Proxy 패턴
개념
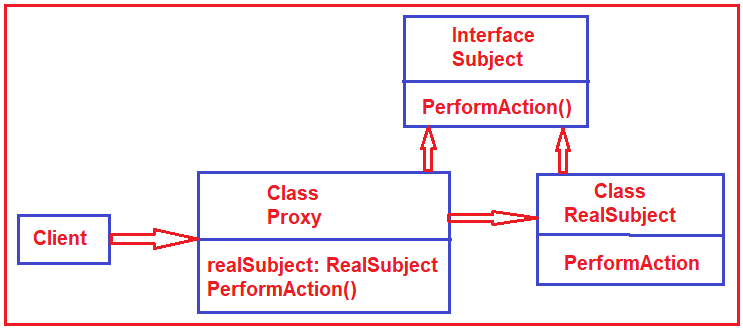
실제 객체 대신 대리 객체를 두고, 대리 객체가 실제 객체로의 접근을 제어하는 패턴.
해결한 문제
- 생성 비용이 큰 객체를 매번 생성하면 리소스 낭비가 발생합니다.
- 객체에 대한 무분별한 접근을 허용하면 보안 문제가 발생합니다.
- 실제 객체에 부가 기능(로깅, 캐싱 등)을 추가하려면 객체를 수정해야 합니다.
Static Proxy
개념
Static Proxy는 컴파일 타임에 프록시 클래스가 이미 존재하는 방식입니다.
개발자가 직접 프록시 클래스를 작성하며, 프록시 클래스는 실제 객체와 동일한 인터페이스를 구현합니다.
구현 예제
// 1. 공통 인터페이스
interface UserService {
void createUser(String name);
User findUser(Long id);
void deleteUser(Long id);
}
// 2. 실제 구현 클래스
class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void createUser(String name) {
System.out.println("사용자 생성: " + name);
}
@Override
public User findUser(Long id) {
System.out.println("사용자 조회: " + id);
return new User(id, "리안");
}
@Override
public void deleteUser(Long id) {
System.out.println("사용자 삭제: " + id);
}
}
// 3. Static Proxy 클래스
class UserServiceProxy implements UserService {
private final UserService target;
public UserServiceProxy(UserService target) {
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public void createUser(String name) {
System.out.println("[LOG] createUser 호출");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
target.createUser(name); // 실제 객체에 위임
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("[LOG] createUser 완료 - " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
@Override
public User findUser(Long id) {
System.out.println("[LOG] findUser 호출");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
User result = target.findUser(id);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("[LOG] findUser 완료 - " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
return result;
}
@Override
public void deleteUser(Long id) {
System.out.println("[LOG] deleteUser 호출");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
target.deleteUser(id);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("[LOG] deleteUser 완료 - " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
}
// 4. 사용 예제
public class StaticProxyExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
UserService realService = new UserServiceImpl();
UserService proxyService = new UserServiceProxy(realService);
proxyService.createUser("리안");
proxyService.findUser(1L);
proxyService.deleteUser(1L);
}
}실행 결과:
[LOG] createUser 호출
사용자 생성: 리안
[LOG] createUser 완료 - 1ms
[LOG] findUser 호출
사용자 조회: 1
[LOG] findUser 완료 - 0ms
[LOG] deleteUser 호출
사용자 삭제: 1
[LOG] deleteUser 완료 - 0ms장/단점
장점
- 런타임 성능 오버헤드 최소
- 프록시 생성 비용 없음
단점
- 코드 중복
- 서비스가 100개면 프록시도 100개 작성
- 확장성 부족
Dynamic Proxy
필요한 이유
// UserServiceProxy - 로깅 코드 반복
class UserServiceProxy implements UserService {
private UserService target;
@Override
public void createUser(String name) {
System.out.println("[LOG] 메서드 호출: createUser");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
target.createUser(name);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("[LOG] 실행 시간: " + (end - start) + "ms");
}
@Override
public User findUser(Long id) {
System.out.println("[LOG] 메서드 호출: findUser");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
User result = target.findUser(id);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("[LOG] 실행 시간: " + (end - start) + "ms");
return result;
}
}
// OrderServiceProxy - 동일한 로깅 코드 반복
class OrderServiceProxy implements OrderService {
private OrderService target;
@Override
public void createOrder(int orderId) {
System.out.println("[LOG] 메서드 호출: createOrder");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
target.createOrder(orderId);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("[LOG] 실행 시간: " + (end - start) + "ms");
}
}
// ProductServiceProxy - 또 동일한 로깅 코드 반복
class ProductServiceProxy implements ProductService {
private ProductService target;
@Override
public void createProduct(String name) {
System.out.println("[LOG] 메서드 호출: createProduct");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
target.createProduct(name);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("[LOG] 실행 시간: " + (end - start) + "ms");
}
}- 로깅 로직이 모든 프록시에 중복
- DRY(Don't Repeat Yourself) 원칙 위반
- 로깅 방식 변경 시 모든 프록시 수정 필요=
JDK Dynamic Proxy
동작 원리
런타임에 인터페이스를 구현하는 프록시 클래스를 동적 생성합니다.
Client → $Proxy0 → InvocationHandler.invoke() → RealObject내부 동작:
// 런타임에 생성되는 프록시 클래스
public final class $Proxy0 extends Proxy implements UserService {
private InvocationHandler h;
public void createUser(String name) {
Method m = UserService.class.getMethod("createUser", String.class);
h.invoke(this, m, new Object[]{name});
}
}핵심 특징:
Proxy클래스를 상속- 지정된 인터페이스를 구현
- 모든 메서드 호출을
InvocationHandler.invoke()로 위임
InvocationHandler 인터페이스
프록시의 모든 메서드 호출을 처리하는 핵심 인터페이스입니다.
public interface InvocationHandler {
Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable;
}파라미터:
proxy: 프록시 인스턴스 자신method: 호출된 메서드 객체 (리플렉션)args: 메서드에 전달된 파라미터 배열
구현 예시:
class LoggingHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private final Object target;
public LoggingHandler(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("[LOG] 메서드: " + method.getName());
// 실제 객체의 메서드 호출
Object result = method.invoke(target, args);
return result;
}
}Proxy.newProxyInstance() 메커니즘
프록시 인스턴스를 생성하는 팩토리 메서드입니다.
public static Object newProxyInstance(
ClassLoader loader, // 프록시 클래스를 정의할 클래스 로더
Class<?>[] interfaces, // 프록시가 구현할 인터페이스 배열
InvocationHandler h // 메서드 호출을 처리할 핸들러
)내부 동작 과정:
// 1단계: 프록시 클래스 생성 (캐싱됨)
Class<?> proxyClass = Proxy.getProxyClass(loader, interfaces);
// 2단계: 프록시 인스턴스 생성
Constructor<?> constructor = proxyClass.getConstructor(InvocationHandler.class);
Object proxyInstance = constructor.newInstance(handler);
// 3단계: 프록시 반환
return proxyInstance;파라미터 상세:
ClassLoader:
// 타겟 클래스의 클래스 로더
ClassLoader loader = target.getClass().getClassLoader();
// 인터페이스의 클래스 로더
ClassLoader loader = UserService.class.getClassLoader();Interfaces:
// 단일 인터페이스
Class<?>[] interfaces = new Class<?>[]{UserService.class};
// 복수 인터페이스
Class<?>[] interfaces = new Class<?>[]{
UserService.class,
Serializable.class
};
// 타겟이 구현한 모든 인터페이스
Class<?>[] interfaces = target.getClass().getInterfaces();구현 예제
기본 로깅 프록시:
// 인터페이스
interface UserService {
void createUser(String name);
User findUser(Long id);
void deleteUser(Long id);
}
// 실제 구현
class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
public void createUser(String name) {
System.out.println("사용자 생성: " + name);
}
public User findUser(Long id) {
System.out.println("사용자 조회: " + id);
return new User(id, "홍길동");
}
public void deleteUser(Long id) {
System.out.println("사용자 삭제: " + id);
}
}
// InvocationHandler
class LoggingHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private final Object target;
public LoggingHandler(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("[LOG] 메서드 호출: " + method.getName());
System.out.println("[LOG] 파라미터: " + Arrays.toString(args));
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object result = method.invoke(target, args);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("[LOG] 실행시간: " + (end - start) + "ms");
return result;
}
}
// 사용
UserService target = new UserServiceImpl();
UserService proxy = (UserService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
UserService.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{UserService.class},
new LoggingHandler(target)
);
proxy.createUser("리안");트랜잭션 프록시:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@interface Transactional { }
interface OrderService {
@Transactional
void createOrder(String orderId);
void findOrder(String orderId);
}
class TransactionalHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private final Object target;
private final TransactionManager txManager;
public TransactionalHandler(Object target, TransactionManager txManager) {
this.target = target;
this.txManager = txManager;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
boolean isTx = method.isAnnotationPresent(Transactional.class);
if (!isTx) {
return method.invoke(target, args);
}
txManager.begin();
try {
Object result = method.invoke(target, args);
txManager.commit();
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
txManager.rollback();
throw e;
}
}
}제약사항
인터페이스 필수
JDK Proxy는 Proxy 클래스를 상속하므로, Java 단일 상속 제약으로 인해 인터페이스만 구현 가능합니다.
// 생성되는 프록시 클래스
public final class $Proxy0 extends Proxy implements UserService {
// Proxy를 extends하므로 다른 클래스 상속 불가
}불가능한 케이스:
// 인터페이스 없는 클래스
class UserService {
public void createUser(String name) { }
}
// 프록시 생성 시도
Proxy.newProxyInstance(
loader,
new Class[]{UserService.class}, // 에러!
handler
);
// 실행 결과
// IllegalArgumentException: UserService is not an interface올바른 사용:
// 인터페이스 정의
interface UserService {
void createUser(String name);
}
// 구현 클래스
class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
public void createUser(String name) { }
}
// 프록시 생성
UserService proxy = (UserService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
UserService.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{UserService.class}, // 성공
new LoggingHandler(new UserServiceImpl())
);복수 인터페이스:
// 여러 인터페이스 동시 구현 가능
interface UserService { }
interface Serializable { }
interface Cloneable { }
UserService proxy = (UserService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
loader,
new Class[]{UserService.class, Serializable.class, Cloneable.class},
handler
);
System.out.println(proxy instanceof UserService); // true
System.out.println(proxy instanceof Serializable); // true
System.out.println(proxy instanceof Cloneable); // trueCGLIB Proxy
동작 원리
클래스를 상속받아 프록시를 생성합니다. ASM을 사용해 런타임에 바이트코드를 생성합니다.
// CGLIB가 생성하는 프록시 클래스
class UserService$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$12345 extends UserService {
// UserService를 상속
}JDK vs CGLIB
// JDK Proxy
class $Proxy0 extends Proxy implements UserService { }
// CGLIB Proxy
class UserService$$EnhancerByCGLIB extends UserService { }핵심 차이
- JDK: 인터페이스 구현 (implements)
- CGLIB: 클래스 상속 (extends)
ASM 프레임워크와의 관계
CGLIB는 내부적으로 ASM 바이트코드 조작 프레임워크를 사용합니다.
CGLIB → ASM → 바이트코드 생성 → 프록시 클래스ASM의 역할
- 바이트코드 직접 생성 (.java 없이 .class 생성)
- 메서드 오버라이딩 바이트코드 작성
- 고성능 처리 (SAX 파서 방식)
CGLIB을 사용하는 이유
- ASM은 JVM 바이트코드 깊은 이해 필요
- CGLIB는 이를 추상화하여 간단한 API 제공
Enhancer와 MethodInterceptor
Enhancer
- JDK의
Proxy.newProxyInstance()에 해당 - 프록시 객체 생성 팩토리
MethodInterceptor
- JDK의
InvocationHandler에 해당 - 메서드 호출 가로채기
public interface MethodInterceptor extends Callback {
Object intercept(
Object obj, // 프록시 객체
Method method, // 호출된 메서드
Object[] args, // 파라미터
MethodProxy proxy // FastClass 메커니즘 (성능 최적화)
) throws Throwable;
}MethodProxy의 특징
method.invoke(target, args)대신proxy.invokeSuper(obj, args)사용- 리플렉션 없이 FastClass 메커니즘 사용
- 더 빠른 성능
구현 예제
기본 예제
// 인터페이스 없는 일반 클래스
class UserService {
public void createUser(String name) {
System.out.println("사용자 생성: " + name);
}
public User findUser(Long id) {
System.out.println("사용자 조회: " + id);
return new User(id, "홍길동");
}
}
// MethodInterceptor 구현
class LoggingInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy proxy)
throws Throwable {
System.out.println("[CGLIB] 메서드 호출: " + method.getName());
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// invokeSuper: 부모 클래스 메서드 호출 (FastClass 사용)
Object result = proxy.invokeSuper(obj, args);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("[CGLIB] 실행시간: " + (end - start) + "ms");
return result;
}
}
// 사용
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(UserService.class);
enhancer.setCallback(new LoggingInterceptor());
UserService proxy = (UserService) enhancer.create();
proxy.createUser("리안");실행 결과
[CGLIB] 메서드 호출: createUser
사용자 생성: 리안
[CGLIB] 실행시간: 1ms프록시 클래스 정보
System.out.println("프록시 클래스: " + proxy.getClass().getName());
System.out.println("부모 클래스: " + proxy.getClass().getSuperclass().getName());
// 출력:
// 프록시 클래스: UserService$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$a1b2c3d4
// 부모 클래스: UserService제약사항
상속 기반이므로 다음과 같은 제약이 있습니다.
final 클래스
public final class UserService {
public void createUser(String name) { }
}
// CGLIB 프록시 생성 시도
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(UserService.class); // 에러!
// Cannot subclass final class UserServicefinal 메서드
public class UserService {
// 일반 메서드: 프록시 적용됨
public void createUser(String name) { }
// final 메서드: 프록시 적용 안됨
public final void systemMethod() { }
}
UserService proxy = (UserService) enhancer.create();
proxy.createUser("리안"); // 프록시 통과
proxy.systemMethod(); // 프록시 우회 (직접 호출)private 메서드
public class UserService {
private void internalMethod() { }
public void publicMethod() {
internalMethod(); // 내부 호출은 프록시를 거치지 않음
}
}static 메서드
public class UserService {
public static void staticMethod() { }
}
// static 메서드는 클래스에 속하므로 프록시 불가생성자 호출
public class UserService {
public UserService() {
System.out.println("UserService 생성자");
}
}
UserService proxy = (UserService) enhancer.create();
// 출력:
// UserService 생성자 (부모 클래스 생성자 자동 호출)JDK Proxy vs CGLIB 비교
동작 방식 차이
| 구분 | JDK Proxy | CGLIB |
|---|---|---|
| 생성 방식 | 인터페이스 구현 | 클래스 상속 |
| 필수 조건 | 인터페이스 필수 | 인터페이스 불필요 |
| 프록시 클래스 | $Proxy0 extends Proxy implements Interface | Target$$EnhancerByCGLIB extends Target |
| 메서드 호출 | InvocationHandler.invoke() | MethodInterceptor.intercept() |
| 기술 | Java 리플렉션 | ASM 바이트코드 생성 |
| 라이브러리 | JDK 표준 | 외부 라이브러리 (cglib) |
코드 비교
// JDK Proxy
interface UserService { }
class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { }
UserService proxy = (UserService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
loader,
new Class[]{UserService.class}, // 인터페이스
invocationHandler
);
// CGLIB Proxy
class UserService { } // 인터페이스 없어도 됨
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(UserService.class); // 클래스
enhancer.setCallback(methodInterceptor);
UserService proxy = (UserService) enhancer.create();성능 비교
과거 (JDK 6 이전)
- JDK Proxy: 느림 (리플렉션 오버헤드)
- CGLIB: 빠름 (FastClass 메커니즘)
현재 (JDK 8 이후)
- JDK Proxy: 크게 개선됨
- CGLIB: 여전히 빠르지만 차이 감소
실무에서
- 프록시 성능보다 비즈니스 로직 실행 시간이 훨씬 큼
- 대부분 경우 성능 차이는 무시 가능
- 설계의 유연성이 더 중요
사용 시나리오
JDK Proxy 사용
인터페이스 기반 설계
interface UserRepository { }
interface UserService { }외부 라이브러리 의존성 최소화
// JDK 표준만 사용Java 모듈 시스템
// CGLIB는 java.lang 패키지 프록시 시 제약CGLIB 사용
레거시 코드:
// 인터페이스 없이 구현된 클래스
public class LegacyService {
public void doSomething() { }
}구체 클래스의 모든 메서드 프록시
class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
public void publicMethod() { } // 인터페이스 메서드
public void extraMethod() { } // 추가 메서드
}
// CGLIB는 extraMethod도 프록시 가능
// JDK Proxy는 인터페이스 메서드만 프록시Spring의 선택
// Spring 기본 전략
if (hasInterface()) {
return JDK_PROXY;
} else {
return CGLIB_PROXY;
}
// 강제로 CGLIB 사용
@EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = true)
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)선택 가이드
| 상황 | 추천 |
|---|---|
| 새 프로젝트, 인터페이스 설계 가능 | JDK Proxy |
| 레거시 코드, 인터페이스 없음 | CGLIB |
| 외부 라이브러리 의존성 최소화 | JDK Proxy |
| 구체 클래스 모든 메서드 프록시 | CGLIB |
| Spring 사용 | 자동 선택 |
