✅ 비교 연산자
비교 연산자는 두 값을 비교하는 데 사용한다. 비교 연산자는 주로 조건문과 함께 사용한다.
✏️ 비교연산자 종류
==: 동등성 (equal to)!=: 불일치 (not equal to)>: 크다 (greater than)<: 작다 (less than)>=: 크거나 같다 (greater than or equal to)<=: 작거나 같다 (less than or equal to)
비교 연산자를 사용하면 참(true) 또는 거짓(false)이라는 결과가 나온다. 참 거짓은 boolean형을 사용한다.
여기서 주의할 점은 =와 ==(=x2)이 다르다는 점이다.
=: 대입 연산자, 변수에 값을 대입한다.==: 비교 연산자, 비교하는 값이 동등한지 확인한다.
불일치 연산자는 !=를 사용한다. !는 반대라는 뜻이다.
✏️ Comp1
package operator;
public class Comp1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 2;
int b = 3;
System.out.println(a == b); // false, a와 b는 같지 않다.
System.out.println(a != b); // true, a와 b는 다르다.
System.out.println(a > b); // false, a는 b보다 크지 않다.
System.out.println(a < b); // ture, a는 b보다 작다.
System.out.println(a >= b); // false, a는 b보다 크거나 같지 않다.
System.out.println(a <= b); // true, a는 b보다 작거나 같다.
// 결과를 boolean 변수에 담을 수 있다.
boolean result = a == b; // a == b : false
System.out.println(result); // false
}
}✅ 문자열 비교
문자열이 같은지 비교할 때는 ==이 아니라 .equals() 메서드를 사용해야 한다.
✏️ Comp2 - 문자열 비교 예시
package operator;
public class Comp2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "문자열1";
String str2 = "문자열2";
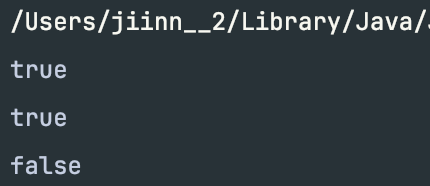
boolean result1 = "hello".equals("hello"); // 리터럴 비교
boolean result2 = str1.equals("문자열1"); // 문자열 변수, 리터럴 비교
boolean result3 = str1.equals(str2); // 문자열 변수 비교
System.out.println(result1);
System.out.println(result2);
System.out.println(result3);
}
}✏️ 실행 결과
💡 단축키
- Complete Current Statement →
command+shift+enter
