using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace cs22_collection
{
class MyList
{
int[] array;
public MyList()
{
array = new int[3];
}
public int Length
{
get { return array.Length; }
}
//인덱서
public int this[int index]
{
get
{
return array[index];
}
set
{
if(index >= array.Length) // 3보다 커지면
{
Array.Resize<int>(ref array, index + 1);
Console.WriteLine("MyList Resized : {0} ", array.Length);
}
array[index] = value; // 값 할당!
}
}
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] array = new int[5];
array[0] = 1;
array[1] = 2;
array[2] = 3;
array[3] = 4;
array[4] = 5;
//Console.WriteLine(array[5]); // IndexOutOfRangeException
char[] oldString = new char[5]; // 문자열 길이 지정해야하니 C에서만 사용
string currString = ""; // 문자열 길이 제한 없음
ArrayList list = new ArrayList(); // 사이즈 제한 없음
list.Add(1);
list.Add(2);
list.Add(3);
list.Add(4);
list.Add(5);
list.Add(6);
ArrayList list2 = new ArrayList();
list2.Add(1);
list2.Add(2);
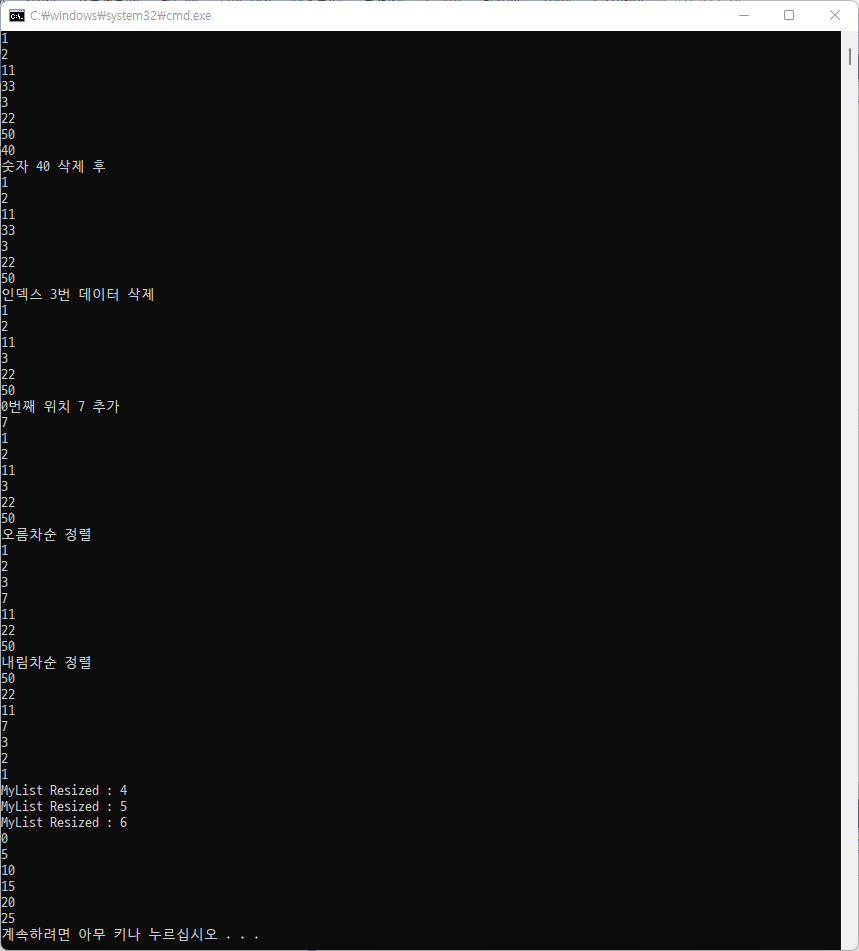
list2.Add(11);
list2.Add(33);
list2.Add(3);
list2.Add(22);
list2.Add(50);
list2.Add(40);
foreach (var item in list2)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
// list에서 데이터 삭제
Console.WriteLine("숫자 40 삭제 후");
list2.Remove(40);
foreach (var item in list2)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
Console.WriteLine("인덱스 3번 데이터 삭제");
list2.RemoveAt(3);
foreach (var item in list2)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
Console.WriteLine("0번째 위치 7 추가");
list2.Insert(0, 7);
foreach (var item in list2)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
Console.WriteLine("오름차순 정렬");
list2.Sort();
foreach (var item in list2)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
Console.WriteLine("내림차순 정렬");
list2.Reverse();
foreach (var item in list2)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
// 새로만든 MyList
MyList myList = new MyList();
for (int i = 1;i<=5;i++)
{
myList[i] = i * 5; // 5, 10, 15, 20 ,,,
}
for(int i=0;i<myList.Length;i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(myList[i]);
}
}
}
}
인덱서
인덱스를 이용햐 객체 내 데이터에 접근하게 하는 프로퍼티
yield 실습
yield return은 메서드를 빠져나가지 않고 값만 반환
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace cs23_collection
{
class CustomEnumerator : IEnumerable //foreach를 쓸 수 있는 객체로 만들어줌 (IEnumerable)
{
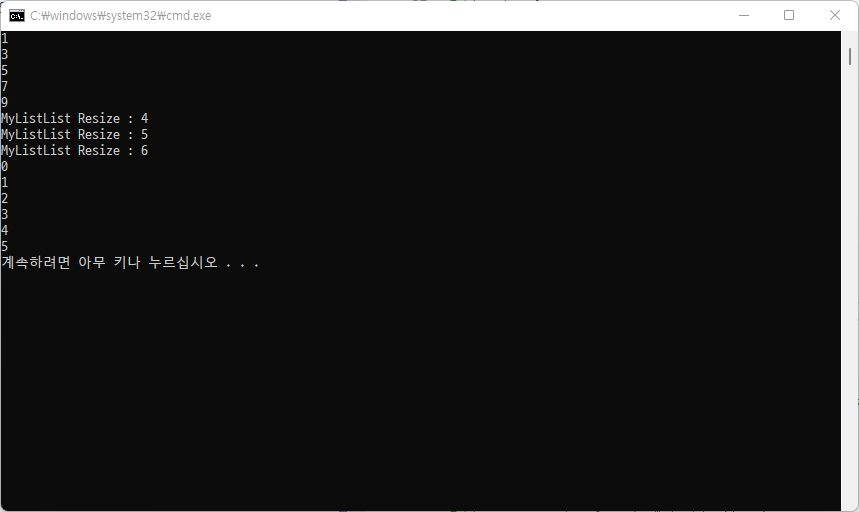
int[] list = { 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 };
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
{
yield return list[0]; // 메서드를 빠져나가지 않고 값만 반환
yield return list[1]; // 리턴과는 달리 값을 보내주고 멈춰있음
yield return list[2];
yield return list[3];
//yield break;
yield return list[4];
}
}
class MyArrayList : IEnumerator,IEnumerable
{
int[] array; // 배열값을 집어넣는 곳
int position = -1; // 인덱스
public MyArrayList()
{
this.array = new int[3]; //기본크기 3으로 초기화
}
//인덱서 프로퍼티
public int this[int index]
{
get { return this.array[index]; }
set
{
if(index >= this.array.Length)
{
Array.Resize<int>(ref this.array, index + 1);
Console.WriteLine("MyListList Resize : {0} ", array.Length);
}
array[index] = value;
}
}
#region <IEnumerable 인터페이스 구현>
public IEnumerator GetEnumerator()
{
for(var i = 0;i <array.Length;i++)
{
yield return array[i];
}
}
public object Current
{
get
{
return array[position];
}
}
#endregion
#region <IEnumerator 인터페이스 구현>
public bool MoveNext()
{
if(position == array.Length - 1)
{
Reset();
return false;
}
position++;
return (position < array.Length);
}
public void Reset()
{
position = -1;
}
#endregion
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var obj = new CustomEnumerator();
foreach (int item in obj)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
var myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
for(var i = 0;i<=5;i++)
{
// indexer 프로퍼티 만들어서 구현 가능
myArrayList[i] = i;
}
// IEnumerable 인터페이스 구현해서 사용가능
foreach(var item in myArrayList)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
}
}
}