✅ 다형성과 메서드 오버라이딩
다형성을 이루는 또 하나의 중요한 핵심 이론은 바로 메서드 오버라이딩이다.
메서드 오버라이딩에서 꼭 기억해야 할 점은 오버라이딩 된 메서드가 항상 우선권을 가진다는 점이다.
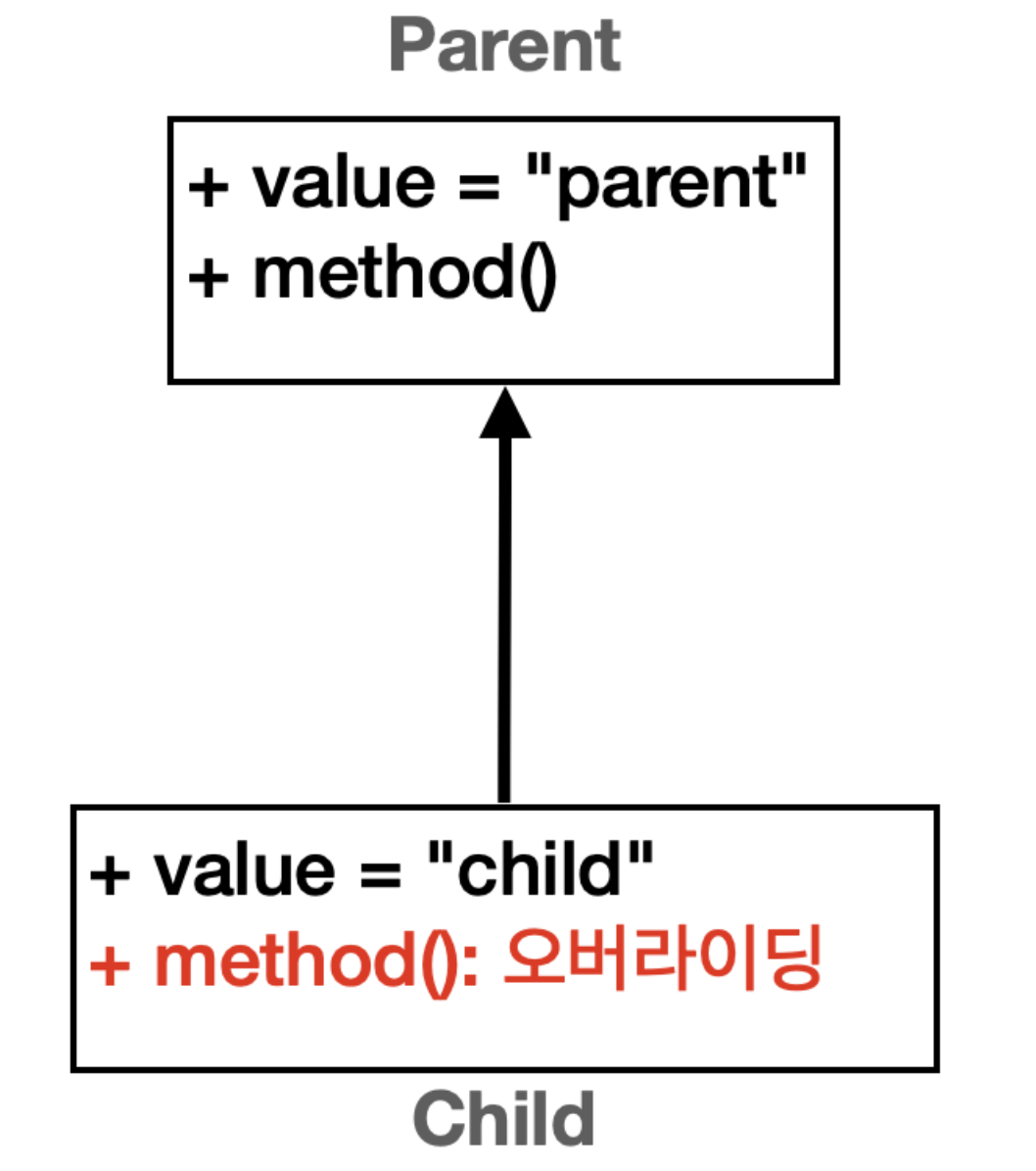
Parent,Child모두value라는 같은 멤버 변수를 가지고 있다.- 멤버 변수는 오버라이딩 되지 않는다.
Parent,Child모두method()라는 같은 메서드를 가지고 있다.Child에서 메서드를 오버라이딩 했다.- 메서드는 오버라이딩 된다.
✏️ Parent
package poly.overriding;
public class Parent {
public String value = "parent";
public void method() {
System.out.println("Parent.method");
}
}
✏️ Child
package poly.overriding;
public class Child extends Parent {
public String value = "child";
@Override
public void method() {
System.out.println("Child.method");
}
}
Child에서Parent의method()를 재정의(오버라이딩)했다.
✏️ OverridingMain
package poly.overriding;
public class OverridingMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 자식 변수가 자식 인스턴스 참조
Child child = new Child();
System.out.println("Child -> Child");
System.out.println("value = " + child.value);
child.method();
// 부모 변수가 부모 인스턴스 참조
Parent parent = new Parent();
System.out.println("Parent -> Parent");
System.out.println("value = " + parent.value);
parent.method();
// 부모 변수가 자식 인스턴스 참조 (다형적 참조)
Parent poly = new Child();
System.out.println("Parent -> Child");
System.out.println("value = " + poly.value); // 변수는 오버라이딩 X
poly.method(); // 메서드 오버라이딩 O
}
}
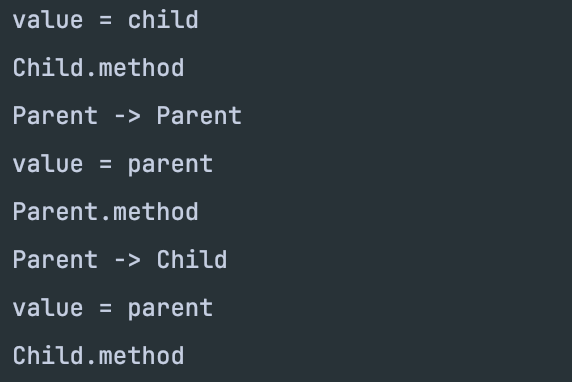
🖥️ 실행 결과
⚙️ 코드 분석
✓ Child → Child
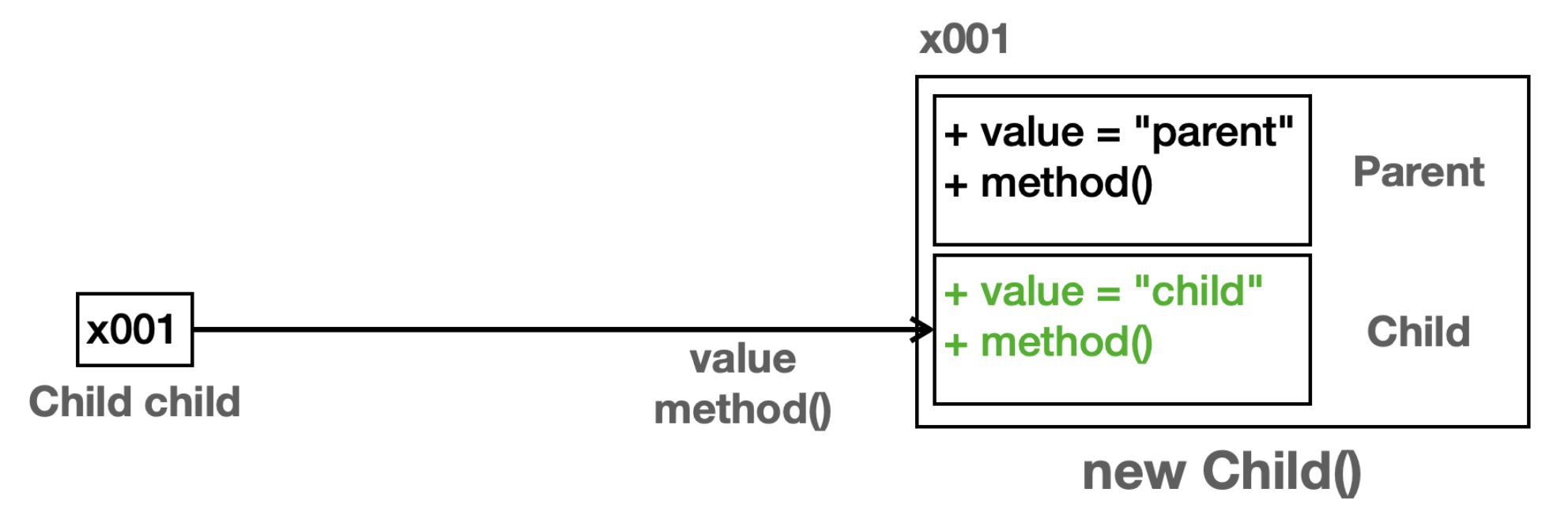
child변수는Child타입이다. 따라서child.value,child.method()를 호출하면 인스턴스의Child타입에서 기능을 찾아서 실행한다.
✓ Parent → Parent

parent변수는Parent타입이다. 따라서parent.value,parent.method()를 호출하면 인스턴스의Parent타입에서 기능을 찾아서 실행한다.
✓ Parent → Child
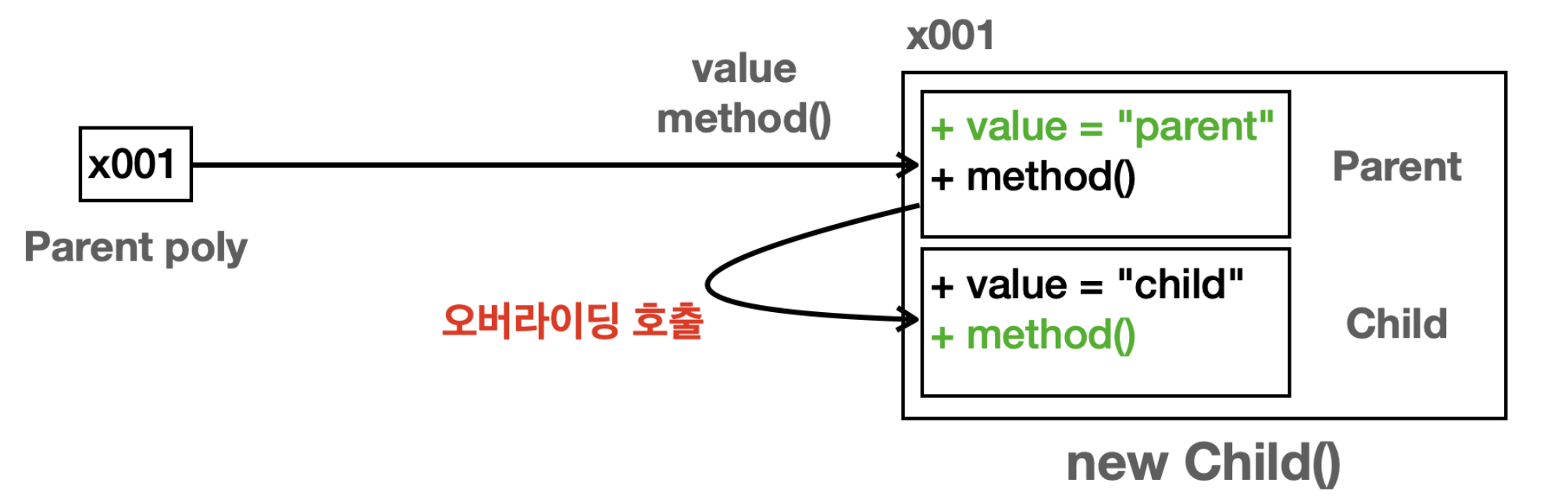
poly변수는Parent타입이다. 따라서poly.value,poly.method()를 호출하면 인스턴스의Parent타입에서 기능을 찾아서 실행한다.poly.value:Parent타입에 있는value값을 읽는다.poly.method():Parent타입에 있는method()를 실행하려고 한다. 그런데 하위 타입인Child.method()가 오버라이딩 되어 있다. 오버라이딩 된 메서드는 항상 우선권을 가진다. 따라서Parent.method()가 아니라Child.method()가 실행된다.
오버라이딩 된 메서드는 항상 우선권을 가진다. 오버라이딩은 부모 타입에서 정의한 기능을 자식 타입에서 재정의하는 것이다. 만약 자식에서도 오버라이딩 하고 손자에서도 같은 메서드를 오버라이딩을 하면 손자의 오버라이딩 메서드가 우선권을 가진다. 더 하위 자식의 오버라이딩 된 메서드가 우선권을 가지는 것이다.
📚 다형성 핵심 이론
- 다형적 참조 : 하나의 변수 타입으로 다양한 자식 인스턴스를 참조할 수 있는 기능
- 메서드 오버라이딩 : 기존 기능을 하위 타입에서 새로운 기능으로 재정의
출처 : 김영한의 실전 자바 - 기본편
https://www.inflearn.com/course/김영한의-실전-자바-기본편/dashboard
