.png)
안녕하세요. 엘림입니다🙇🏻♀️
Swift 공식 문서 정독하기 5편입니다!
제 스타일대로 정리했으니 추가적으로 더 필요한 정보는
공식문서 링크를 눌러 확인해주세용!
좀 더 편하게 보기위해 한국어로 번역된 사이트를 함께 확인했습니다!ㅎㅎ
자, 그럼 시작해볼까요
이 글은 공부하면서 작성한 글이기 때문에 잘못된 정보가 있을 수 있습니다.🥺
금방 잊어버릴... 미래의 저에게 다시 알려주기 위한 글이다보니
혹시라도 틀린 부분이 있다면, 댓글로 친절하게 알려주시길 부탁드립니다.🙏
반복문
For-In
for-in문는 배열, 숫자, 문자열을 순서대로 순회(iterate)하기 위해 사용합니다.
let names = ["Anna", "Alex", "Brian", "Jack"]
for name in names {
print("Hello, \(name)!")
}
// Hello, Anna!
// Hello, Alex!
// Hello, Brian!
// Hello, Jack!dictionary에서 반환된 키(key)-값(value) 쌍으로 구성된 튜플을 순회하며 제어할 수도 있습니다. dictionary에 담긴 콘텐츠는 정렬이 되지 않은 상태입니다. 사전에 넣었던 순서대로 순회되지 않습니다.
let numberOfLegs = ["spider": 8, "ant": 6, "cat": 4]
for (animalName, legCount) in numberOfLegs {
print("\(animalName)s have \(legCount) legs")
}
// ants have 6 legs
// spiders have 8 legs
// cats have 4 legs아래와 같이 숫자 범위를 지정해 순회할 수 있습니다.
for index in 1...5 {
print("\(index) times 5 is \(index * 5)")
}
// 1 times 5 is 5
// 2 times 5 is 10
// 3 times 5 is 15
// 4 times 5 is 20
// 5 times 5 is 25for-in문을 순서대로 제어할 필요가 없다면, 변수자리에 _키워드를 사용하면 성능을 높일 수 있습니다.
let base = 3
let power = 10
var answer = 1
for _ in 1...power {
answer *= base
}
print("\(base) to the power of \(power) is \(answer)")
// Prints "3 to the power of 10 is 59049"범위 연산자와 함께 사용할 수 있습니다.
let minutes = 60
for tickMark in 0..<minutes {
// render the tick mark each minute (60 times)
}stride(from:to:by:)를 사용하여, 연속된 숫자가 아니라 규칙성 있는 숫자 배열로 접근할 수 있습니다. (to는 포함되지 않으며, stride(from:through:by:)의 through는 포함됩니다.)
let minuteInterval = 5
for tickMark in stride(from: 0, to: minutes, by: minuteInterval) {
// render the tick mark every 5 minutes (0, 5, 10, 15 ... 45, 50, 55)
}
let hours = 12
let hourInterval = 3
for tickMark in stride(from: 3, through: hours, by: hourInterval) {
// render the tick mark every 3 hours (3, 6, 9, 12)
}While
조건(condition)이 거짓(false)일때까지 구문(statements)을 반복합니다.
while condition {
statements
}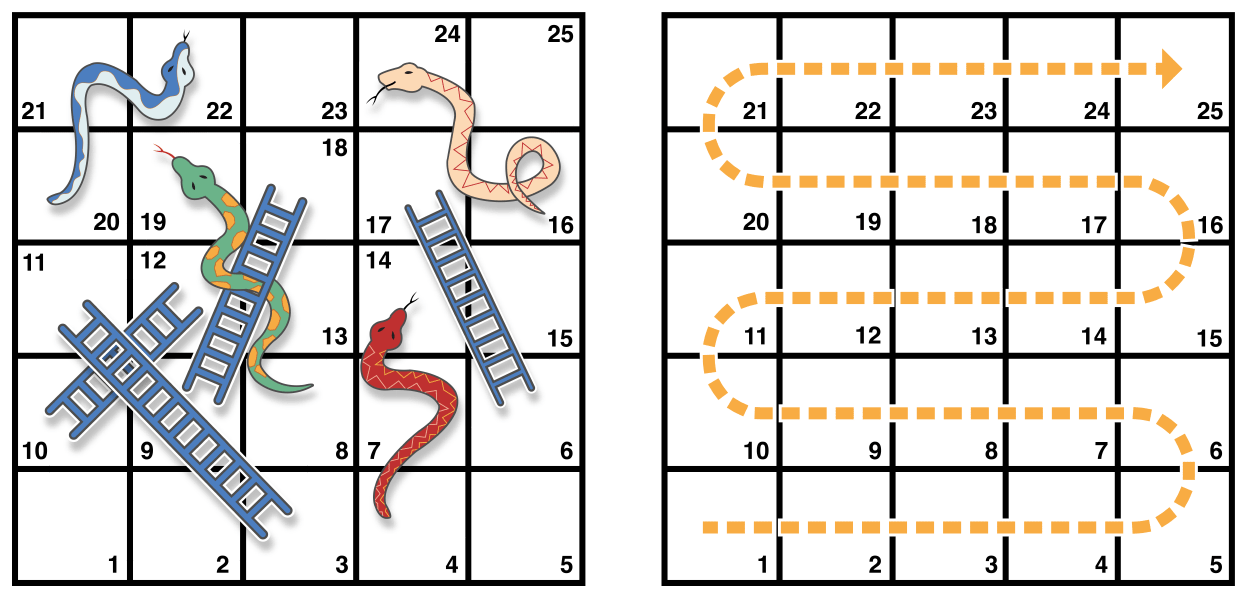
- 보드에는 25개의 사각형이 있고, 목표는 25번 사각형이나 그 이상에 도착하는 것입니다.
- 시작은 왼쪽 모서리 하단에 0입니다.
- 각 턴마다 주사위를 굴려서 점선을 따라 그 수 만큼 칸을 이동합니다.
- 사다리에서 아래에서 끝나면 사다리 위로 올라가고, 뱀의 머리에서 끝나면 뱀의 꼬리로 이동합니다.
let finalSquare = 25
var board = [Int](repeating: 0, count: finalSquare + 1) // 0에서 시작해서 1 더해줌
board[03] = +08; board[06] = +11; board[09] = +09; board[10] = +02
board[14] = -10; board[19] = -11; board[22] = -02; board[24] = -08
var square = 0
var diceRoll = 0
while square < finalSquare {
// roll the dice, 난수를 생성하지 않고 그냥 1씩 더해주는 방식 사용
diceRoll += 1
if diceRoll == 7 { diceRoll = 1 } // 주사위가 7 이상이면 안되니까
square += diceRoll // 실제 이동
if square < board.count {
// 보드 안에 있을때, 사다리나 뱀 등에 의해 위치 조정
square += board[square] // 보드안에 있는지 체크 안하면, 런타임 오류날 수 있음
}
}
print("Game over!")repeat-while
reapeat-while문은 다른 언어의 do-while문과 유사한 while문입니다.
구문(statements)을 최소 한번 이상 실행하고 while 조건이 거짓일 때까지 반복합니다.
repeat {
statements
} while condition위의 보드게임을 reapeat-while문으로 작성해보겠습니다.
repeat {
// move up or down for a snake or ladder
square += board[square]
// roll the dice
diceRoll += 1
if diceRoll == 7 { diceRoll = 1 }
// move by the rolled amount
square += diceRoll
} while square < finalSquare
print("Game over!")조건문
If
(예1) If만 사용
var temperatureInFahrenheit = 30
if temperatureInFahrenheit <= 32 {
print("It's very cold. Consider wearing a scarf.")
}
// Prints "It's very cold. Consider wearing a scarf."(예2) else를 사용
temperatureInFahrenheit = 40
if temperatureInFahrenheit <= 32 {
print("It's very cold. Consider wearing a scarf.")
} else {
print("It's not that cold. Wear a t-shirt.")
}
// Prints "It's not that cold. Wear a t-shirt."(예3) else, else-if를 사용
temperatureInFahrenheit = 90
if temperatureInFahrenheit <= 32 {
print("It's very cold. Consider wearing a scarf.")
} else if temperatureInFahrenheit >= 86 {
print("It's really warm. Don't forget to wear sunscreen.")
} else {
print("It's not that cold. Wear a t-shirt.")
}
// Prints "It's really warm. Don't forget to wear sunscreen."(예4) else-if 만 사용
temperatureInFahrenheit = 72
if temperatureInFahrenheit <= 32 {
print("It's very cold. Consider wearing a scarf.")
} else if temperatureInFahrenheit >= 86 {
print("It's really warm. Don't forget to wear sunscreen.")
}Switch
모든 switch문장은 철저 해야 합니다. 즉, 고려 중인 타입의 모든 가능한 값이 switch경우 중 하나와 일치해야 합니다. 가능한 모든 값에 대해 케이스를 제공하는 것이 적절하지 않은 경우 명시적으로 처리되지 않은 값을 포함하도록 default키워드로 기본 케이스를 정의할 수 있습니다.
switch some value to consider {
case value 1:
respond to value 1
case value 2,
value 3:
respond to value 2 or 3
default:
otherwise, do something else
}문자를 비교해 처리하는 경우 아래와 같이 사용할 수 있습니다.
let someCharacter: Character = "z"
switch someCharacter {
case "a":
print("The first letter of the alphabet")
case "z":
print("The last letter of the alphabet")
default:
print("Some other character")
}
// Prints "The last letter of the alphabet"암시적 진행이 없음
C와 Objective-C의 switch 구문과는 달리 Swift의 switch구문은 암시적인 진행을 하지 않습니다. 즉, 모든 case를 순회하지 않고, 해당하는 case만 완료하고 종료됩니다.
그렇게 때문에 break가 필수적이지 않으며, 특정 지점에 멈추게 할때에만 사용됩니다.
let anotherCharacter: Character = "a"
switch anotherCharacter {
case "a": // Invalid, case문에 body가 없으므로 에러가 발생합니다.
case "A":
print("The letter A")
default:
print("Not the letter A")
}
// 컴파일 에러 발생!
let anotherCharacter: Character = "a"
switch anotherCharacter {
case "a", "A":
print("The letter A")
default:
print("Not the letter A")
}
// Prints "The letter A"기존의 C와 Objective-C의 switch처럼 케이스를 비우는 것이 아니라, 두 케이스에 모두 해당하길 윈한다면 혼합해서 사용해야합니다.
만약, 명시적으로 switch-case 문의 특정 지점의 끝까지 실행하고 싶다면 조금 있다 살펴볼 fallthrough 키워드를 사용할 수 있습니다.
인터벌 매칭 (Interval Matching)
숫자의 특정 범위를 조건으로 사용할 수 있습니다.
let approximateCount = 62
let countedThings = "moons orbiting Saturn"
let naturalCount: String
switch approximateCount {
case 0:
naturalCount = "no"
case 1..<5:
naturalCount = "a few"
case 5..<12:
naturalCount = "several"
case 12..<100:
naturalCount = "dozens of"
case 100..<1000:
naturalCount = "hundreds of"
default:
naturalCount = "many"
}
print("There are \(naturalCount) \(countedThings).")
// Prints "There are dozens of moons orbiting Saturn."튜플 (Tuple)
튜플을 조건으로 사용할 수 있습니다.
let somePoint = (1, 1)
switch somePoint {
case (0, 0):
print("\(somePoint) is at the origin")
case (_, 0):
print("\(somePoint) is on the x-axis")
case (0, _):
print("\(somePoint) is on the y-axis")
case (-2...2, -2...2):
print("\(somePoint) is inside the box")
default:
print("\(somePoint) is outside of the box")
}
// Prints "(1, 1) is inside the box"값 바인딩 (Value Bindings)
특정 x, y 값을 각각 다른 case에 정의하고 그 정의된 상수를 또 다른 case에서 사용할 수 있습니다. 이런 기법을 값-바인딩(value bindings)이라 부릅니다.
let anotherPoint = (2, 0)
switch anotherPoint {
case (let x, 0):
print("on the x-axis with an x value of \(x)")
case (0, let y):
print("on the y-axis with a y value of \(y)")
case let (x, y):
print("somewhere else at (\(x), \(y))")
}
// Prints "on the x-axis with an x value of 2"Where 문
case에 where로 추가 조건을 사용할 수 있습니다.
let yetAnotherPoint = (1, -1)
switch yetAnotherPoint {
case let (x, y) where x == y:
print("(\(x), \(y)) is on the line x == y")
case let (x, y) where x == -y:
print("(\(x), \(y)) is on the line x == -y")
case let (x, y):
print("(\(x), \(y)) is just some arbitrary point")
}
// Prints "(1, -1) is on the line x == -y"혼합 케이스 (Compound Cases)
case에 콤마(,)로 구분해 여러 조건을 혼합해 사용할 수 있습니다.
let someCharacter: Character = "e"
switch someCharacter {
case "a", "e", "i", "o", "u":
print("\(someCharacter) is a vowel")
case "b", "c", "d", "f", "g", "h", "j", "k", "l", "m",
"n", "p", "q", "r", "s", "t", "v", "w", "x", "y", "z":
print("\(someCharacter) is a consonant")
default:
print("\(someCharacter) is not a vowel or a consonant")
}
// Prints "e is a vowel"혼합 케이스에서도 값-바인딩을 사용할 수 있습니다.
let stillAnotherPoint = (9, 0)
switch stillAnotherPoint {
case (let distance, 0), (0, let distance):
print("On an axis, \(distance) from the origin")
default:
print("Not on an axis")
}
// Prints "On an axis, 9 from the origin"흐름 제어
흐름 제어 구문은 코드의 진행을 계속 할지 말지를 결정하거나, 실행되는 코드의 흐름을 바꾸기 위해 사용합니다. Swift에서는 다음 다섯 가지의 제어 전송 구문을 제공합니다.
- continue
- break
- fallthrough
- return
- throw
(return과 throw에 대한 설명은 없음)
continue
continue문은 현재 loop를 중지하고 다음 loop를 수행하도록 합니다.
let puzzleInput = "great minds think alike"
var puzzleOutput = ""
let charactersToRemove: [Character] = ["a", "e", "i", "o", "u", " "]
for character in puzzleInput {
if charactersToRemove.contains(character) {
continue
} else {
puzzleOutput.append(character)
}
}
print(puzzleOutput)
// Prints "grtmndsthnklk"Break
break문은 전체 제어문의 실행을 즉각 중지 시킵니다. break문은 loop나 switch문에서 사용할 수 있습니다.
let numberSymbol: Character = "三" // 중국어로 3을 의미하는 문자입니다.
var possibleIntegerValue: Int?
switch numberSymbol {
case "1", "١", "一", "๑":
possibleIntegerValue = 1
case "2", "٢", "二", "๒":
possibleIntegerValue = 2
case "3", "٣", "三", "๓":
possibleIntegerValue = 3
case "4", "٤", "四", "๔":
possibleIntegerValue = 4
default:
break
}
if let integerValue = possibleIntegerValue {
print("The integer value of \(numberSymbol) is \(integerValue).")
} else {
print("An integer value could not be found for \(numberSymbol).")
}fallthrough
fallthrough 키워드는 이후의 case에 대해서도 실행하게 합니다. 앞에서 언급했던 것 처럼 Swift에서는 한번 특정 case를 타면 바로 그 switch 문은 종료됩니다. 마치 case 안에 break를 자동으로 넣은 것과 같은 기능을 하는 것이죠. 하지만 이 fallthrough 를 사용하면 이 자동으로 break가 사용되는 것을 막는 효과를 가져옵니다. 다만,만,
let integerToDescribe = 5
var description = "The number \(integerToDescribe) is"
switch integerToDescribe {
case 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19:
description += " a prime number, and also"
fallthrough
default:
description += " an integer."
}
print(description)
// Prints "The number 5 is a prime number, and also an integer."fallthrough 는 case 조건을 확인하지 않고 그냥 다음 case를 실행하게 만듭니다. 그래서 위 내용을 아래처럼 살짝 바꾸면 CASE 1으로 코드가 진행되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
let integerToDescribe = 5
var description = "The number \(integerToDescribe) is"
switch integerToDescribe {
case 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19:
description += " a prime number, and also"
fallthrough
case 1:
print("갑자기 이걸 먼저 출력하겠지?")
default:
description += " an integer."
}
print(description)
// Prints "갑자기 이걸 먼저 출력하겠지?"
"The number 5 is a prime number, and also"레이블 구문 (Labeled Statements)
아래와 같은 형태로 label 이름과 while 조건을 넣어 특정 구문을 실행하는 구문으로 사용할 수 있습니다.
label name: while condition {
statements
}위에서 진행했던 주사위 게임의 규칙중, 게임이 끝나는 조건을 25번 칸에 정확히 멈춘다.로 변경하고 아래와 같이 코드를 변경하였습니다.
gameLoop: while square != finalSquare {
diceRoll += 1
if diceRoll == 7 { diceRoll = 1 }
switch square + diceRoll {
case finalSquare:
// diceRoll will move us to the final square, so the game is over
break gameLoop // switch 내부이기 때문에, switch와 while 중에 어떤것을 멈출지 모르기 때문에 라벨을 사용하였다.
case let newSquare where newSquare > finalSquare:
// diceRoll will move us beyond the final square, so roll again
continue gameLoop
default:
// this is a valid move, so find out its effect
square += diceRoll
square += board[square]
}
}
print("Game over!")추가로 continue gameLoop에서 라벨을 사용하지 않아도 됩니다. 왜냐면 switch에는 따로 continue를 사용하지 않기 때문입니다.
Early Exit
guard문을 이용해 특정 조건을 만족하지 않으면 이 후 코드를 실행하지 않도록 방어코드를 작성할 수 있습니다.
func greet(person: [String: String]) {
guard let name = person["name"] else {
return
}
print("Hello \(name)!")
guard let location = person["location"] else {
print("I hope the weather is nice near you.")
return
}
print("I hope the weather is nice in \(location).")
}
greet(person: ["name": "John"])
// Prints "Hello John!"
// Prints "I hope the weather is nice near you."
greet(person: ["name": "Jane", "location": "Cupertino"])
// Prints "Hello Jane!"
// Prints "I hope the weather is nice in Cupertino."이용가능한 API 버전 확인 (Checking API Availability)
Swift에서는 기본으로 특정 플랫폼 (iOS, macOS, tvOS, watchOS)과 특정 버전을 확인하는 구문을 제공해 줍니다. 이 구문을 활용해 특정 플랫폼과 버전을 사용하는 기기에 대한 처리를 따로 할 수 있습니다. 구문의 기본 형태는 다음과 같습니다.
if #available(platform name version, ..., *) {
statements to execute if the APIs are available
} else {
fallback statements to execute if the APIs are unavailable
}실제 사용 (예)
if #available(iOS 10, macOS 10.12, *) {
// Use iOS 10 APIs on iOS, and use macOS 10.12 APIs on macOS
} else {
// Fall back to earlier iOS and macOS APIs
}오늘은 스위프트 공식문서에서 Control Flow를 읽어보았습니다~
다음에는 Functions를 읽어보도록 하겠습니다!
감사합니다🙇🏻♀️
