문제 설명📖
최근 코딩 테스트에서 자주 마주할 수 있는 구현 카테고리 중 Simulation에 해당하는 문제로 매 시뮬레이션 마다 수행해야 하는 작업이 많아, 코드를 작성하기 전 어떤 기능(메소드)을 어떤 순서로 구현해야하는지를 먼저 정리해보는 게 매우 중요하다.
풀이 방법✏️
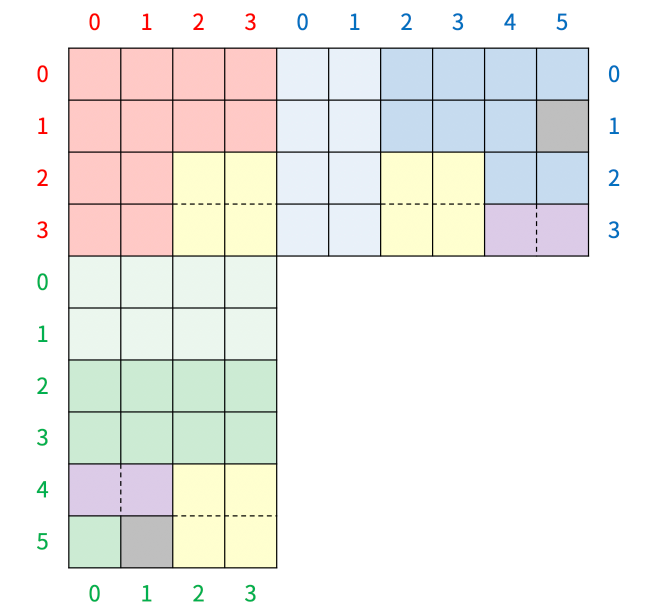
위 이미지에서 볼 수 있는 격자 판(10x10)에서 수행되는 시뮬레이션은 파란색 보드에서의 시뮬레이션과 초록색 보드에서의 시뮬레이션으로 구분된다. 두 보드에서 수행하는 시뮬레이션은 크게 4가지 작업으로 구성된다.
1. 빨간색 보드에서 시작하여 경계에 도달하거나 다른 블록을 만날 때 까지 파란색, 초록색 보드로 블록을 이동
1-1. 파란색 영역은 오른쪽으로 초록색 영역은 밑으로 한 칸 씩 이동해가며 블록이 이동할 수 있는지 확인
1-2. 두 칸짜리 블록이라면 두 칸 모두 다음 지점으로 이동이 가능한 지 먼저 확인 후 가능하다면 이동2. 파란색, 초록색 보드 내 꽉찬 열 또는 행이 있는 지 확인
3. 2번 과정에서 찾은 꽉 찬 라인(행 or 열)을 제거 후 제거한 라인 이전 라인들을 땡겨 줌
4. 특별한 작업을 수행해야 하는 라인에 블록이 존재하는지 확인 후 블록이 존재하는 라인의 개수 만큼 가장 마지막 라인 제거 후 당겨주는 작업 반복
4-1. 특별한 작업을 수행해야 하는 라인은 10x10 격자 기준 4, 5번째 행 또는 열이다.
4-2. 특정 라인을 제거하고 당겨주는 작업은 3번 과정과 동일 => 라인을 제거하고 당겨주는 작업을 메소드화 하여 3번, 4번 과정 모두에서 사용할 수 있도록 한다.소스 코드(feat. 알찬 주석)⌨️
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class BJ_20061 {
static int N, point;
static int[][] grid;
static Block[] blocks;
static class Block{
int type, x, y;
public Block(int type, int x, int y) {
this.type = type;
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
static class Point {
int x, y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
static int[] dx = {0, 1};
static int[] dy = {1, 0};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
point = 0;
grid = new int[10][10];
blocks = new Block[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int type = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int x = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
int y = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
blocks[i] = new Block(type, x, y);
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
Block block = blocks[i];
simulation(block, "blue"); // 파란색 영역애 블록을 둠
simulation(block, "green"); // 초록색 영역애 블록을 둠
}
System.out.println(point);
System.out.println(findBlockCnt());
}
private static void simulation(Block block, String boardColor){
moveBlock(block, boardColor); // 블록을 알맞은 위치로 이동
List<Integer> fullLines = findFullLines(boardColor); // 꽉 찬 행 또는 열이 있는지 확인
point += fullLines.size();
boom(fullLines, boardColor); // 꽉찬 행 또는 열이 있다면 터뜨리고 위에 줄을 당겨줌
special(boardColor); // 특별한 행 또는 열에 블록이 있는지 확인 후 있다면 문제에서 주어진 작업 처리
}
private static void moveBlock(Block block, String boardColor) {
int x = block.x;
int y = block.y;
int type = block.type;
List<Point> points = new ArrayList<>(); // 블록이 존재하는 격자의 위치들을 저장
points.add(new Point(x, y));
if (type == 2) { // 2번 블록일 경우
points.add(new Point(x, y + 1));
}
if (type == 3) { // 3번 블록일 경우
points.add(new Point(x + 1, y));
}
// 이동할 보드의 색깔에 따른 방향 설정
int dir = 0;
if (boardColor.equals("green")) {
dir = 1;
}
while (true) { // 블록 이동
boolean canMove = true;
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) { // 블록이 이동 가능한지 검사
Point point = points.get(i);
int nx = point.x + dx[dir];
int ny = point.y + dy[dir];
if (!inRange(nx, ny)) { // 격자를 벗어나는 경우
canMove = false;
break;
}
if (grid[nx][ny] == 1) { // 이동 중 기존에 있던 블록과 맞닿는 경우
canMove = false;
break;
}
}
if (!canMove) { // 이동할 수 없는 경우
break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) { // 블록이 이동 가능한 경우 블록 이동
Point point = points.get(i);
point.x += dx[dir];
point.y += dy[dir];
}
}
for (Point point : points) { // 격자에 블록의 위치를 1로 표시
grid[point.x][point.y] = 1;
}
}
private static boolean inRange(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && x < 10 && y >= 0 && y < 10;
}
private static List<Integer> findFullLines(String boardColor) { // 보드에 색깔에 따라 꽉찬 행 또는 열을 찾아줌
List<Integer> fullLines = new ArrayList<>();
// 파란색 보드의 꽉 찬 열 반환
if (boardColor.equals("blue")) {
for (int col = 6; col <= 9; col++) {
boolean isFull = true;
for (int row = 0; row <= 3; row++) {
if (grid[row][col] != 1) { // 블록이 없다면
isFull = false;
}
}
if (isFull) { // 꽉 차 있는 열이라면
fullLines.add(col);
}
}
}
// 초록색 보드의 꽉 찬 행 반환
if (boardColor.equals("green")) {
for (int row = 6; row <= 9; row++) {
boolean isFull = true;
for (int col = 0; col <= 3; col++) {
if (grid[row][col] != 1) { // 블록이 없다면
isFull = false;
}
}
if (isFull) { // 꽉 차 있는 행이라면
fullLines.add(row);
}
}
}
return fullLines;
}
private static void boom(List<Integer> lines, String boardColor) { // 리스트 값들에 해당하는 열 또는 행을 제거 후 그 이전 행 또는 열들을 당겨줌
for (int i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++) {
if (boardColor.equals("blue")) { // 파란색 보드일 경우
// 1. 라인 제거
int col = lines.get(i);
for (int row = 0; row <= 3; row++) {
grid[row][col] = 0;
}
// 2. 이전 라인들을 땡겨줌
for (int j = col; j >= 4; j--) {
for (int row = 0; row <= 3; row++) {
grid[row][j] = grid[row][j - 1];
}
}
}
if (boardColor.equals("green")) { // 초록색 보드일 경우
// 1. 라인 제거
int row = lines.get(i);
for (int col = 0; col <= 3; col++) {
grid[row][col] = 0;
}
// 2. 이전 라인들을 땡겨줌
for (int j = row; j >= 4; j--) {
for (int col = 0; col <= 3; col++) {
grid[j][col] = grid[j-1][col];
}
}
}
}
}
private static void special(String boardColor) { // 특별한 칸에 존재하는 블록 처리
// 1. 블록이 있는 특별한 행 또는 열의 개수를 찾음
int specialCnt = findSpecialCnt(boardColor);
// 2. 찾은 개수 만큼 제거
List<Integer> boomLines = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < specialCnt; i++) {
boomLines.add(9);
}
boom(boomLines, boardColor);
}
private static int findSpecialCnt(String boardColor) { // 블록이 있는 특별한 행 또는 열의 개수를 찾아줌
int specialCnt = 0; // 특별한 열 또는 행의 수
for (int i = 4; i <= 5; i++) { // 4~5번째 행 또는 열이 특별한 라인이다.
boolean isBlock = false;
if (boardColor.equals("blue")) {
for (int j = 0; j <= 3; j++) {
if (grid[j][i] == 1) { // 특별한 칸에 블록이 존재한다면
isBlock = true;
}
}
if (isBlock) {
specialCnt++;
}
}
if (boardColor.equals("green")) {
for (int j = 0; j <= 3; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) { // 특별한 칸에 블록이 존재한다면
isBlock = true;
}
}
if (isBlock) {
specialCnt++;
}
}
}
return specialCnt;
}
private static int findBlockCnt() { // 최종 블록 개수 return
int blueCnt = 0;
int greenCnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= 3; i++) {
for (int j = 6; j <= 9; j++) {
blueCnt += grid[i][j];
greenCnt += grid[j][i];
}
}
return blueCnt + greenCnt;
}
}
