[Android] JetPack Compose Codelab 2 : BasicLayoutsCodelab
오늘은 지난번(BasicCodelab)에 이어서 BasicLayoutsCodelab의 내용을 둘러보고자 한다.
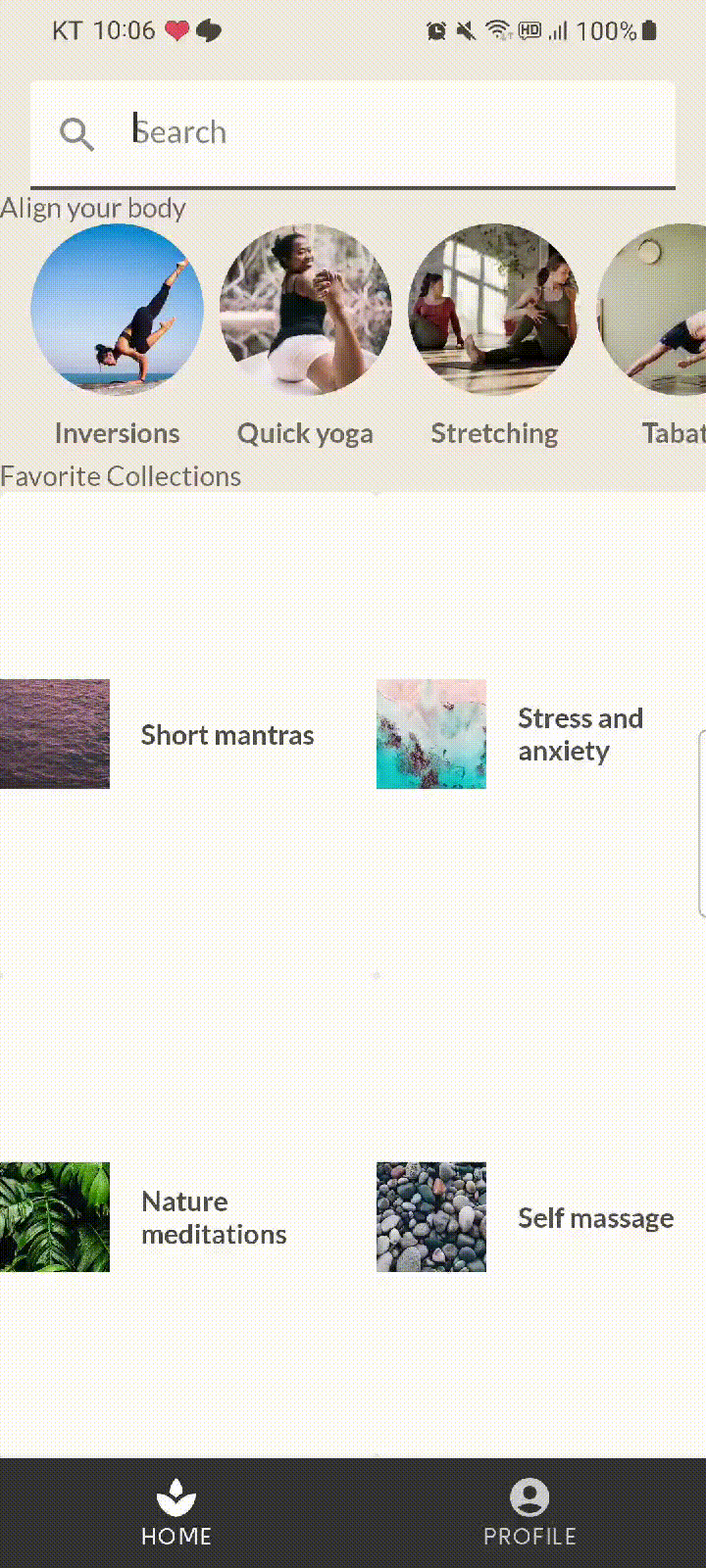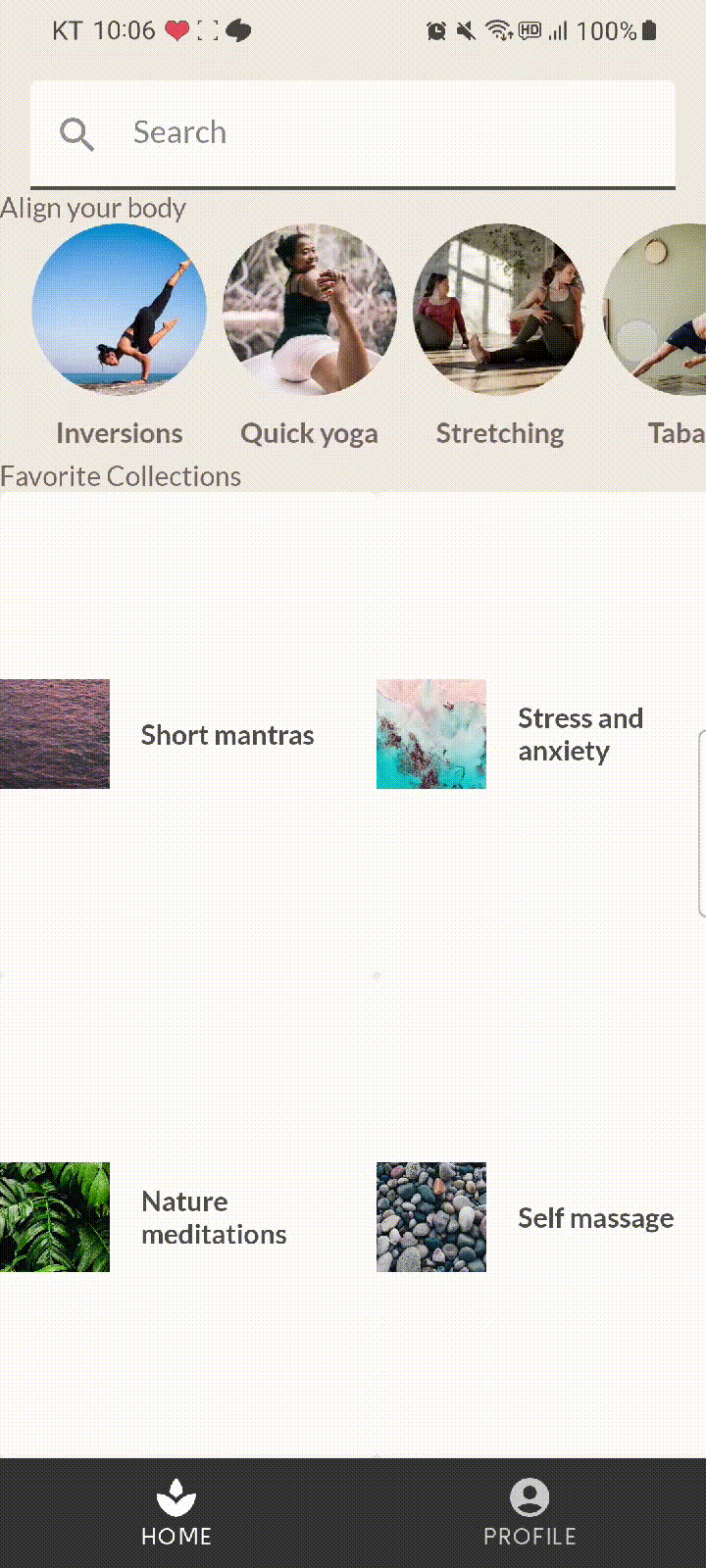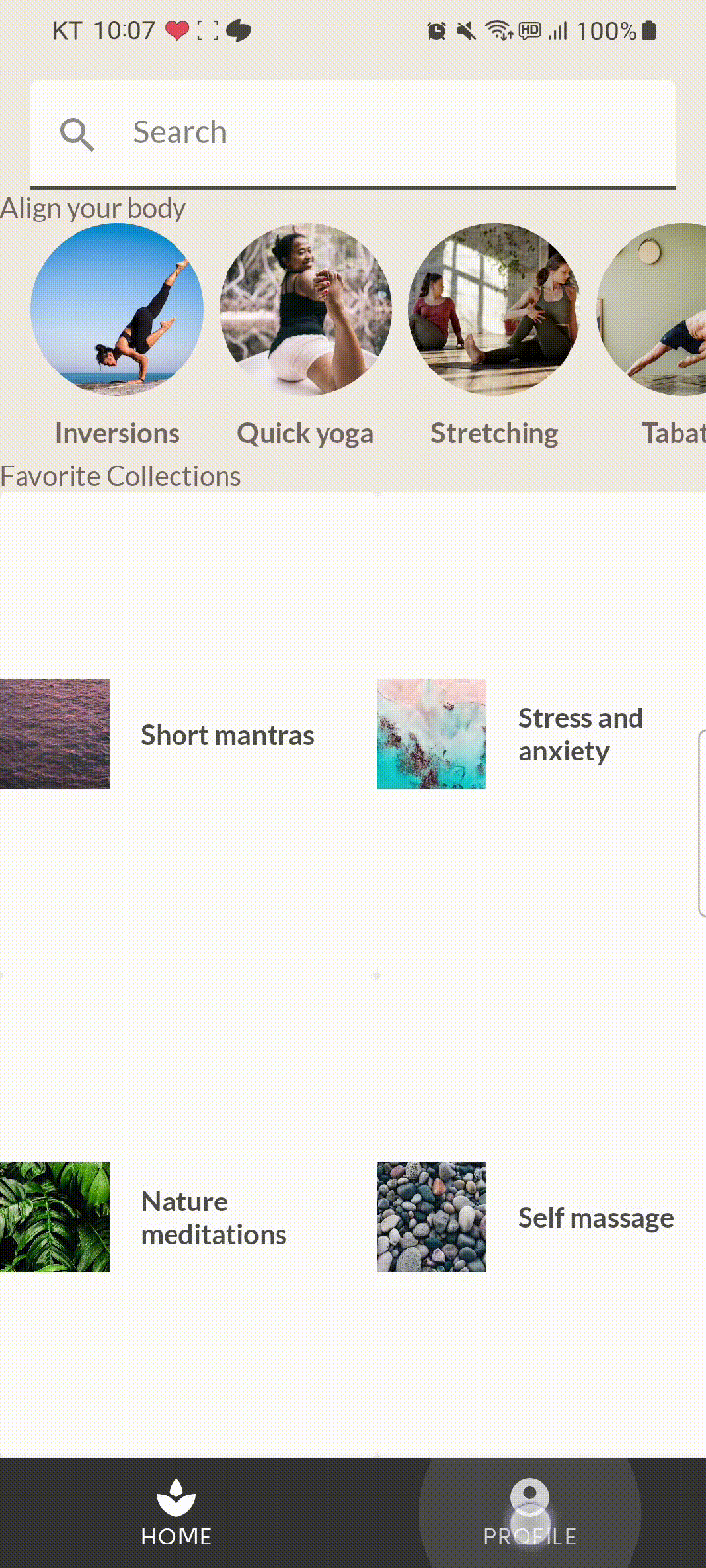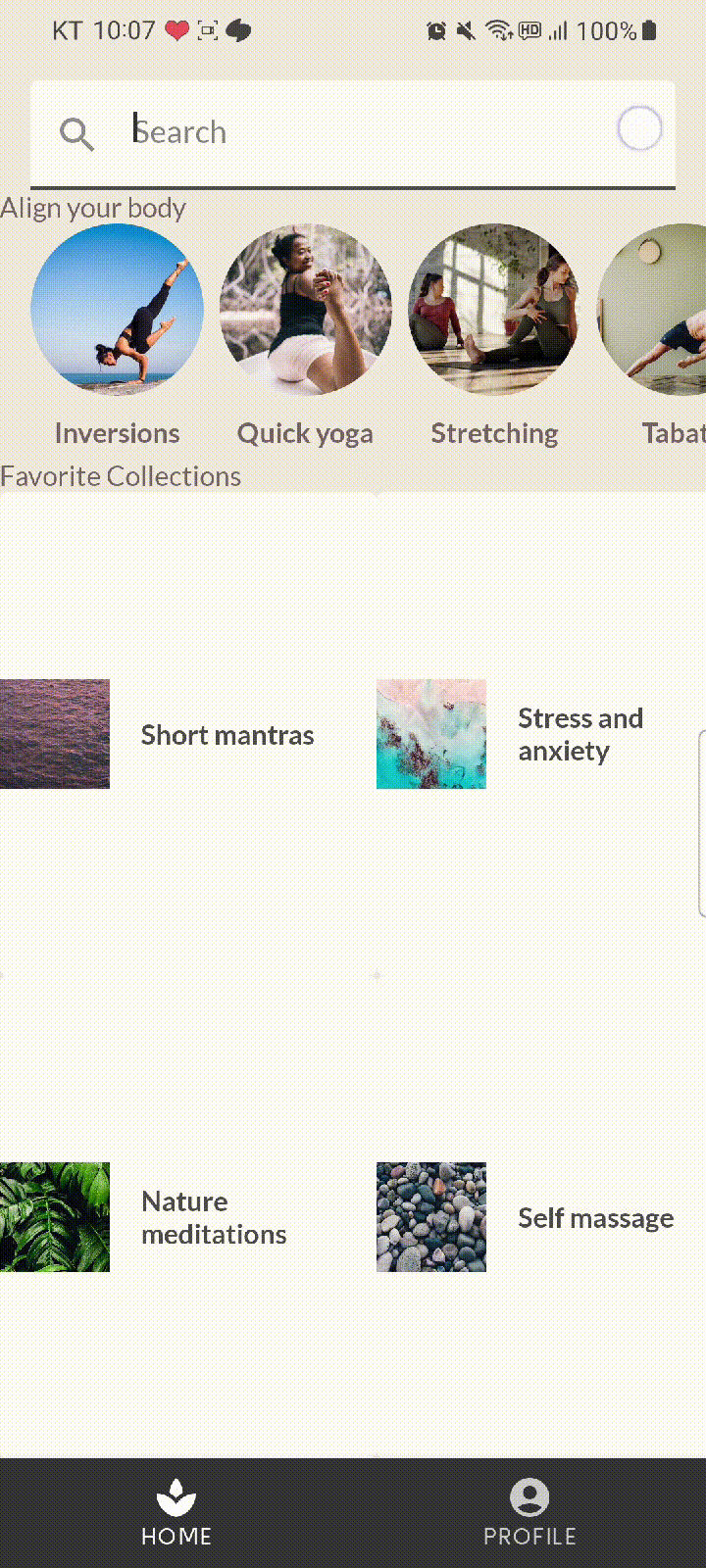
상단의 검색창, 중앙에 리스트 두개, 그리고 바텀내비게이션 바가 있는 앱이다.
- MySootheApp > SootheBottomNavigation, HomeScreen
@Composable
fun MySootheApp() {
MySootheTheme {
Scaffold(
bottomBar = { SootheBottomNavigation() },
) { padding ->
HomeScreen(Modifier.padding(padding))
}
}
}Scaffold를 사용하여, 바텀 내비를 설정했고, 하위 화면은 HomeScreen으로 설정했다.
- SootheBottomNavigation
@Composable
private fun SootheBottomNavigation(modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
BottomNavigation(modifier) {
BottomNavigationItem(
icon = {
Icon(
imageVector = Icons.Default.Spa,
contentDescription = null,
)
},
label = {
Text(stringResource(R.string.bottom_navigation_home))
},
selected = true,
onClick = {},
)
BottomNavigationItem(
icon = {
Icon(
imageVector = Icons.Default.AccountCircle,
contentDescription = null,
)
},
label = {
Text(stringResource(R.string.bottom_navigation_profile))
},
selected = false,
onClick = {},
)
}
}네비게이션을 통해 바텀 내비의 화면전환을 하고자 한 것으로 확인되고, 아이콘과 아이콘 하단의 텍스트만 설정되어 있다. 하지만 라우팅이 작용하고 있지는 않은 상태로, 자세한 사항은 이곳에서 확인해보도록 하자.
- HomeScreen > SearchBar, HomeSection(AlignYourBodyRow), HomeSection(FavoriteCollectionsGrid)
@Composable
fun HomeScreen(modifier: Modifier = Modifier) {
Column(modifier) {
Spacer(Modifier.height(16.dp))
SearchBar(Modifier.padding(horizontal = 16.dp))
HomeSection(title = R.string.align_your_body) {
AlignYourBodyRow()
}
HomeSection(title = R.string.favorite_collections) {
FavoriteCollectionsGrid()
}
Spacer(Modifier.height(16.dp))
}
}
@Composable
fun HomeSection(
@StringRes title: Int,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
content: @Composable () -> Unit,
) {
Column(modifier) {
Text(stringResource(title))
content()
}
}Spacer로 상하단의 간격을 제시하고, 검색창, 첫번째 리스트, 두번째 리스트가 Column을 사용하여 구현했다. HomeSection은 리스트의 타이틀을 달아주기 위한 또 한꺼풀의 껍질이다.
- SearchBar
@Composable
fun SearchBar(
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
) {
TextField(
value = "",
onValueChange = {},
leadingIcon = {
Icon(
imageVector = Icons.Default.Search,
contentDescription = null,
)
},
colors = TextFieldDefaults.textFieldColors(
backgroundColor = MaterialTheme.colors.surface,
),
placeholder = {
Text(stringResource(R.string.placeholder_search))
},
modifier = modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.heightIn(min = 56.dp),
)
}TextField로 검색창을 구현했고, 아이콘(leadingIcon으로 앞단에 배치)과 색, 힌트 문구, 규격을 제시한다.
- AlignYourBodyRow > AlignYourBodyElement
@Composable
fun AlignYourBodyRow(
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
) {
LazyRow(
horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.spacedBy(8.dp),
contentPadding = PaddingValues(horizontal = 16.dp),
modifier = modifier,
) {
items(alignYourBodyData) { item ->
AlignYourBodyElement(item.drawable, item.text)
}
}
}
@Composable
fun AlignYourBodyElement(
@DrawableRes drawable: Int,
@StringRes text: Int,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
) {
Column(
modifier = modifier,
horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally,
) {
Image(
painter = painterResource(drawable),
contentDescription = null,
contentScale = ContentScale.Crop,
modifier = Modifier
.size(88.dp)
.clip(CircleShape),
)
Text(
text = stringResource(text),
style = MaterialTheme.typography.h3,
modifier = Modifier.paddingFromBaseline(
top = 24.dp,
bottom = 8.dp,
),
)
}
}첫 번째 리스트이다. LazyRow를 통해 구현됐으며, AlignYourBodyElement를 아이템 뷰의 형태를 받고 있다. 이렇다 할 특징은 없지만, 리스트를 구현하는 방식이다. Lazy하게 그리며, 리사이클러뷰와 비슷한 기능을 compose 구현한 것이다.
- AlignYourBodyRow > AlignYourBodyElement
@Composable
fun FavoriteCollectionsGrid(
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
) {
LazyHorizontalGrid(
rows = GridCells.Fixed(2),
modifier = modifier,
) {
items(favoriteCollectionsData) { item ->
FavoriteCollectionCard(item.drawable, item.text)
}
}
}
@Composable
fun FavoriteCollectionCard(
@DrawableRes drawable: Int,
@StringRes text: Int,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
) {
Surface(
shape = MaterialTheme.shapes.small,
modifier = modifier,
) {
Row(
verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically,
modifier = Modifier.width(192.dp),
) {
Image(
painter = painterResource(drawable),
contentDescription = null,
contentScale = ContentScale.Crop,
modifier = Modifier.size(56.dp),
)
Text(
text = stringResource(text),
style = MaterialTheme.typography.h3,
modifier = Modifier.padding(horizontal = 16.dp),
)
}
}
}두 번째 리스트이다. LazyHorizontalGrid를 통해 구현됐으며, FavoriteCollectionCard를 아이템 뷰의 형태를 받고 있다. Lazy하게 그리며, GridListView와 비슷한 기능을 compose 구현한 것이다.
다음 포스팅은 Basic State codelab 이다.