용하는 경우</h1>
<h2>렌더링 횟수: {count}</h2>
<input type="text" value={message} onChange={(e) => setMessage(e.target.value)} />
</>
);
});
};
const App = () => {
return <ChangeCountWithLocalVariable />;
};
export default App;
상태변수가 바뀌어서 리렌더링 된다. 일반 변수인 count는 계속 reset된다. => 상태변수로 바꿔보자 !
useState 사용
const ChangeCountWithStateVariable = () => {
const [message, setMessage] = useState('');
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
console.log('#1', { message, count });
// 의존성 배열을 정의하지 않았기 때문에 마운트될 때와 업데이트될 때 이펙트 함수가 실행
useEffect(() => {
console.log('렌더링 되었습니다.');
setCount(count + 1);
return (
<>
<h1>지역변수를 사용하는 경우</h1>
<h2>렌더링 횟수: {count}</h2>
<input type="text" value={message} onChange={(e) => setMessage(e.target.value)} />
</>
);
});
이렇게 하면 상태변수가 계속 달리게 된다ㅜㅜ
카운트가 상태변수이면 상태변수가 바뀌는 순간 또 리렌더링 된다. -> 무한루프
그래서 쓸 수 없다ㅠ
이럴 때 필요한 게 useRef 이다 !!
useRef 사용
const ChangeCountWithRefVariable = () => {
const [message, setMessage] = useState('');
const count = useRef(0);
console.log('#3', { message, count: count.current });
// 의존성 배열을 정의하지 않았기 때문에 마운트될 때와 업데이트될 때 이펙트 함수가 실행
useEffect(() => {
console.log('렌더링 되었습니다.');
count.current++;
return (
<>
<h1>지역변수를 사용하는 경우</h1>
<h2>렌더링 횟수: {count.current}</h2>
<input type="text" value={message} onChange={(e) => setMessage(e.target.value)} />
</>
);
});
};상태변수처럼 값을 지속적으로 유지시키고 싶은데 리렌더링되지 않도록 하려면 ! useRef를 쓰자

ex2) 타이머 조작
로컬 변수 사용
import { useState } from 'react';
const CounterWithLocalVariable = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
let intervalId = 0;
console.log(`렌더링... count: ${count}, intervalId: ${intervalId}`)
const startCounter = () => {
intervalId = setInterval(() => {
setCount((count) => count + 1);
}, 1000);
console.log(`카운터 시작... intervalId: ${intervalId}`)
};
const stopCounter = () => {
clearInterval(intervalId); // id 값이 있어야만 중지시킬 수 있다.
console.log(`카운터 정지... intervalId: ${intervalId}`);
};
return (
<>
<p>카운트: {count}</p>
<button onClick={startCounter}>시작</button>
<button onClick={stopCounter}>정지</button>
</>
);
};
export default function App() {
return (
<>
<CounterWithLocalVariable />
</>
);
}setInterval(() => { ... }, 1000); ms 단위. 1초 단위로 이 함수가 호출된다
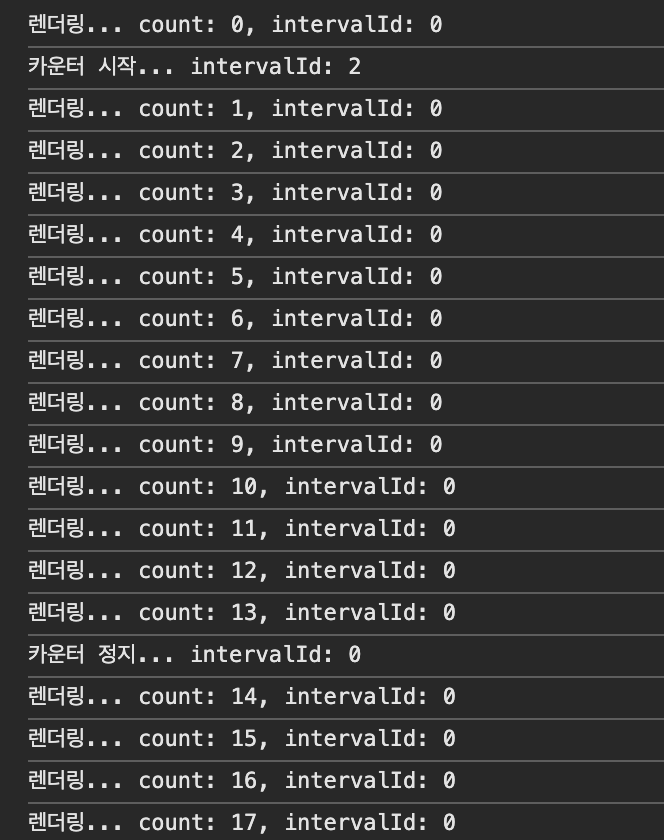
지역변수로 선언했기 때문에 intervalId가 2인데 intervalId가 자꾸 초기화 돼서 0인 것만 죽기 때문에 stop이 안 된다. 렌더링이 되더라도 계속 유지시켜줘야 한다.
useState 사용
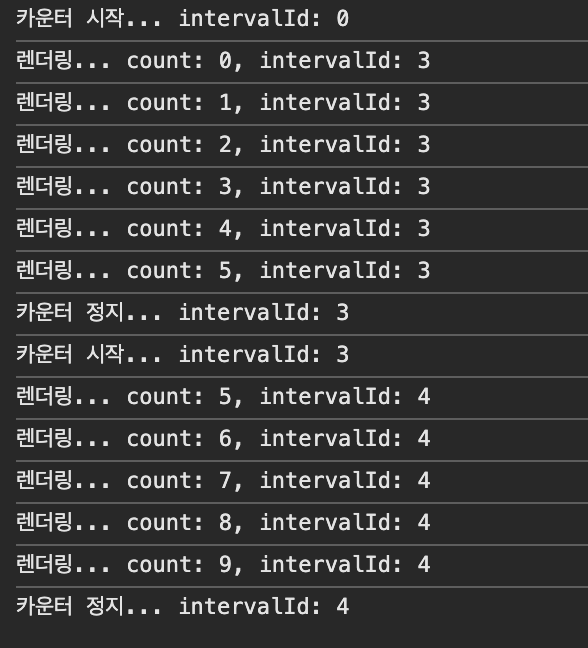
상태변수로 만들면 원하는 대로 잘 동작하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
const CounterWithStateVariable = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const [intervalId, setIntervalId] = useState(0);
console.log(`렌더링... count: ${count}, intervalId: ${intervalId}`);
const startCounter = () => {
const id = setInterval(() => {
setCount((count) => count + 1);
}, 1000);
setIntervalId(id);
console.log(`카운터 시작... intervalId: ${intervalId}`);
};
const stopCounter = () => {
clearInterval(intervalId); // id 값이 있어야만 중지시킬 수 있다.
console.log(`카운터 정지... intervalId: ${intervalId}`);
};
return (
<>
<p>카운트: {count}</p>
<button onClick={startCounter}>시작</button>
<button onClick={stopCounter}>정지</button>
</>
);
};
useRef 사용
ref를 사용하면 상태변수를 이용하지 않고도 저 값을 유지시킬 수 있다.
const CounterWithRefVariable = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const intervalId = useRef(0);
console.log(`렌더링... count: ${count}, intervalId: ${intervalId.current}`);
const startCounter = () => {
intervalId.current = setInterval(() => {
setCount((count) => count + 1);
}, 1000);
console.log(`카운터 시작... intervalId: ${intervalId.current}`);
};
const stopCounter = () => {
clearInterval(intervalId.current); // id 값이 있어야만 중지시킬 수 있다.
console.log(`카운터 정지... intervalId: ${intervalId.current}`);
};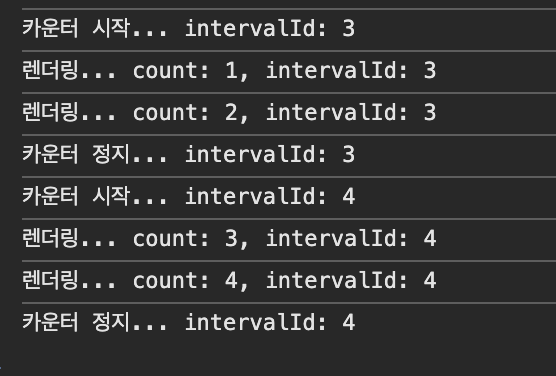
잘 작동하는 것을 확인할 수 있다 !!