어노테이션이란?
Annotations, a form of metadata, provide data about a program that is not part of the program itself.
Annotations have no direct effect on the operation of the code they annotate.
자바 공식 문서(https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/annotations/)
에 따르면 어노테이션은 메타데이터이며, 코드에는 영향을 미치지 않는다고 한다.
어노테이션의 사전적 정의는 주석 이며 실제 데이터가 아닌
데이터의 데이터 즉 메타데이터이다.
-
Information for the compiler — Annotations can be used by the compiler to detect errors or suppress warnings.
-
Compile-time and deployment-time processing — Software tools can process annotation information to generate code, XML files, and so forth.
-
Runtime processing — Some annotations are available to be examined at runtime.
어노테이션의 용도는 3가지가 있으며
-
컴파일러에 대한 정보
-
컴파일 및 배포 시간 처리
-
런타임 처리
이다.
어노테이션의 정의
어노테이션을 정의하기 위해선 다양한 요소가 필요하다.
@Retention: 어노테이션의 동작 범위를 지정한다.
Enum 타입인 RetentionPolicy을 열어보면 다음과 같이 작성되어 있다.
public enum RetentionPolicy {
/**
* Annotations are to be discarded by the compiler.
*/
SOURCE,
/**
* Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler
* but need not be retained by the VM at run time. This is the default
* behavior.
*/
CLASS,
/**
* Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler and
* retained by the VM at run time, so they may be read reflectively.
*
* @see java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement
*/
RUNTIME
}-
SOURCE : 컴파일 시간에 동작하지 않고 소스에서 표시만 된다.
-
CLASS : 컴파일 시간에 동작하지만 런타임에서는 동작하지 않는다.
-
RUNTIME : 런타임에서 동작한다. 실제로 많이 사용한다.
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)이런 방식으로 어노테이션의 동작 범위를 지정할 수 있다.
@Target: 어노테이션의 작용 범위를 지정한다.
Target의 범위를 작성해놓은 Enum 타입인 ElementType의 내용은 다음과 같다.
public enum ElementType {
/** Class, interface (including annotation interface), enum, or record
* declaration */
TYPE,
/** Field declaration (includes enum constants) */
FIELD,
/** Method declaration */
METHOD,
/** Formal parameter declaration */
PARAMETER,
/** Constructor declaration */
CONSTRUCTOR,
/** Local variable declaration */
LOCAL_VARIABLE,
/** Annotation interface declaration (Formerly known as an annotation type.) */
ANNOTATION_TYPE,
/** Package declaration */
PACKAGE,
/**
* Type parameter declaration
*
* @since 1.8
*/
TYPE_PARAMETER,
/**
* Use of a type
*
* @since 1.8
*/
TYPE_USE,
/**
* Module declaration.
*
* @since 9
*/
MODULE,
/**
* Record component
*
* @jls 8.10.3 Record Members
* @jls 9.7.4 Where Annotations May Appear
*
* @since 16
*/
RECORD_COMPONENT;
}위의 Type들을 지칭해서 해당 어노테이션이 어디에 적용 가능한 지 제한할 수 있다.
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)현재 어노테이션은 어노테이션에만 적용 가능하도록 제한하고 있다.
@Documented: javadoc에 어노테이션에 대한 설명을 빼도록 도와준다.
@Documented annotation indicates that whenever the specified annotation is used those elements should be documented using the Javadoc tool. (By default, annotations are not included in Javadoc.) For more information
- Java Document -
스프링에서 빈을 등록하는 과정 with @
우리는 어떻게 자바 객체를 스프링 빈으로 등록해 사용할까?
@Service , @Repository, @Controller, @Component 같은 어노테이션만 붙이면 스프링이 알아서 빈으로 등록해 호출해주는 과정을 알아보자.
@Component는 해당 클래스를 스프링 빈으로 등록하겠다는 의미이다.
public @interface Component {
/**
* The value may indicate a suggestion for a logical component name,
* to be turned into a Spring bean name in case of an autodetected component.
* @return : the suggested component name, if any (or empty String otherwise)
*/
String value() default "";
}value = 를 통해 특정 이름으로 지정할 수도 있다.
@Component는 @Service , @Repository, @Controller에 포함되어 있다.
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Controller {
/**
* Alias for {@link Component#value}.
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = Component.class)
String value() default "";
}위에서 살펴본 내용으로 해석해보자면
-
해당 어노테이션은 Type에만 적용 가능하다.
-
해당 어노테이션은 런타임에서 작동한다.
-
javadoc에서 해당 어노테이션의 설명을 제외한다.
-
컴포넌트 즉 스프링 빈으로 등록한다.
이다.
이를 통해 우리는 클래스를 스프링 빈으로 등록한다.
스프링 빈은 스프링 컨테이너인 ApplicationContext에서 관리한다.
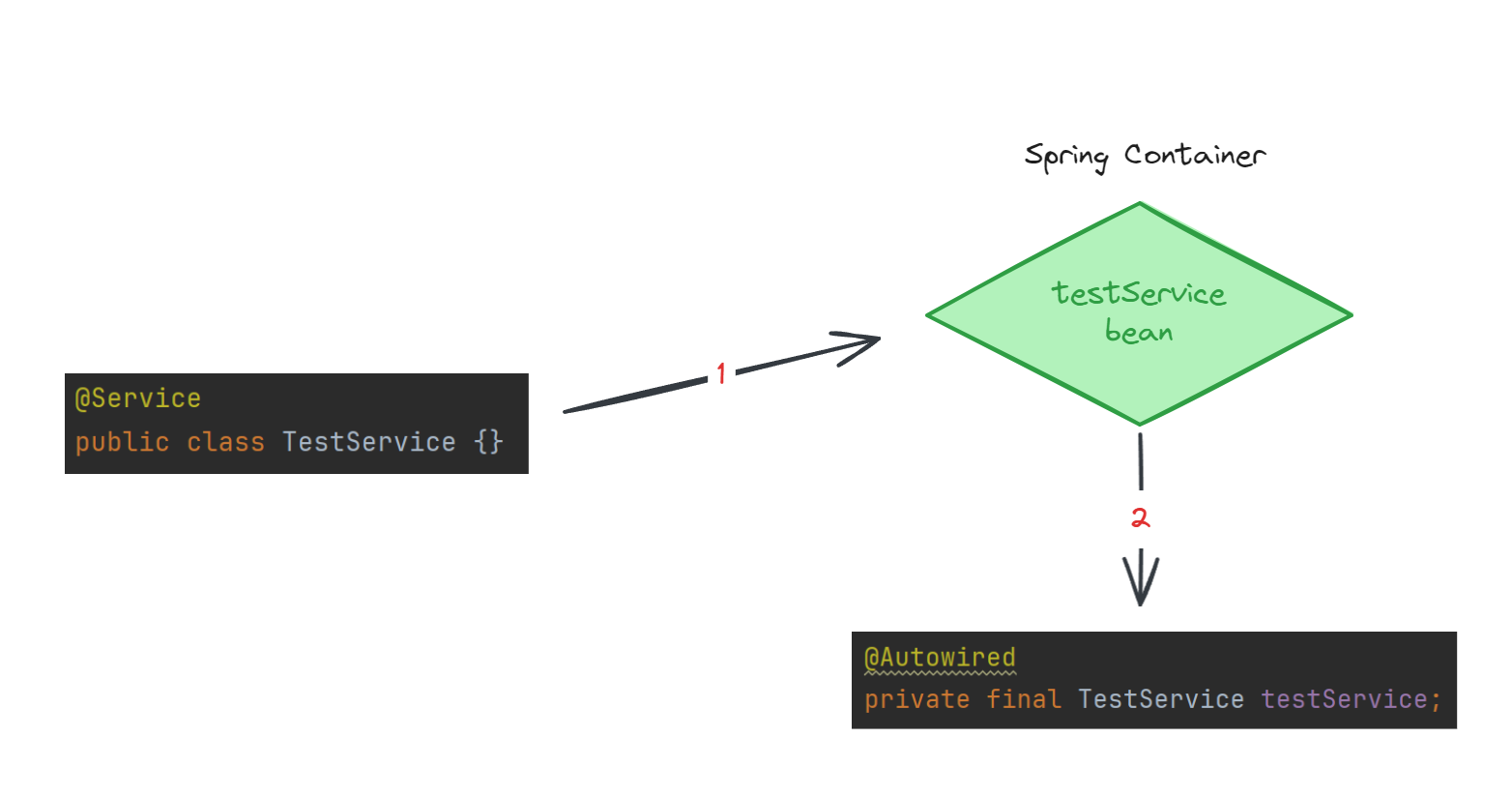
먼저 @Service 어노테이션을 통해 TestService 클래스를 스프링 빈으로 등록한다.
testService 빈은 Spring Container에서 관리한다.
@Autowired 를 통해 해당 빈을 요청받으면 Container에서 Dependency Injection을 통해 의존성을 주입해준다.
Component Scan
그럼 @Component가 붙은 클래스라는 것을 누가, 언제 확인할까?
애플리케이션 파일에서 스프링부트 프로젝트를 시작할 때 @SpringBootApplication을 붙이곤 한다.
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}해당 어노테이션의 정의를 살펴보면 다음과 같은 어노테이션이 등록되어있다.
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
...@ComponentScan 을 통해 범위과 대상을 지정해 @Component가 붙은 클래스들을 모두 빈으로 등록한다.
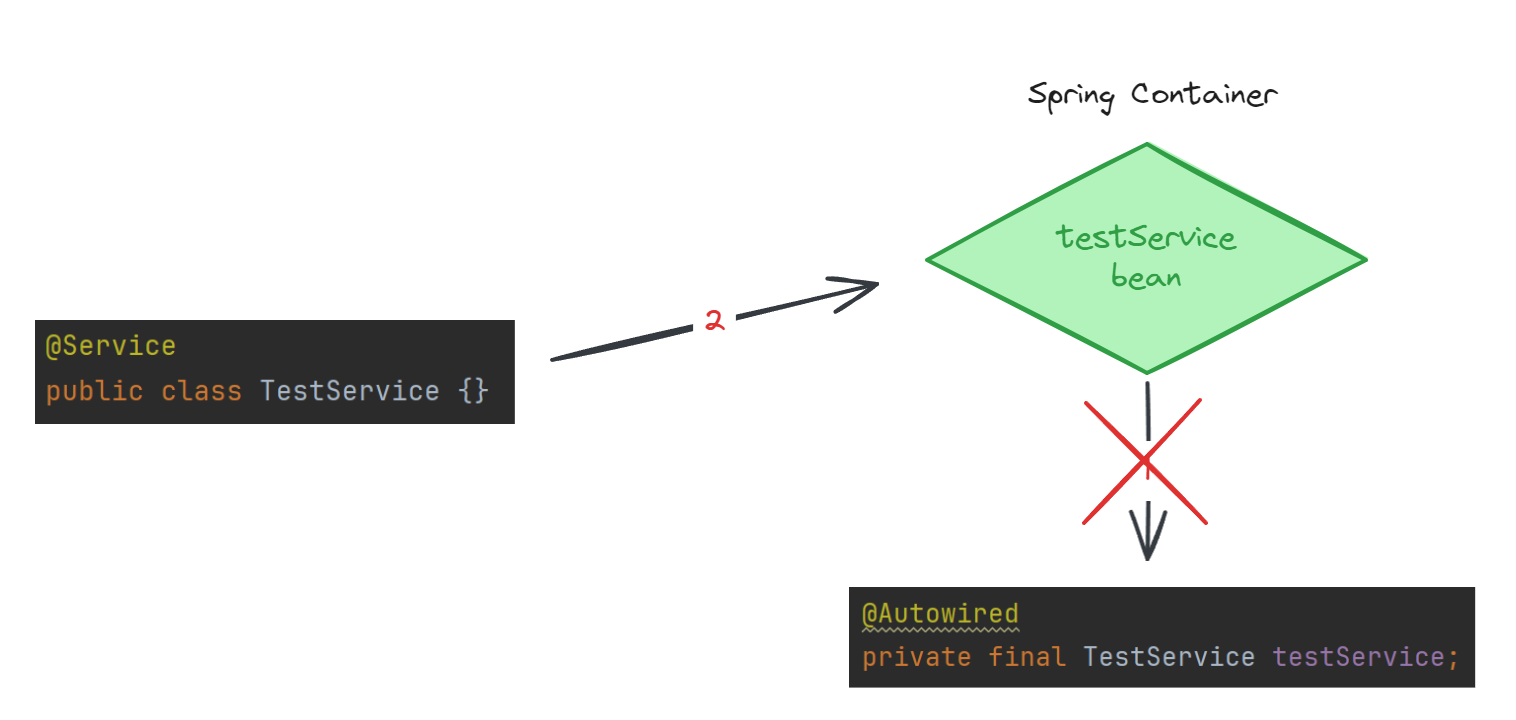
이때 등록되는 시점이 매우 중요하다.
만약 빈으로 등록되지도 않았는데 DI를 시도한다면 당연히 에러가 발생할 것이다.
@ComponentScan 은 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 구현체가 적용되어있고
@Autowired 은 BeanPostProcessor 구현체가 적용되어 있다.
@ComponentScan가 먼저 실행되어 컴포넌트들을 빈으로 자동 등록한 후에 @Autowired 가 실행되어 빈으로 등록된 컴포넌트들을 스프링 컨테이너에서 찾아서 의존성을 주입해준다.
