문제 설명
생각 정리
기존에 풀었던 탐색문제와 거의 똑같다. 하나 다른 점이 있다면, '상하좌우'의 4방향을 탐색하는 것이 아니라 8방향을 탐색하는 것이다.
정리된 생각에 대한 논리
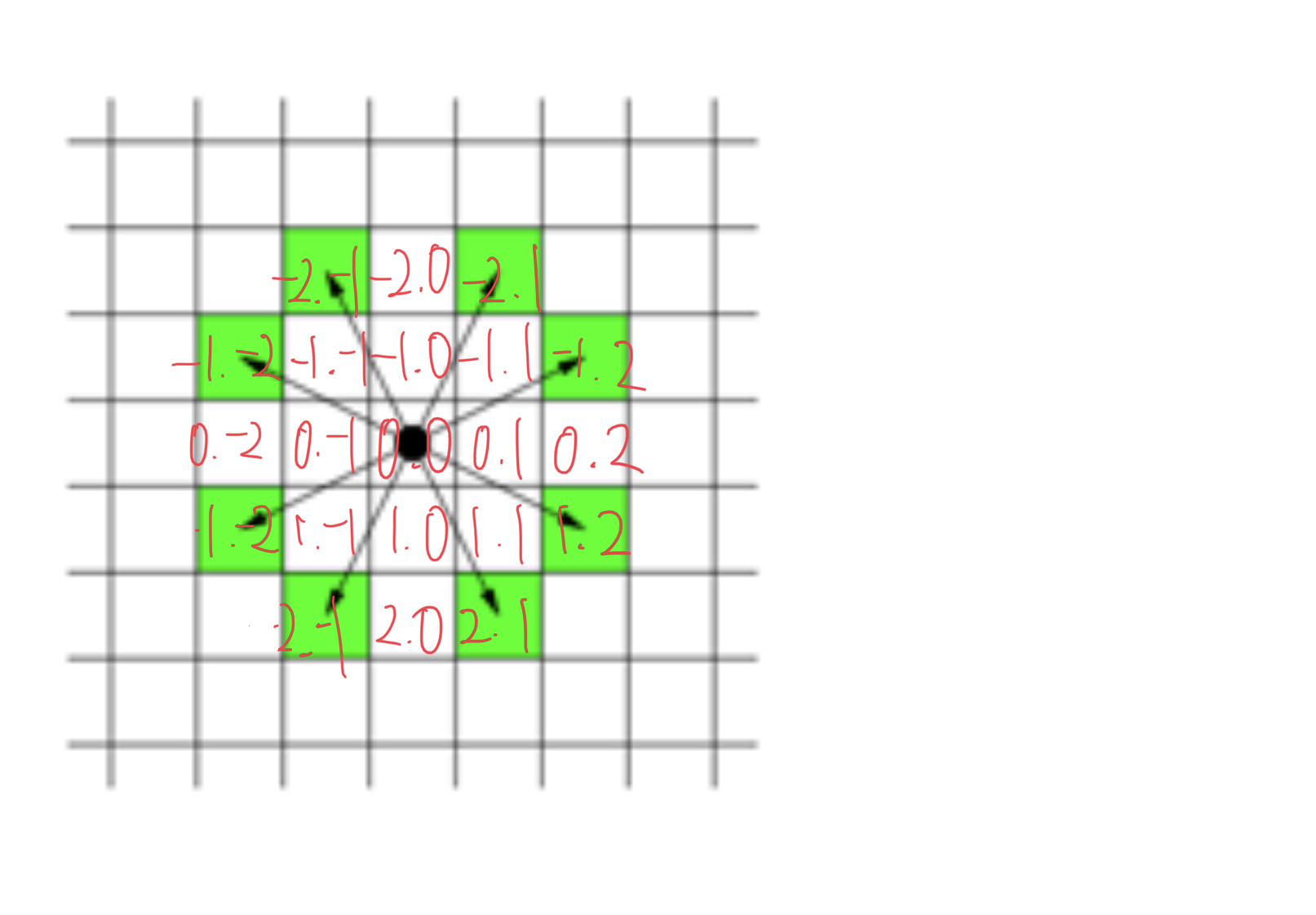
(n, m)을 기준으로 초록색 방향들을 접근하면 된다.
dx[] = {-2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2}
dy[] = {1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1}
//탐색해야 할 위치들을 전역변수로 선언했다.완성
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
class Position {
int x, y;
Position(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
public class BOJ7562 {
static int T, l, startX, startY, endX, endY;
static int[][] position;
static boolean[][] visited;
static int[][] dis;
static int[] dx = {-2, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2};
static int[] dy = {1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
T = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
for(int i=0; i<T; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
l = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
position = new int[l][l];
visited = new boolean[l][l];
dis = new int[l][l];
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
startX = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
startY = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
endX = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
endY = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
if(startX == endX && startY == endY)
System.out.println(0);
else
bfs(startX, startY);
}
}
static void bfs(int x, int y) {
Queue<Position> queue = new LinkedList<>();
visited[x][y] = true;
queue.add(new Position(x, y));
int cnt = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
Position p = queue.poll();
for(int i=0; i<8; i++) {
int nextX = p.x + dx[i];
int nextY = p.y + dy[i];
if(nextX<0 || nextY<0 || nextX>=l || nextY>=l) continue;
else if(visited[nextX][nextY] == true) continue;
else {
visited[nextX][nextY] = true;
queue.add(new Position(nextX, nextY));
dis[nextX][nextY] = dis[p.x][p.y] + 1;
cnt = dis[nextX][nextY];
if(nextX == endX && nextY == endY) {
System.out.println(cnt);
return ;
}
}
}
}
}
}

