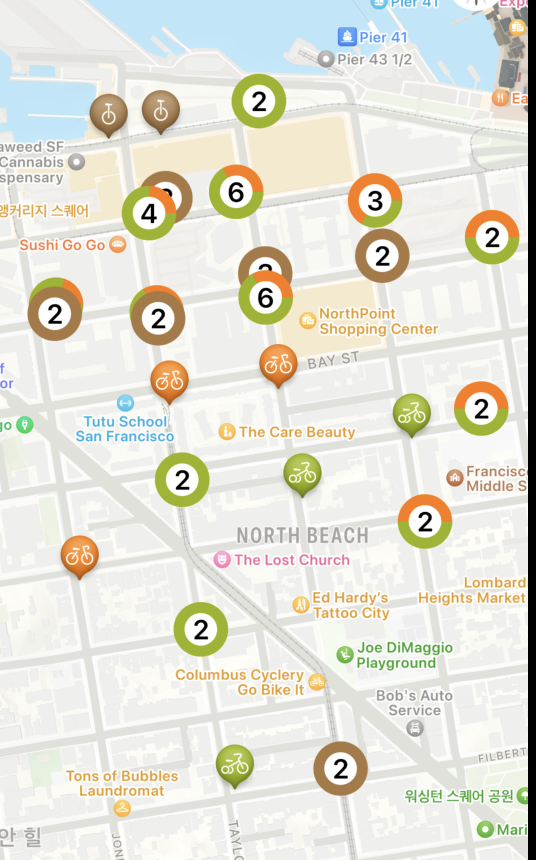
클러스터 어노테이션뷰 파해치기
아래와 같은 링크를 참고해 하나씩 뜯어 파해쳐 보기로 하려고 합니다.
Let’s Go~
Decluttering a Map with MapKit Annotation Clustering | Apple Developer Documentation
MKAnnotation 설정
import MapKit
class Cycle: NSObject, Decodable, MKAnnotation {
//MARK: 자전거의 타입을 분리한다.
enum CycleType: Int, Decodable {
case unicycle // 외발자전거?
case bicycle // 자전거
case tricycle // 세발 자전거 ..?
}
//MARK: 기본적으론 타입을 외발자전거로 한다.
var type: CycleType = .unicycle
private var latitude: CLLocationDegrees = 0
private var longitude: CLLocationDegrees = 0
// This property must be key-value observable, which the `@objc dynamic` attributes provide.
// 이 속성은 키-값 관찰 가능이어야 하며, `@objc dynamic` 속성이 제공합니다.
// 라고 되어있는데 그것은 KVC 파트 + KVO 파트 (노션에 있답니다.) 를 보고 오면 이해가 될것 같다.
@objc dynamic var coordinate: CLLocationCoordinate2D {
// For most uses, `coordinate` can be a standard property declaration without the customized getter and setter shown here.
// The custom getter and setter are needed in this case because of how it loads data from the `Decodable` protocol.
// 위에 영어에 따르면 갑자기 Decodable 이야기가 나와 당황스러웠는데 해석을 해보자.
// Decodable: `외부의 데이터` 를 보통은 JSON 이겠지만 암튼 받아와서 데이터 모델 인스턴스로 변환할수 있는 프로토콜을 말하는건데
// "커스텀 게터 세터가 필요할 지도? 디코더블 통해 데이터 로드할때. "
// 뭔말이냐? CLLocationCoordinate2D 는 lat long을 동시에 원하지만
// 때에따라 2개를 동시에 줄수 없을것 같다면 커스텀 세터를 통해 초기화 하라는 말인거다.
get {
return CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: latitude, longitude: longitude)
}
set {
latitude = newValue.latitude
longitude = newValue.longitude
}
}
}
/// ViewController 에서...
// MARK: 현재 해당 앱에서는 예시로 실제 디코더블을 통해 이를 설명하고 있다.
private func loadDataForMapRegionAndBikes() {
/// 앱의 메인 번들에서 Data.plist 파일의 URL을 얻는다.
guard let plistURL = Bundle.main.url(forResource: "Data", withExtension: "plist") else {
fatalError("Failed to resolve URL for `Data.plist` in bundle.")
}
do {
// url -> Data 시도
let plistData = try Data(contentsOf: plistURL)
// propertyListDecoder:
// plist 데이터를 디코드 할수 있는 디코더객체를 생성한다.
let decoder = PropertyListDecoder()
// plist 디코더를 통해 MapData로 변환 가능한지 시도한다.
let decodedData = try decoder.decode(MapData.self, from: plistData)
// 맵뷰의 범위를 설정
mapView.region = decodedData.region
// 맵뷰에 어노테이션들을 설정
mapView.addAnnotations(decodedData.cycles)
} catch {
fatalError("Failed to load provided data, error: \(error.localizedDescription)")
}
}
MKMarkerAnnotation 설정
class UnicycleAnnotationView: MKMarkerAnnotationView {
// 재사용 아이디 설정
static let ReuseID = "unicycleAnnotation"
/// - Tag: ClusterIdentifier
override init(annotation: MKAnnotation?, reuseIdentifier: String?) {
super.init(annotation: annotation, reuseIdentifier: reuseIdentifier)
// MARK: 클러스터링 아이덴티 파이어를 설정합니다.
clusteringIdentifier = "unicycle"
}
override func prepareForDisplay() {
super.prepareForDisplay()
// MARK: displayPriority: MKFeatureDisplayPriority
displayPriority = .defaultLow
/*
1. required : 무조건(가능한) 항상 표시되게한다.
2. defaultHigh : 높은 우선 순위
3. defaultLow : 가장 낮은 우선 순위
// -> 우선순위가 높을수록 지도상의 공간이 부족할때에도 숨지 않는다.
*/
// 마커의 색상을 무엇으로 할건가
markerTintColor = UIColor.unicycleColor
// 이미지는 어떤것을 할건가 아래와 같이 #imageLiteral() 을 하게 되면 이미지가 코드에 이미지가 보인다!
glyphImage = #imageLiteral(resourceName: "unicycle")
}
required init?(coder aDecoder: NSCoder) {
fatalError("init(coder:) has not been implemented")
}
}대망의 ClusterAnnotationView
위에 것들만 봐도 사실 이미 어질 어질 하였다.
나는 저런 스타일로 하지 않았었다…!
하지만 위에있는 스타일 너무 탐나자나
아무튼 코드가 너무 길어 부분 부분 잘라서 설명 하겠다.
class ClusterAnnotationView: MKAnnotationView {
override init(annotation: MKAnnotation?, reuseIdentifier: String?) {
super.init(annotation: annotation, reuseIdentifier: reuseIdentifier)
// MARK: collisionMode:
// MKAnnotationView 들이 겹침을 감지 하고 처리하는 프로퍼티이다.
/*
collisionMode 종류
1. .circle : 감지 영역이 원형이다. -> 어노테이션 중앙 기준 원형인데 동그란 어노테이션엔 유용
2. .rectangle : 감지 영역이 직사각형이다. -> 이건 반대로 사각형일때 유용
*/
collisionMode = .circle
centerOffset = CGPoint(x: 0, y: -10) // Offset center point to animate better with marker annotations
}override func prepareForDisplay() {
super.prepareForDisplay()
// 만약 어노테이션이 MKClusterAnnotation 라면
if let cluster = annotation as? MKClusterAnnotation {
// 토탈 자전거수는 = cluster.memberAnnotations.count
// ??? 뭐일까 이친구는 했지만
let totalBikes = cluster.memberAnnotations.countcluster.memberAnnotations.count 이건 뭘까 하였지만 사진을 보면 살짝의 감이
올것 같다.
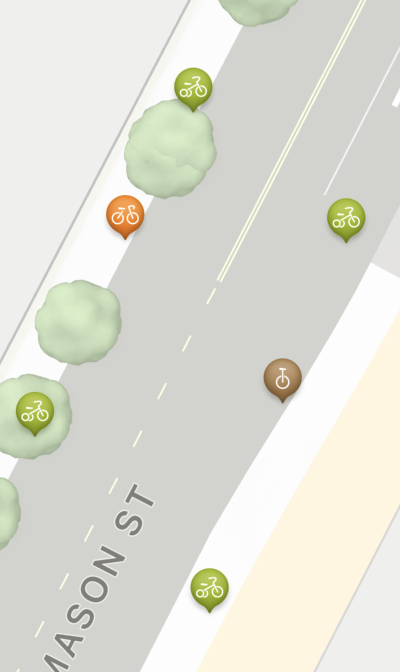
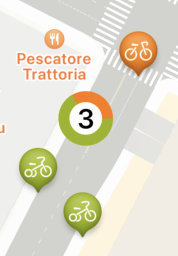
다시 이어가 보면,
override func prepareForDisplay() {
super.prepareForDisplay()
// 만약 어노테이션이 MKClusterAnnotation 라면
if let cluster = annotation as? MKClusterAnnotation {
// 클러스터링된 친구들은 서로를 참조할수 있다.
// 친구들이 가까워지면 하나의 클러스터로 표시할수 있는데 이때 몇명인가요 하는것.
let totalBikes = cluster.memberAnnotations.count
// 만약 외발자전거가 0보다 많으면
if count(cycleType: .unicycle) > 0 {
// 이미지에는 외발자전거 사진을 넣을거야.
image = drawUnicycleCount(count: totalBikes)
} else {
// 없다면 세발자전거? 갯수를 확인할께
let tricycleCount = count(cycleType: .tricycle)
// 이미지에 세발자전거 넣을꺼야
image = drawRatioBicycleToTricycle(tricycleCount, to: totalBikes)
}
// 만약 외발자전거 갯수가 0보다 크다면
if count(cycleType: .unicycle) > 0 {
// 우선순위를 가장 낮게
displayPriority = .defaultLow
} else {
// 없다면 우선순위를 높게
displayPriority = .defaultHigh
}
}
}
private func count(cycleType type: Cycle.CycleType) -> Int {
// 클러스터 어노테이션이 있나요?
guard let cluster = annotation as? MKClusterAnnotation else {
return 0
}
// 그중에 해당하는 친구 있나요?.count
return cluster.memberAnnotations.filter { member -> Bool in
guard let bike = member as? Cycle else {
fatalError("Found unexpected annotation type")
}
return bike.type == type
}.count
}나는 이 코드에서 상당히 애를 먹었는데 특히
조건식에서 머리가 너무 아팠다
가정을 해보고 이해해 보자.
어노테이션이 5개가 있다고 하자
어노테이션은 ( 외발, 외발, 외발, 세발, 세발 ) 이렇게 있었다고 할때외발자전거가 1개 이상인지 확인할때 True
외발자전거 수 (2개)를 나타내는 이미지가 설정될것이다.
세발자전거 수는 세지도 않는다.이것도 사진을 보며 이해해 보자
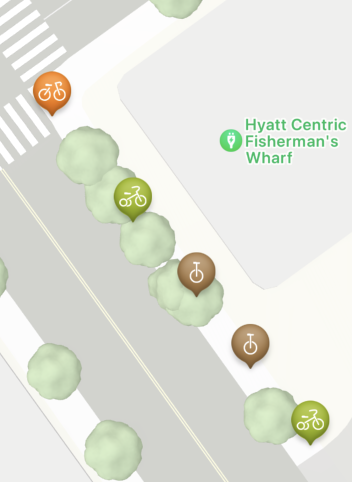
위 사진과 같이 일자로
아주 좋은 예시를 가져왔다.
외발 자전거가 모이면 빨간색으로
나오게 수정하였는데
아무튼 여기서 집중
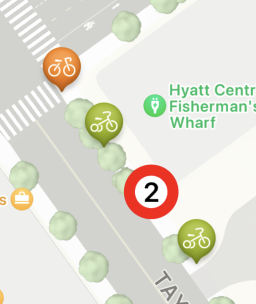
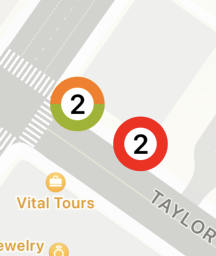
흠… 별일 없네? 라고 생각할수 있겠지만
총 5개가 아니라 4개가 되었다는것을
생각해보자 즉 빨간 친구는 1놈을 무시한다.
private func drawRatioBicycleToTricycle(_ tricycleCount: Int, to totalBikes: Int) -> UIImage {
return drawRatio(tricycleCount, to: totalBikes, fractionColor: UIColor.tricycleColor, wholeColor: UIColor.bicycleColor)
}
private func drawUnicycleCount(count: Int) -> UIImage {
return drawRatio(0, to: count, fractionColor: nil, wholeColor: UIColor.red)
}
private func drawRatio(_ fraction: Int, to whole: Int, fractionColor: UIColor?, wholeColor: UIColor?) -> UIImage {
// MARK: UIGraphicsImageRenderer -> 이미지 리사이징 편을 보고와주세요
let renderer = UIGraphicsImageRenderer(size: CGSize(width: 40, height: 40))
return renderer.image { _ in
// Fill full circle with wholeColor
// 그래픽스 컨텍스트 채우기 색 설정이다.
wholeColor?.setFill() // 이것을 만약 여기가 아니라 리턴문 위에서 하게 된다면 엄청난 경고문을 받게 될것....
// 종류는 2가지 정도 setFill 이냐 setStroke 이냐
// 채울것인가 선색상을 설정할거냐 이다.
// 코어그래픽스 편을 만들어야겠다....
// 핵심은 원을 만드는 거다.
UIBezierPath(ovalIn: CGRect(x: 0, y: 0, width: 40, height: 40)).fill()
// Fill pie with fractionColor
fractionColor?.setFill()
let piePath = UIBezierPath() // 파이 경로 라는 아이의 경로를 만듬
piePath.addArc(
withCenter: CGPoint(x: 20, y: 20), // 원의 중심점을 x20 y20 즉 저위에 원만든거 중심임
radius: 20, // 반지름을 20으로 함
startAngle: 0, // 시작 각도를 0 (우측 가로줄부터) 끝각도는 계산됨
endAngle: (
CGFloat //전체 원의 원주율의 2를 곱하고 외발자전거 갯수만큼 곱한것을 전체 자전거 갯수만큼 나눔
.pi * 2.0 * CGFloat(fraction)
) / CGFloat(whole),
clockwise: true // 시계방향으로 그릴거임
)
piePath.addLine(to: CGPoint(x: 20, y: 20)) // 경로를 시작점으로 다시 연결.
piePath.close() // 경로를 끝내고 모양 완성
piePath.fill() // 채우기
// Fill inner circle with white color
UIColor.white.setFill()
UIBezierPath(ovalIn: CGRect(x: 8, y: 8, width: 24, height: 24)).fill()
// Finally draw count text vertically and horizontally centered
let attributes = [ NSAttributedString.Key.foregroundColor: UIColor.black,
NSAttributedString.Key.font: UIFont.boldSystemFont(ofSize: 20)]
let text = "\(whole)"
let size = text.size(withAttributes: attributes)
let rect = CGRect(x: 20 - size.width / 2, y: 20 - size.height / 2, width: size.width, height: size.height)
text.draw(in: rect, withAttributes: attributes)
}