백준 11724번
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/11724
문제
방향 없는 그래프가 주어졌을 때, 연결 요소 (Connected Component)의 개수를 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
입력
첫째 줄에 정점의 개수 N과 간선의 개수 M이 주어진다. (1 ≤ N ≤ 1,000, 0 ≤ M ≤ N×(N-1)/2) 둘째 줄부터 M개의 줄에 간선의 양 끝점 u와 v가 주어진다. (1 ≤ u, v ≤ N, u ≠ v) 같은 간선은 한 번만 주어진다.
출력
첫째 줄에 연결 요소의 개수를 출력한다.
예제 입력
6 5
1 2
2 5
5 1
3 4
4 6예제 출력
2생각하기
이번 문제는 floyd-warshall 알고리즘으로 가장 먼저 풀었다.
쉽게 말해서 완전 탐색으로 풀었다는 얘기..
제한 시간이 3초길래 그냥 floyd-warshall로 풀었다.
하지만, DFS/BFS로 푸는게 정석인 문제이기 때문에
종합적으로 3가지 방법 모두 사용해서 풀었다.
동작
푸는 방식은 3가지 알고리즘이지만 모두 동일하다.
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 정점의 개수
int M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 간선의 개수
arr = new int[N+1][N+1];
for(int i=0; i<M; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int x = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int y = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
// 무방향 그래프 특성.
arr[x][y] = 1;
arr[y][x] = 1;
}무방향 그래프를 먼저 생성해야한다.
int count = 0;
boolean node[] = new boolean[N+1];
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) {
// 이미 등록된 노드는 탐색할 필요없음
if(node[i] == true) { >
continue;
}
for(int j=1; j<=N; j++) {
if(arr[i][j] == 1 && node[j] == false) {
node[j] = true;
}
}
count ++;
}node라는 배열만 이해하면된다.
우리가 처음시작하는 곳에서 찾아갈 수 있는 노드들은 node배열에서 true처리를 하면,
방문할 수 있고, 연결되어 있다는 것을 알 수 있다.
이 연결된 부분들은 true처리를 하고 더 이상 갈 수 없는 곳은
다시 node에서 false인 부분을 찾아서 하나씩 node의 전체가 true가 될 때 까지 반복하면 된다.
이 과정을 어떤 알고리즘과 방식을 사용할거냐의 차이지
전체적인 동작은 모두 동일하다.
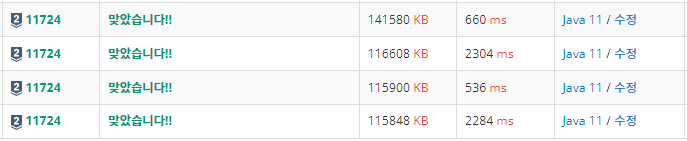
메모리는 똑같은 그래프 배열이다 보니 아무래도 비슷할 수 밖에 없다.
하지만 완전 탐색을 하는 floyd가 확실히 시간 복잡도가 많을 수 밖에 없어서 그런지 어마무시한 시간이 걸렸다.
DFS가 역시나 가장 빠른 시간에 해결할 수 있고, 항상 1인분은 하는 BFS는 적당한 시간이 나온 모습을 볼 수 있다.
코드
floyd-warshall
import java.util.*; import java.io.*; public class Main { static int arr[][]; static int N; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); StringTokenizer st = null; st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 정점의 개수 int M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 간선의 개수 arr = new int[N+1][N+1]; for(int i=0; i<M; i++) { st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); int x = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); int y = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 무방향 그래프 특성. arr[x][y] = 1; arr[y][x] = 1; } floyd(); int count = 0; boolean node[] = new boolean[N+1]; for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) { // 이미 등록된 노드는 탐색할 필요없음 if(node[i] == true) { > continue; } for(int j=1; j<=N; j++) { if(arr[i][j] == 1 && node[j] == false) { node[j] = true; } } count ++; } System.out.println(count); } // End of main static void floyd() { for(int k=0; k<=N; k++) { for(int i=0; i<=N; i++) { for(int j=0; j<=N; j++) { if(arr[i][k] == 1 && arr[k][j] == 1) { arr[i][j] = 1; } } } } } // End of floyd } // End of class
DFS
import java.util.*; import java.io.*; public class Main { static int arr[][]; static boolean node[]; static int N, count; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); StringTokenizer st = null; st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 정점의 개수 int M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 간선의 개수 arr = new int[N+1][N+1]; node = new boolean[N+1]; for(int i=0; i<M; i++) { st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); int x = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); int y = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 무방향 그래프 특성. arr[x][y] = 1; arr[y][x] = 1; } count = 0; for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) { if(node[i] == false) { DFS(i); count++; } } System.out.println(count); } // End of main static void DFS(int value) { if(node[value] == true) { return; } node[value] = true; for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) { if(arr[value][i] == 1) { DFS(i); } } } } // End of class
BFS
import java.util.*; import java.io.*; public class Main { static List<ArrayList<Integer>> nearList = new ArrayList<>(); static boolean node[]; static int N, count; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); StringTokenizer st = null; st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 정점의 개수 int M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 간선의 개수 // node와 인접리스트 생성 node = new boolean[N+1]; for(int i=0; i<=N; i++) { nearList.add(new ArrayList<>()); } while(M-->0) { st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); int x = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); int y = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); nearList.get(x).add(y); nearList.get(y).add(x); } int count = 0; for(int i=1; i<=N; i++) { if(node[i] == false) { BFS(i); count ++; } } System.out.println(count); } // End of main static void BFS(int value) { Queue<Integer> que = new LinkedList<>(); que.offer(value); while( !que.isEmpty() ) { int num = que.poll(); int size = nearList.get(num).size(); for(int i=0; i<size; i++) { int new_value = nearList.get(num).get(i); if(node[new_value] == false) { que.offer(new_value); node[new_value] = true; } } } } // End of BFS } // End of class
