
📄 Description
Given an array of positive integers nums and a positive integer target, return the minimal length of a contiguous subarray of which the sum is greater than or equal to target. If there is no such subarray, return 0 instead.
Example 1:
Input: target = 7, nums = [2,3,1,2,4,3]
Output: 2
Explanation: The subarray [4,3] has the minimal length under the problem constraint.Example 2:
Input: target = 4, nums = [1,4,4]
Output: 1Example 3:
Input: target = 11, nums = [1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1]
Output: 0Constraints:
1 <= target <= 1091 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= nums[i] <= 105
🎈 Follow up:
If you have figured out the O(n) solution, try coding another solution of which the time complexity is O(n log(n)).
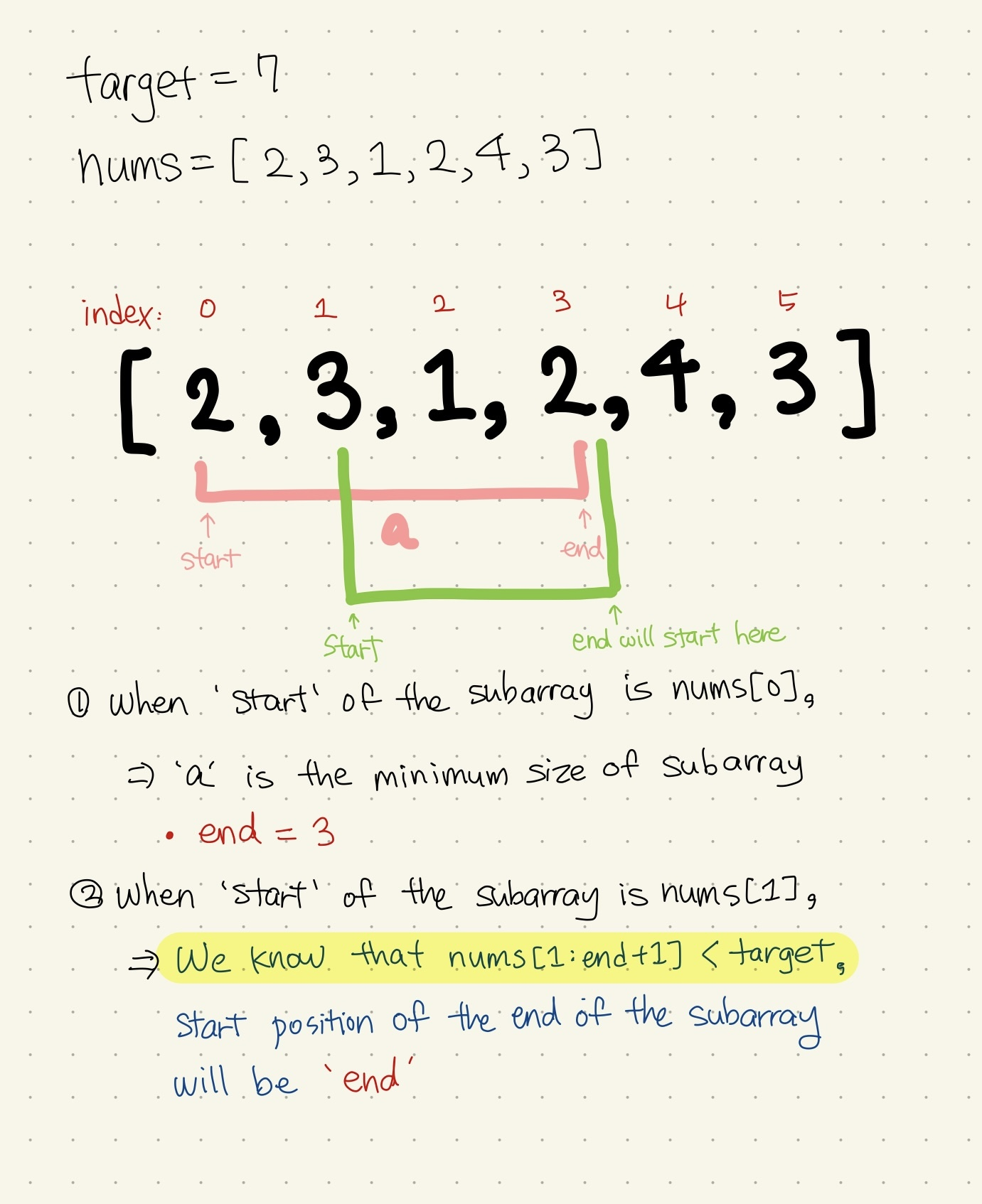
🔨 Several Tries
- Find the
max(nums)and divde it to theleftandrightpart that includesmax(nums). Then find the minimum length of subarray in both part and return the smaller one.💭 What was the problem?
There is no guarantee that themax()value will be included in the minimum size subarray.For example
The right subarray should be# target=10 nums=[5,5,1,1,7,1,1][5,5]but through above approach, it will return[1,1,7].
🔨 My Solution
💻 My Submission
class Solution:
def minSubArrayLen(self, target: int, nums: List[int]) -> int:
min_end=0
min_len=len(nums)
w_sum=nums[0]
if sum(nums)<target: return 0
if nums[-1]>=target: return 1
for i in range(len(nums)-1):
if i>0:
w_sum-=nums[i-1]
if i>min_end:
min_end=i
# find the min subarray
while min_end<len(nums):
if w_sum<target:
min_end+=1
if min_end==len(nums):break
w_sum+=nums[min_end]
if w_sum>=target:
min_len=min(min_len,min_end-i+1)
break
# print("-------------")
return min_len🕐 Complexity
Time Complexity: O(N)
The worst case is when the minumum subarry is nums array itself.
Space Complexity: O(1)
💡 Other Better Solutions
1. O(N) Appraoach
class Solution:
def minSubArrayLen(self, s, nums):
total = left = 0
result = len(nums) + 1
for right, n in enumerate(nums):
total += n
while total >= s:
result = min(result, right - left + 1)
total -= nums[left]
left += 1
return result if result <= len(nums) else 0What is different?
- Nested Loop
- My code: outer loop is for
leftand inner loop is for `right - Better solution: outer loop is for
rightand inner loop is forleft
- Default value for
min_len
2. O(NlogN) Approach
class Solution:
def minSubArrayLen(self, target, nums):
result = len(nums) + 1
for idx, n in enumerate(nums[1:], 1):
nums[idx] = nums[idx - 1] + n
left = 0
for right, n in enumerate(nums):
if n >= target:
left = self.find_left(left, right, nums, target, n)
result = min(result, right - left + 1)
return result if result <= len(nums) else 0
def find_left(self, left, right, nums, target, n):
while left < right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if n - nums[mid] >= target:
left = mid + 1
else:
right = mid
return leftReferences
