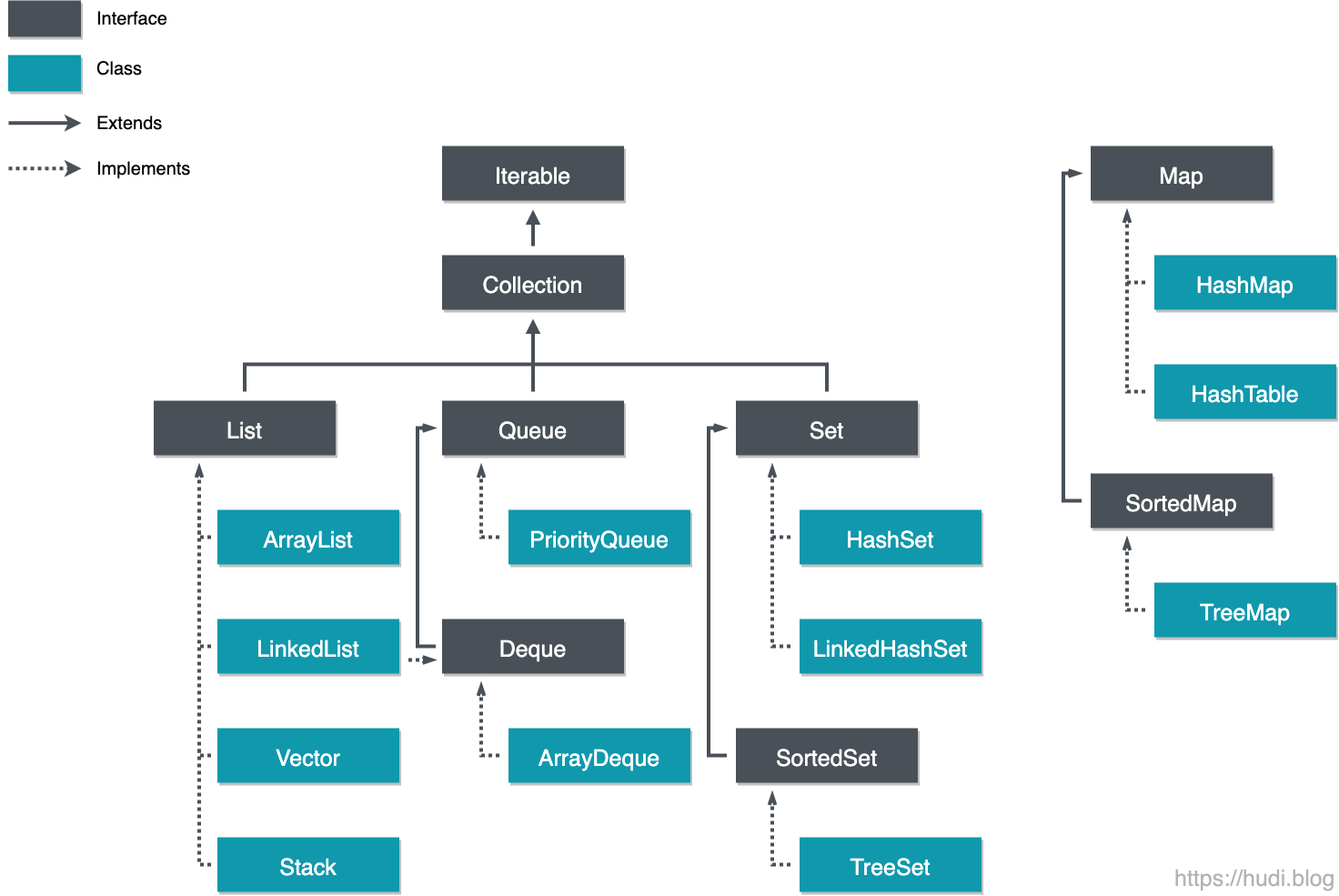
List
순서가 있는 집합. 데이터의 중복을 허용한다.
구현 클래스
- ArrayList
- LinkedList
- Stack
ArrayList
ArrayList 만들기
List<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
값 넣기
list.add(value);
3번 인덱스에 요소 삽입
list.add(3, "A");
2번 인덱스 요소 삭제
list.remove(2);
지정된 인덱스의 요소 반환
list.get(0);
ArrayList의 길이(데이터가 몇개 들어있는지 확인)
list.size();
ArrayList가 비어있는지 확인
list.isEmpty();
ArrayList 비우기
list.clear();Stack
스택 만들기
Stack<T> stack = new Stack<>();
스택 값 넣기
stack.push(value);
스택 값 꺼내기
stack.pop();
스택에서 나올 값 확인 (데이터는 꺼내지 않는다)
stack.peek();
스택의 길이(데이터가 몇개 들어있는지 확인)
stack.size();
스택이 비어있는지 확인
stack.isEmpty();
스택 비우기
stack.clear();Queue
큐 만들기
Queue<T> queue = new LinkedList<>();
큐 값 넣기
queue.offer(value);
큐 값 꺼내기
queue.poll();
큐에서 나올 값 확인 (데이터는 꺼내지 않는다)
queue.peek();
큐의 길이(데이터가 몇개 들어있는지 확인)
queue.size();
큐가 비어있는지 확인
queue.isEmpty();
큐 비우기
queue.clear();Map
key, value 쌍으로 구성된 집합. 순서는 유지되지 않는다.
key는 중복되지 않고 value는 중복을 허용한다.
구현 클래스
- HashMap
- TreeMap
- Hashtable
HashMap
map 만들기
Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map 값 넣기
for (char x : result.toCharArray()) {
map.put(x, map.getOrDefault(x, 0)+1);
}
key를 이용해 value 찾기
int max=0;
for (Character key : map.keySet()) {
if (map.get(key)>max) {
max=map.get(key);
answer=key;
}
}
key를 이용해 data 삭제
map.remove(arr[lt]);
map.containsKey(c)
Set
순서를 유지하지 않는 집합. 중복을 허용하지 않는다.
구현 클래스
- HashSet
- TreeSet
HashSet을 기본적으로 사용하고, 정렬이 필요할 때만 TreeSet을 고려하는 것이 일반적인 패턴이다. TreeSet은 데이터가 자동으로 정렬되어 출력된다.
