백준 1992번
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1992
문제
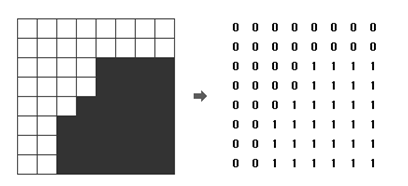
첫째 줄에는 영상의 크기를 나타내는 숫자 N 이 주어진다. N 은 언제나 2의 제곱수로 주어지며, 1 ≤ N ≤ 64의 범위를 가진다. 두 번째 줄부터는 길이 N의 문자열이 N개 들어온다. 각 문자열은 0 또는 1의 숫자로 이루어져 있으며, 영상의 각 점들을 나타낸다.
생각하기
- 분할정복을 해야한다.
- 재귀 구현을 고민해보자.
(물론 나는 못했음..)
동작
private static void solution(int x, int y, int size) {
if(checkPossibility(x, y, size)) {
sb.append(arr[x][y]);
return;
}
int newSize = size / 2;
sb.append('(');
solution(x, y, newSize);
solution(x, y + newSize, newSize);
solution(x + newSize, y, newSize);
solution(x + newSize, y + newSize, newSize);
sb.append(')'); solution 메소드는 재귀를 통해서 전체 arr배열을 분할정복하는 역할을 한다.
checkPossibility의 return값의 여부로 계속해서 newSize를 갱신해가며 새로운크기의 size로 메소드를 재귀 실행한다.
private static boolean checkPossibility(int x, int y, int size) {
int value = arr[x][y];
for(int i=x; i<x + size; i++) {
for(int j=y; j<y + size; j++) {
// 하나라도 다른 값이 나오게되면 곧바로 false를 return
if(value != arr[i][j]) return false;
}
}
return true;
checkPossibility 메소드를 통해서 해당 size로 arr을 분할 했을 때, 모두 값은 값인지 아닌지를 확인한다.
만약 size의 값만큼 회전을 했을 때, 전체가 같은 값일 경우(value == arr[i][j]) true를 return해서 가능하다는 것을 의미함
하나라도 다른 값이 나올 경우 곧바로 중단하고 false를 return


코드
Java
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static int N;
static int arr[][];
static StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
arr = new int[N][N];
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) {
char ch[] = br.readLine().toCharArray();
for(int j=0; j<N; j++) {
arr[i][j] = ch[j] - '0';
}
}
// 0부터 시작해서 재귀를 통해서 전체 탐색
solution(0, 0, N);
bw.write(sb.toString());bw.flush();bw.close();
} // End of main
private static void solution(int x, int y, int size) {
if(checkPossibility(x, y, size)) { // 압축이 가능할 경우. 곧바로 해당 값을 출력
sb.append(arr[x][y]);
return;
}
// 압축이 불가능 할 경우 작은 사이로 다시 새로운 사이즈를 정의
int newSize = size / 2; // 현재 사이즈에서 1 0으로 분리가 안될 경우 다시 압축
sb.append('('); // 사이즈가 수정 될 경우 ( 를 앞에 생성
solution(x, y, newSize);
solution(x, y + newSize, newSize);
solution(x + newSize, y, newSize);
solution(x + newSize, y + newSize, newSize);
sb.append(')'); // 괄호 닫기
} // End of solution
private static boolean checkPossibility(int x, int y, int size) {
int value = arr[x][y];
for(int i=x; i<x + size; i++) {
for(int j=y; j<y + size; j++) {
// 하나라도 다른 값이 나오게되면 곧바로 false를 return
if(value != arr[i][j]) return false;
}
}
return true;
} // End of checkPossibility
} // End of Main classKotlin
import java.io.*
private var N = 0
private lateinit var arr : Array<CharArray>
private var sb = StringBuilder()
fun main() {
val br = BufferedReader(InputStreamReader(System.`in`))
val bw = BufferedWriter(OutputStreamWriter(System.`out`))
N = br.readLine().toInt()
arr = Array(N){CharArray(N)}
for(i in 0 until N) {
var ch = br.readLine().toCharArray()
for( j in 0 until N) arr[i][j] = ch[j]
}
solution(0, 0, N)
bw.write(sb.toString());bw.flush();bw.close()
} // End of main
fun solution(x : Int , y : Int, size : Int) {
if(checkPossibility(x, y, size)) {
sb.append(arr[x][y])
return
}
var newSize = size/2
sb.append('(')
solution(x, y, newSize)
solution(x, y + newSize, newSize)
solution(x + newSize, y, newSize)
solution(x + newSize, y + newSize, newSize)
sb.append(')')
} // End of solution
fun checkPossibility(x : Int, y : Int, size : Int) : Boolean {
val value = arr[x][y]
for(i in x until x+size) {
for( j in y until y+size) {
if( !value.equals(arr[i][j]) ) return false
}
}
return true
} // End of checkPossibility