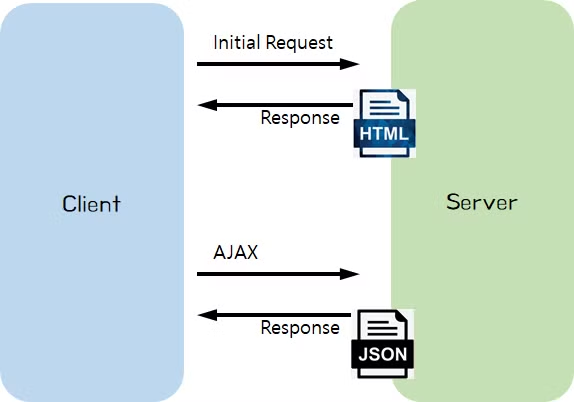
데이터를 Client에 반환하는 방법
- 최근 경향은 서버가 직접 뷰를 구형하여 반환하기보단 특정 정보만 반환하는것을 선호. (느슨한결합을 지향)
- 그 중
JSON형태로 반환하는것을 선호.- JSON 은 JS형태로도 읽어지기에 악성 공격에 주의해야함.
- JSON형태는 JAVA가 지원하지않음 따로 방법이 필요함
- JSON형태로 묶어서 String 전달 (text 형태)
// [Response header]
// Content-Type: text/html
// [Response body]
// {"name":"Robbie","age":95}
@GetMapping("/response/json/string")
@ResponseBody
public String helloStringJson() {
return "{\"name\":\"Robbie\",\"age\":95}";
}- Java 객체로 묶어서 전달 (Json 형태)
// [Response header]
// Content-Type: application/json
// [Response body]
// {"name":"Robbie","age":95}
@GetMapping("/response/json/class")
@ResponseBody
public Star helloClassJson() {
return new Star("Robbie", 95);
}-
Java Class 를 return 할 경우 json 형태로 Spring이 자동변환 해준다.
-
@RestController = @Controller + @ResponseBody
- 해당 클래스의 모든 메서드에
@ResponseBody어노테이션 효과를 부여. - View(html)를 반환해야하는가 Json데이터를 반환해야하는가에 차이.
- 해당 클래스의 모든 메서드에
Jackson
- JSON 데이터 구조를 처리해주는 라이브러리, Spring 3.0 이상부턴 자동으로 제공해주고 있음.
- Object를 JSON으로 JSON을 Object로 변환
- 직접 JSON 데이터를 처리해야할 때는 Jackson 라이브러리의
ObjectMapper를 사용할 수 있음.
- Object To JSON
@Test
@DisplayName("Object To JSON : get Method 필요")
void test1() throws JsonProcessingException {
Star star = new Star("Robbie", 95);
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(); // Jackson 라이브러리의 ObjectMapper
String json = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(star);
System.out.println("json = " + json);
}
=====================================================
json = {"name":"Robbie","age":95}- JAVA 는 JSON을 인식하지 못하기 때문에 String 타입으로 변환해줌.
- 직렬화를 통해 String으로 변환시키기에
Getter가 필요하다.
- JSON To Object
@Test
@DisplayName("JSON To Object : 기본 생성자 & (get OR set) Method 필요")
void test2() throws JsonProcessingException {
String json = "{\"name\":\"Robbie\",\"age\":95}"; // JSON 타입의 String
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(); // Jackson 라이브러리의 ObjectMapper
Star star = objectMapper.readValue(json, Star.class);
System.out.println("star.getName() = " + star.getName());
}
===============================================================
star.getName() = Robbie
star.getAge() = 95- JSON을 객체화 시키는 메소드.
- 객체로 변환시키기 위해서 해당 객체의 Class 와 기본생성자 혹은 get 혹은 set 메서드가 필요 (String을 들고 객체화시키기 때문에)
- 필드명도 제대로 맞춰줘야함. String 가지고 객체만들기와 동일.
- 역직렬화 구조.
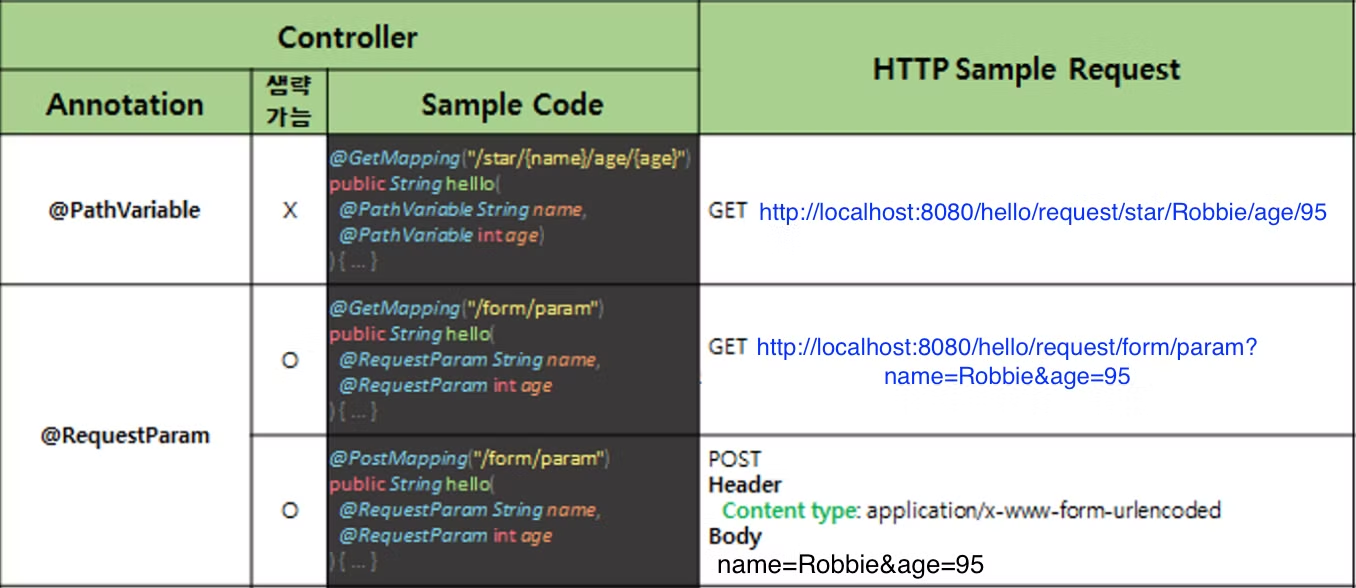
Path Variable과 Request Param
-
클라이언트가 서버로 요청을 보낼때 데이터를 함께보낼수 있음.
-
서버에서는 데이터를 받아 사용할때 보내는방식이 여러가지기에 모든방식에 대한 처리가 필요.
-
Path Variable 방식
- 서버에 보내려는 데이터를 URL 경로에 추가
http://localhost:8080/hello/request/star/Robbie/age/95
- 서버에 보내려는 데이터를 URL 경로에 추가
// [Request sample]
// GET http://localhost:8080/hello/request/star/Robbie/age/95
@GetMapping("/star/{name}/age/{age}")
@ResponseBody
public String helloRequestPath(@PathVariable String name, @PathVariable int age)
{
return String.format("Hello, @PathVariable.<br> name = %s, age = %d", name, age);
}-
데이터를 받기 위해서는
/star/{name}/age/{age}이처럼 URL 경로에서 데이터를 받고자 하는 위치의 경로에 {data} 중괄호를 사용 -
(@PathVariable String name, @PathVariable int age)- 메소드 파라미터로 선언한 변수Name 과 Type 을 선언하여 경로의 데이터를 받을 수 있음.
-
Request Param 방식
- 서버에 보내려는 데이터를
?와&를 사용하여 추가.
http://localhost:8080/hello/request/form/param?name=Robbie&age=95
- 서버에 보내려는 데이터를
// [Request sample]
// GET http://localhost:8080/hello/request/form/param?name=Robbie&age=95
@GetMapping("/form/param")
@ResponseBody
public String helloGetRequestParam(@RequestParam String name, @RequestParam int age) {
return String.format("Hello, @RequestParam.<br> name = %s, age = %d", name, age);
}-
데이터를 받는
?name=Robbie&age=95부분에서 key부분에 설정한 네이밍 부분과 매칭하여 데이터를 받아옴. -
(@RequestParam String name, @RequestParam int age)
위에 패스밸류 방식과 동일. -
form 태그 POST
POST http://localhost:8080/hello/request/form/param
// [Request sample]
// POST http://localhost:8080/hello/request/form/param
// Header
// Content type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
// Body
// name=Robbie&age=95
@PostMapping("/form/param")
@ResponseBody
public String helloPostRequestParam(@RequestParam String name, @RequestParam int age) {
return String.format("Hello, @RequestParam.<br> name = %s, age = %d", name, age);
}- POST 방식의 전송이기 때문에 HTTP Body 부분에
name=Robbie&age=95형태로 담겨져서 전달.
// [Request sample]
// GET http://localhost:8080/hello/request/form/param?name=Robbie&age=95
@GetMapping("/form/param")
@ResponseBody
public String helloGetRequestParam(@RequestParam(required = false) String name, int age) {
return String.format("Hello, @RequestParam.<br> name = %s, age = %d", name, age);
}- @RequestParam은 생략이 가능
@RequestParam(required = false)required 옵션을 설정하면 Client로 부터 값이 포함되어있지 않아도 오류가 발생하지 않음@PathVariable(required = false)도 가능하다.- 단 해당 변수는
NULL값으로 지정됌!
HTTP 데이터를 객체로 처리하는 방법
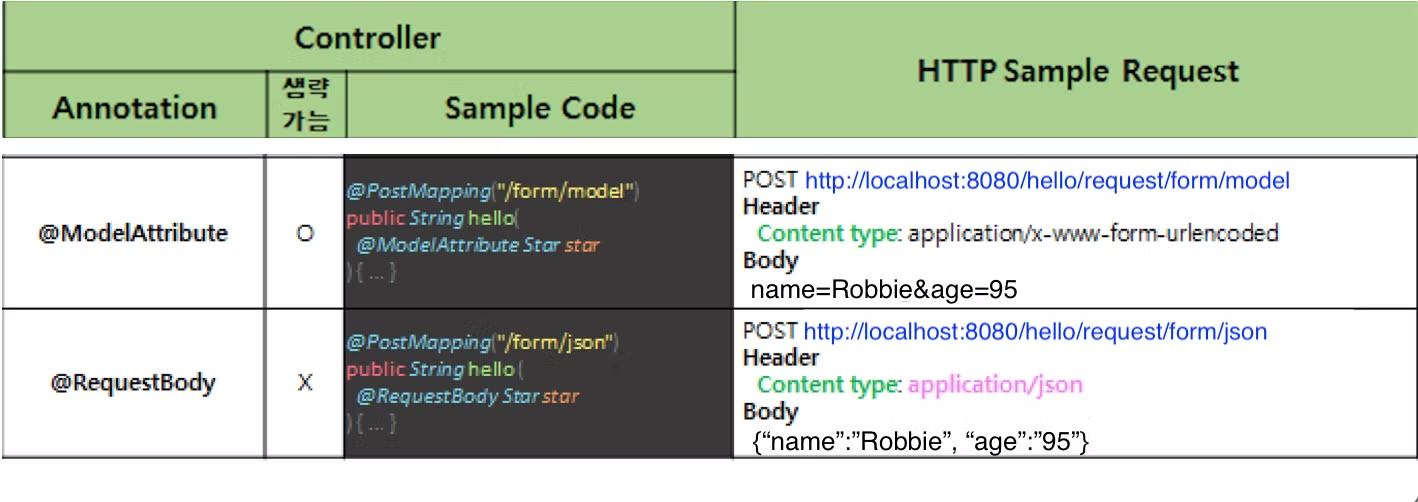
@ModelAttribute
1.POST 방식
// [Request sample]
// POST http://localhost:8080/hello/request/form/model
// Header
// Content type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
// Body
// name=Robbie&age=95
@PostMapping("/form/model")
@ResponseBody
public String helloRequestBodyForm(@ModelAttribute Star star) {
return String.format("Hello, @ModelAttribute.<br> (name = %s, age = %d) ", star.name, star.age);
}- POST형식으로 받은 데이터의 Body 데이터를 받아올 객체로 선언해서 객체화.
- 이미 선언된 Class의 Object로 받기 때문에 확장성이 떨어짐.
- Setter 혹은 생성자가 필수임. 객체내의 정보를 주입해야하기 때문에.
- GET 방식
// [Request sample]
// GET http://localhost:8080/hello/request/form/param/model?name=Robbie&age=95
@GetMapping("/form/param/model")
@ResponseBody
public String helloRequestParam(@ModelAttribute Star star) {
return String.format("Hello, @ModelAttribute.<br> (name = %s, age = %d) ", star.name, star.age);
}-
@RequestParam 의 경우 받는 데이터수가 적다면 문제가 없지만 여러개가 있을시 하나씩 받아오기가 힘듬.
-
@ModelAttribute 애너테이션을 사용하면 Java의 객체로 데이터를 받아올 수 있음.
-
생략이 가능하다. 그런데 @ModelAttribute뿐만 아니라 @RequestParam도 생략이 가능그렇다면 Spring은 이를 어떻게 구분??
- 파라미터(매개변수)가 SimpleValueType이라면 @RequestParam으로 간주하고 아니라면 @ModelAttribute가 생략되어있다 판단
- SimpleValueType은 원시타입(int), Wrapper타입(Integer), Date등의 타입을 의미 (Object 외 타입)
-
@RequestBody
-
HTTP Body 부분에 JSON 형태로 서버에 전달할때 받는 어노테이션
// [Request sample]
// POST http://localhost:8080/hello/request/form/json
// Header
// Content type: application/json
// Body
// {"name":"Robbie","age":"95"}
@PostMapping("/form/json")
@ResponseBody
public String helloPostRequestJson(@RequestBody Star star) {
return String.format("Hello, @RequestBody.<br> (name = %s, age = %d) ", star.name, star.age);
}- 데이터를 객체로 받아올때는 Set or Get 메서도 또는 오버로딩 생성자가 필요.
- 위에 요소가 없을 경우 객체의 필드에 담아줄수가 없음.
