1. TIL
escape 문법 : String data = "{\"id\":\"dev\"}";
json에서 문자로 나타낼 떄 "" 를 사용하는데 백슬래쉬 뒤에 오는 문자를 문자열로 인식하게함
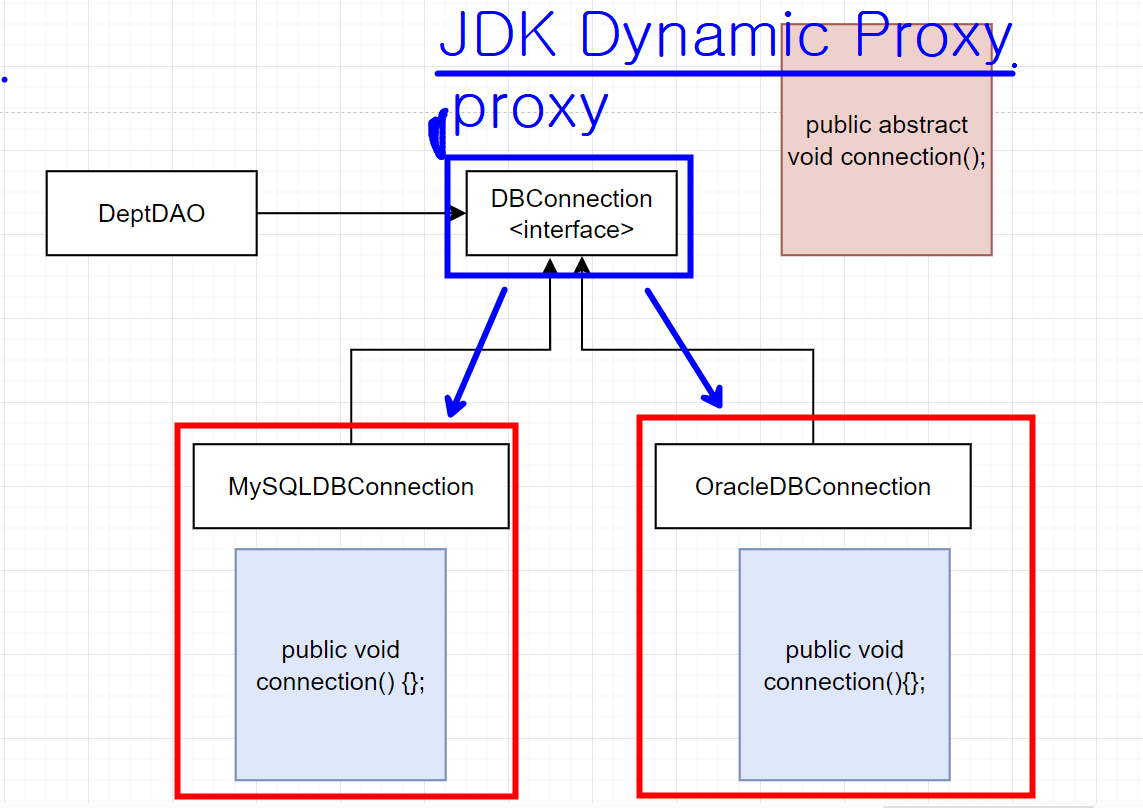
interface는 메소드(추상 메소드)를 선언만 할 수 있음 (프록시의 역할을 해줌)
-
Java에서는 JDK Dynamic Proxy 라고함
-
: 제어자(ex) public, private)
.. : 파라미터 0개 이상 (있어도되고 없어도 됨)
cglib : class를 proxy로 사용할 수 있게 해주는 library
Advice
- method: 수행하고자하는 메소드
<context:annotation-config /> : 주로 의존성 주입 어노테이션을 활성화
<context:component-scan /> : 패키지를 스캔하여 어노테이션(컴포넌트)를 스캔함
Joinpoint: Advice 적용 위치 및 시점
Pointcut: 적용될 시점 (ex 특정 메소드가 실행될 때)
A. AOP (Aspect Oriented Programming)
1. AOP
관점 지향 프로그래밍, 공통 기능을 분리하여 모듈화하여 지정 시점에 해당 로직이 실행하게 함
Advice (수행하고자하는 기능)
-
공통 기능의 코드, 메소드
-
동작 시점
-
Before: 메소드 실행 전에 동작 -
After: 메소드 실행 후에 동작 -
After-returning: 메소드가 정상적으로 실행된 후에 동작 -
After-throwing: 예외가 발생한 후에 동작 -
Around: 메소드 호출 이전, 이후, 예외발생 등 모든 시점에서 동작
-
Joinpoint
- Advice 적용 위치 및 시점
Pointcut
-
특정 조건에 의해 필터링된 조인포인트
-
execution([수식어] 리턴타입 [클래스이름].이름(파라미터))
-
execution(public String com.sping.aop.*.*(*)) -
execution(* com.sping..*.get*(..)) -
execution(* com.sping.spring..*Service.*(..))
-
-
within(타입패턴, 패키지 별로)
-
within(com.spring.aop.SomeService) -
within(com.spring.aop.*) -
within(com.spring.aop..*)
-
Weaving
- AOP Framework가 공통 코드를 핵심 코드에 삽입하는 것
Aspect (관점 = 대상 + 언제)
- Pointcut + Advice
Annotations
-
@Aspect: AOP로 정의하는 클래스 지정 -
@Pointcut: 메소드, Annotation 등 적용 지점 설정 -
@Before: 메소드 실행 전 -
@After: 메소드 성공 실행 후(예외 발생 되더라도 실행) -
@AfterReturning: 메소드가 정상적으로 종료 -
@AfterThrowing: 메소드에서 예외가 발생 -
@Around: Before + After 모두 제어 (에외 발생 되더라도 실행)
JoinPoint 인터페이스
-
비즈니스 메소드의 정보 제공 API
-
메소드
-
Signature getSignature()클라이언트가 호출한 메소드의 시그니처(리턴타입, 이름, 매개변수) 정보가 저장된 Signature 객체 리턴 -
Object getTarget()클라이언트가 호출한 비즈니스 메소드를 포함하는 비즈니스 객체 리턴 -
Object[] getArgs()클라이언트가 메소드를 호출할 때 넘겨준 인자 목록을 Object 배열 로 리턴
-
-
Signature API
String getName()클라이언트가 호출한 메소드 이름 리턴String toLongString()클라이언트가 호출한 메소드의 리턴타입, 이름, 매개변수(시그니처)를 패키지 경로까지 포함 하여 리턴String toShortString()클라이언트가 호출한 메소드 시그니처를 축약한 문자열로 리턴
2. AOP (NoticeAspect)
test.java
public class CarTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aop.xml"); // 어플리케이션 컨텍스트를 가져옴
Car car = context.getBean("bizCar", Car.class);
car.buy();
car.buyReturn();
try {
car.sellMoney(500);
} catch (Exception e) {}
}
}aop.xml
biz.Car (Car 클래스), common.NoticeAspect (Advice)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<bean id="bizCar" class="biz.Car"/>
<bean id="common" class="common.NoticeAspect"/>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* biz.Car.buy(..))" id="buyLogic"/>
<aop:aspect ref="common">
<aop:before method="noticeBuyStart"
pointcut-ref="buyLogic"/>
<aop:after method="noticeBuyEnd"
pointcut-ref="buyLogic"/>
<aop:after-returning method="noticeReturnValue"
pointcut="execution(* biz.Car.buyReturn(..))"
returning="value" />
<aop:after-throwing method="noticeException"
pointcut="execution(* biz.Car.sellMoney(..))"
throwing="e"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
3. AOP(AroundAspect)
@Around 적용 순서
-
@Around("execution(* biz.Car.*(..))")
Car의 모든 메소드가 실행될 때를 시점으로 지정 -
파라미터로 (JoinPoint joinPoint) 를 받아야함
메소드(target, 비즈니스 로직)의 before/after 시점 지정이 불가능하므로 이를 해결하기 위해 JoinPoint라는 Interface를 사용함 -
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
Interface이므로 JoinPoint에서 Signature를 받아옴
Car.buy()를 AroundAspect -> JoinPoint를 통해 얻을 수 있음 -
ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint = (ProceedingJoinPoint)joinPoint;
ProceedingJoinPoint는 Interface이므로 형변환 해줘야함
joinPoint에 담긴 메소드를 사용하기 위해서 형변환함
Object returnValue = (String) proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
proceed() 에는 메소드의 반환 값이 있음 하지만 메소드 자체는 Objcet이므로 return type에 맞게 형변환 해줘야함
biz.Car (DTO)
@Component
public class Car {
// buy : 구매
public void buy() {
System.out.println("자동차 구매");
}
// buyMoney : 구매 금액 확인
public void buyMoney(int money) {
System.out.println("자동차 구매 금액 : " + money);
}
// buyReturn : 구매 성공시 동작
public String buyReturn() {
return "구매 성공";
}
// selMoney : 판매 금액 1000이하면 예외 발생
public void sellMoney(int money) throws Exception {
if(money < 1000) {
throw new Exception("1000 이하로는 판매 금지 : 예외");
}
}
}CarTest
public class CarTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aop.xml"); // 어플리케이션 컨텍스트를 가져옴
Car car = context.getBean("bizCar", Car.class);
car.buy();
car.buyReturn();
try {
car.sellMoney(500);
} catch (Exception e) {}
}
}common (Annotation)
@Aspect
@Component
public class AroundAspect {
@Around("execution(* biz.Car.*(..))")
public void aroundAspect(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
// 편리함, 그러나 해당 메소드(target)의 before/after 시점 지정이 불가함
// 이를 해결하기 위해 나온 interface -> joinpointInterface
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature(); // Car.buy()를 AroundAspect -> JoinPoint를 통해 얻을 수 있음
System.out.println(signature.toLongString());
ProceedingJoinPoint proJoinPoint = (ProceedingJoinPoint)joinPoint;
try {
System.out.println("자동차를 구매 예정이신가요?");
Object returnValue = (String) proJoinPoint.proceed(); // Object라서 String(리턴 타입)으로 형변환
System.out.println("자동차 구매를 완료했습니다.");
System.out.println(returnValue);
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("문제 발생 : " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}NoticeAspect
// 공통 기능
@Aspect
@Component
public class NoticeAspect {
// @Before("execution(* biz.Car.buy(..))")
public void noticeBuyStart() {
System.out.println("자동차를 구매 예정이신가요?");
}
// @After("execution(* biz.Car.buy(..))")
public void noticeBuyEnd() {
System.out.println("자동차 구매를 완료했습니다.");
}
// @AfterReturning(pointcut = "execution(* biz.Car.buyReturn(..))", returning="value")
public void noticeReturnValue(String value) {
if(value != null) {
System.out.println(value);
}
}
// @AfterThrowing(pointcut = "execution(* biz.Car.sellMoney(..))", throwing="e")
public void noticeException(Exception e) {
System.out.println("문제 발생 : " + e.getMessage());
}
}
aop.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd">
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
<context:component-scan base-package="biz" />
<context:component-scan base-package="common" />
</beans>
B. Spring Web MVC
Spring Reference
https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/3.0.0.M4/spring-framework-reference/html/ch15s02.html
DispatcherServlet : FrontController이고 요청을 전달시켜주는 첫번째 컨트롤러
🔥Web Context 안에 Spring Context(MVC, Web Servlet)가 있음
🔥Filter는 WebContext에 있음, Spring Context 아님!
root-context.xml : Spring에 관련된 것을 설정
web-xml : 전반적인 모든 것을 설정
-
spring context, web context 영역이 있음
-
load-on-startup 1: dispather servlet 을 1번째로 실행
servlet-context.xml : servlet 관련 설정
-
controller가 resources (정적인 것을 가져옴)
-
view Resolves : .jsp로 직접 연결하지 못하게 함 /WEB-INF/views/ 를 통해 연결하게 함
Controller
-
Annotation
-
@Controller: controller 역할의 bean 등록 -
@RestController: controller 역할의 bean 등록 -
@RequestMapping: 해당 메소드의 url 매핑 및 method 등 여러가지 설정 값 지정 -
@*Mapping: 메소드별 Mapping 어노테이션 -
@RequestParam: server로 전송되는 parameter 획득 -
@PathVariable: url path를 통해 전달되는 parameter 획득
-
Model, ModelAndView
Model
| Method | 설명 |
|---|---|
| addAttribute | Model에 속성추가 |
| getAttribute | Model에 있는 속성을 조회 |
| addAttributes | Model에 속성을 여러개 추가 |
| getAttributes | Model에 속성을 여러개 조회 |
ModelAndView
| Method | 설명 |
|---|---|
| setViewName | view 이름을 설정 |
| getViewName | view 이름을 조회 |
| setView | view 설정 |
| getView | view 조회 |
| hasView | 설정되어있는 view 존재 여부 확인 |
| getModelMap | 내부의 모델 Map 조회 |
| getModel | 내부 모델 조회 |
| getStatus | 상태 설정 |
Controller 리턴타입
-
String: sevlet-context.xml 정의가 되어 있는 것 처럼 jsp 파일의 이름 -
void: 호출하는 URL과 동일한 이름의 jsp -
DTO: JSON 타입의 데이터로 변환, @ResponseBody, Jackson lib 사용 -
Model, ModelAndView: 데이터 반환시 화면까지 지정하는 경우 -
ResponseEntity: 응답시, HTTP 헤더 정보와 내용을 가공 -
HttpHeaders: 응답 내용 없이 HTTP 헤더 메세지만 리턴
MIME type https://developer.mozilla.org/ko/docs/Web/HTTP/Basics_of_HTTP/MIME_types
Spring MVC Ex)
1. DTO
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
@Component
public class Student {
private String id;
private int age;
}2. ParameterAspect
@Aspect
@Component
public class ParameterAspect {
@Around("execution(* com.spring.mvc.*.*(..))")
public void parameterAspect(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("메소드명 : " + signature.getName());
System.out.println("파라미터");
Object[] agrs = joinPoint.getArgs();
for(Object arg : agrs) {
int i = 1;
System.out.println("파라미터" + i + " : " +arg);
}
try {
((ProceedingJoinPoint)joinPoint).proceed();
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}3. Controller
@Controller
public class MVCController {
// Request
// http://localhost:8082/mvc/test1
@RequestMapping(value = "/test1", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void test1() {
System.out.println("MVCController : test1");
}
// http://localhost:8082/mvc/test2?id=dev
@RequestMapping(value = "/test2", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void test2(HttpServletRequest request) {
System.out.println("MVCController : test2");
System.out.println("id : " + request.getParameter("id"));
}
// http://localhost:8082/mvc/test3?asdf=dev
@RequestMapping(value = "/test3", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void test3(@RequestParam("asdf") String id) {
System.out.println("MVCController : test3");
System.out.println("id : " + id);
}
// http://localhost:8082/mvc/test4?id=dev&age=28
@RequestMapping(value = "/test4", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void test4(@RequestParam("id") String id, @RequestParam("age") int age) {
System.out.println("MVCController : test4");
System.out.println("id : " + id);
System.out.println("age : " + age);
Student student = new Student(id, age);
System.out.println(student);
}
// http://localhost:8082/mvc/test5?id=dev&age=28
@RequestMapping(value = "/test5", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void test5(@ModelAttribute Student newStudent) {
System.out.println("MVCController : test4");
// Student 객체 생성 확인
System.out.println(newStudent);
}
// http://localhost:8082/mvc/test6/emp/7346/ename/SMITH/id=dev&age=28
// emp 테이블의 SMITH를 검색할 때 :
@RequestMapping(value = "/test6/emp/{empno}/ename/{ename}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void test6(@PathVariable int empno, @PathVariable String ename, @ModelAttribute Student student) {
System.out.println("MVCController : test5");
// Student 객체 생성 확인
System.out.println("empno : " + empno);
System.out.println("ename : " + ename);
System.out.println("student : " + student);
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------
// return : void: page로 이동
// http://localhost:8082/mvc/test7
@RequestMapping(value = "/test7", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public void test7() {
System.out.println("MVCController : test7");
// return "test7" ;
}
//DTO
// http://localhost:8082/mvc/test8?id=dev&age=28
@RequestMapping(value = "/test8", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public Student test8(Student newStudent) { // 아직안됨
System.out.println("MVCController : test8");
return newStudent ;
}
// ModelAndView
// http://localhost:8082/mvc/test9?id=dev&age=28
@RequestMapping(value = "/test9", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView test9(Student newStudent) {
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
String testname = "abcd";
System.out.println("MVCController : test7");
System.out.println(newStudent);
mv.addObject("student", newStudent);
mv.addObject("testname", testname);
mv.setViewName("test9");
return mv;
}
// ResponseEntity
// http://localhost:8082/mvc/test10
@RequestMapping(value = "/test10", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ResponseEntity<String> test10() {
System.out.println("MVCController : test10");
String data = "{\"id\":\"dev\"}";
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
headers.add("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=UTF-8");
return new ResponseEntity<String>(data, headers, HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
4. servlet-context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans:beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd">
<!-- DispatcherServlet Context: defines this servlet's request-processing infrastructure -->
<!-- Enables the Spring MVC @Controller programming model -->
<annotation-driven />
<!-- Handles HTTP GET requests for /resources/** by efficiently serving up static resources in the ${webappRoot}/resources directory -->
<resources mapping="/resources/**" location="/resources/" />
<!-- Resolves views selected for rendering by @Controllers to .jsp resources in the /WEB-INF/views directory -->
<beans:bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<beans:property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/" />
<beans:property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</beans:bean>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.spring.mvc" />
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
</beans:beans>
2. 에러
예외 : No converter found for return value of type
리턴 타입으로 객체를 반환하려고할 때 리턴에 대한 변환기를 찾을 수 없다고 함,
해결 방법 : Jackson 라이브러리를 추가하여 해결함
Json, XML, YAML, CSV 등 다양한 형식의 데이터를 지원하는 data-processing tool
3. 보완 해야 할 것
MVC를 배우면서 STS 자체의 설정, Project설정, xml 파일들의 설정에 대한 부분이 많아서 설정에 대한 이해, 설정 후 어떤 변화가 있을지 예상해야하는 능력을 키워야할 것 같음
4. 느낀점
AOP는 Filter가 하나 더 생긴 느낌이였음
오늘은 유독 정신이 너무 없어서 계속 복기하면서 흐름을 이해하는데 집중해야할 것으로 예상됨