복사생성자
- 자신과 같은 클래스 타입의 다른 객체에 대한 참조(reference)를 인수로 전달받아, 그 참조를 가지고 자신을 초기화하는 방법
- 복사생성자를 정의하지 않으면, 멤버 대 멤버의 복사를 진행하는 디폴트 복사 생성자가 자동으로 삽입
- 얕은 복사
- 깊은 복사

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Myclass
{
int num; //stack영역
public:
Myclass(int n) : num(n) { //콜론 초기화
cout << "생성자 호출" << endl;
}
Myclass(Myclass& copy) { // 객체를 매개변수(Myclass copy)로 받으면 무한루프 ,,, !매개변수는 무조건 참조형으로!
cout << "복사생성자 호출" << endl;
num = copy.num*2;
}
void getData();
};
void Myclass::getData()
{
cout << num << endl;
}
int main()
{
Myclass m1(10); //객체 생성
Myclass m2 = m1; // 복사생성자 호출 ... int num1 = num2
Myclass m3(m2); // 복사생성자 호출 ... int num3 = num2(num1)
// 복사생성자도 만들어주지 않아도 default(얕은 복사)로 만들어지기 때문에 위 코드가 실행됨
//stack영역은 얕은 복사
//heap 영역의 깊은 복사는 문제가 발생
m1.getData();
m2.getData();
m3.getData();
return 0;
}
explicit
C타입에서 객체 초기화를 할 때 대입연산자"="를 사용하는데, 복사생성자를 호출할 때 대입연산자를 통해
SoSimple sim2=sim1;이런식으로 복사생성자를 호출한다면
SoSimple sim2(sim1);과 같이 묵시적 변환이 발생하기 때문에 대입연산자를 사용하는것을 지양하기 위해
explicit 키워드를 사용한다.
그러면 대입연산자를 통한 객체 초기화를 못하게 한다.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class SoSimple
{
private:
int num1;
int num2;
public:
SoSimple(int n1, int n2) : num1(n1), num2(n2)
{
}
explicit SoSimple(SoSimple& copy) :num1(copy.num1), num2(copy.num2)
{
cout << "Called SoSimple(SoSimple ©)" << endl;
}
void ShowSimpleData()
{
cout << num1 << endl;
cout << num2 << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
SoSimple sim1(15, 30);
cout << "생성 및 초기화 직전" << endl;
SoSimple sim2(sim1); // Sosimple sim2=sim1 과 동일,,,explicit 키워드를 사용하면 대입연산자 사용불가
cout<< "생성 및 초기화 직후" << endl;
sim1.ShowSimpleData();
printf("---------------\n");
sim2.ShowSimpleData();
return 0;
}
위 코드의 경우 복사생성자 선언을 할 때, explicit를 사용했기 때문에 대입연산자를 이용한 객체의 생성 및 초기화는 불가능하다.
묵시적 변환이 많이 발생하는 코드일수록 코드의 결과를 예측하기 어려우니 코드의 명확함을 더하기 위해서는 explicit를 자주 사용하는 것이 좋다.
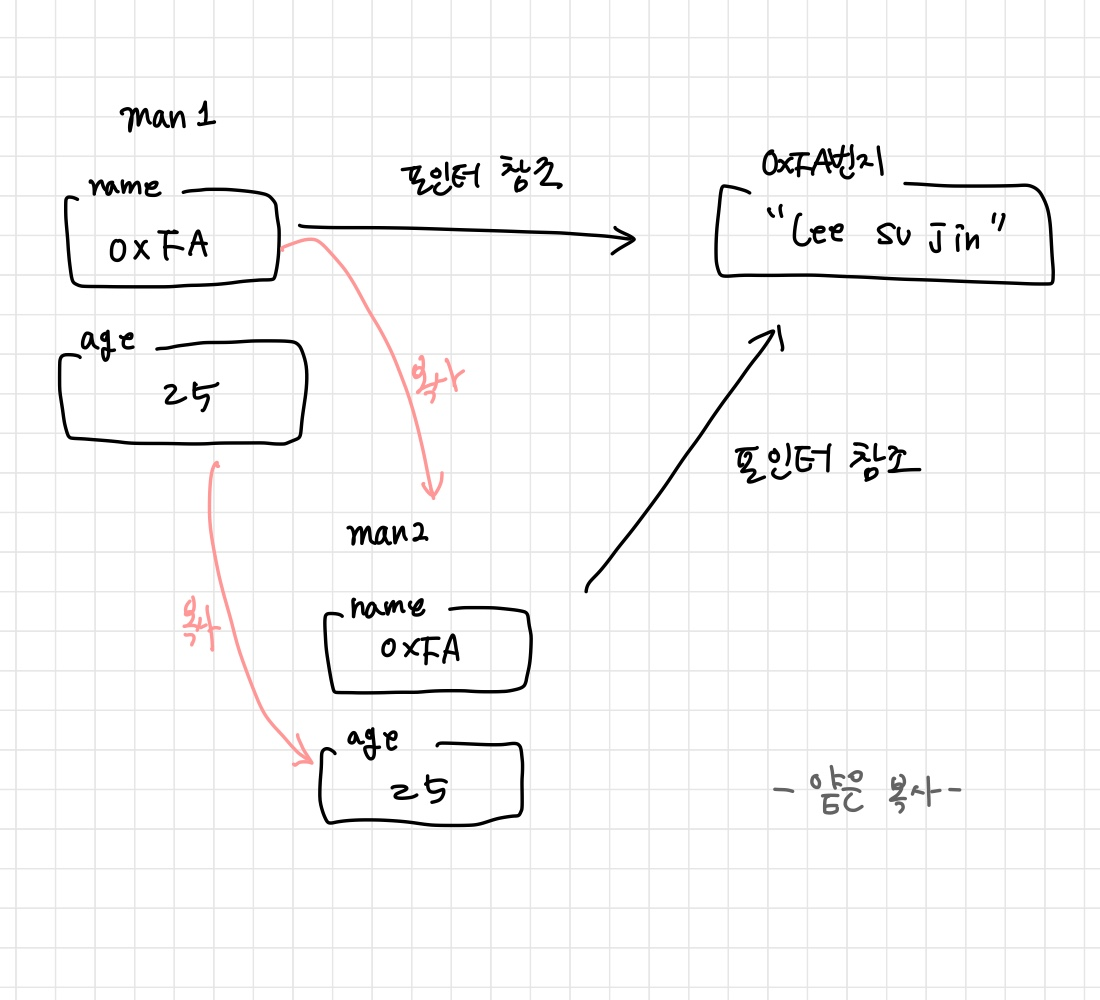
'깊은 복사'와 '얕은 복사'
얕은복사
Person(const Person& copy) { this->name = copy.name; this->age = copy.age; }깊은복사
Person(const Person& copy) { this->name = new char[strlen(copy.name)+1]; strcpy(this->name, copy.name); this->age = copy,age; }
얕은복사
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
class Person
{
private:
char* name;
int age;
public:
Person(char* name, int age)
{
int len = (int)strlen(name) + 1;
this->name = new char[len];
strcpy(this->name, name);
age = age;
}
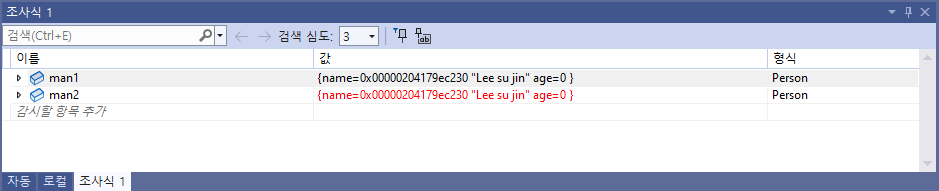
explicit Person(const Person& copy)
{
cout << "복사생성자 호출" << endl;
this->name = copy.name;
this->age = copy.age;
}
void ShowPersonInfo() const
{
cout << "이름: " << this->name << endl;
cout << "나이: " << this->age << endl;
}
~Person()
{
delete[] this->name;
cout << "Called destructor" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Person man1("Lee su jin", 25);
Person man2(man1); //
man1.ShowPersonInfo();
man2.ShowPersonInfo();
return 0;
}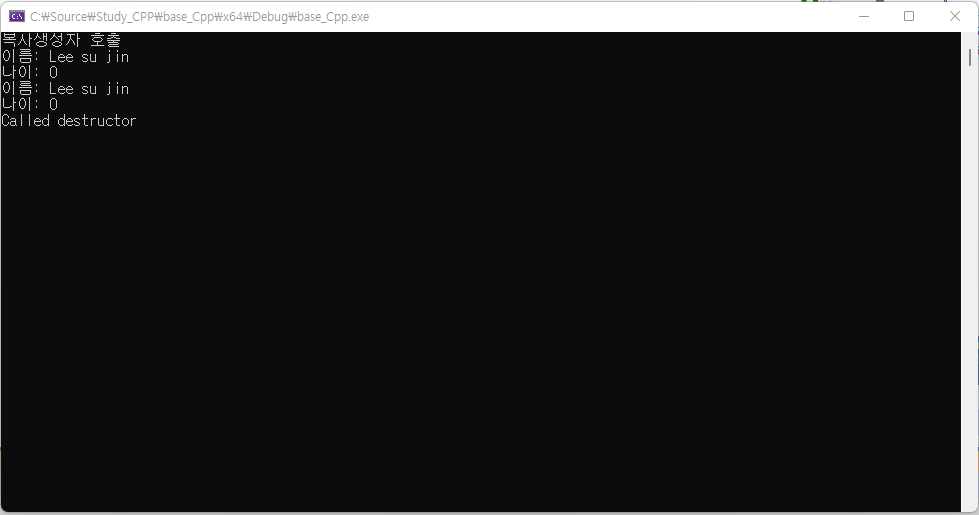
실행이 중단됨
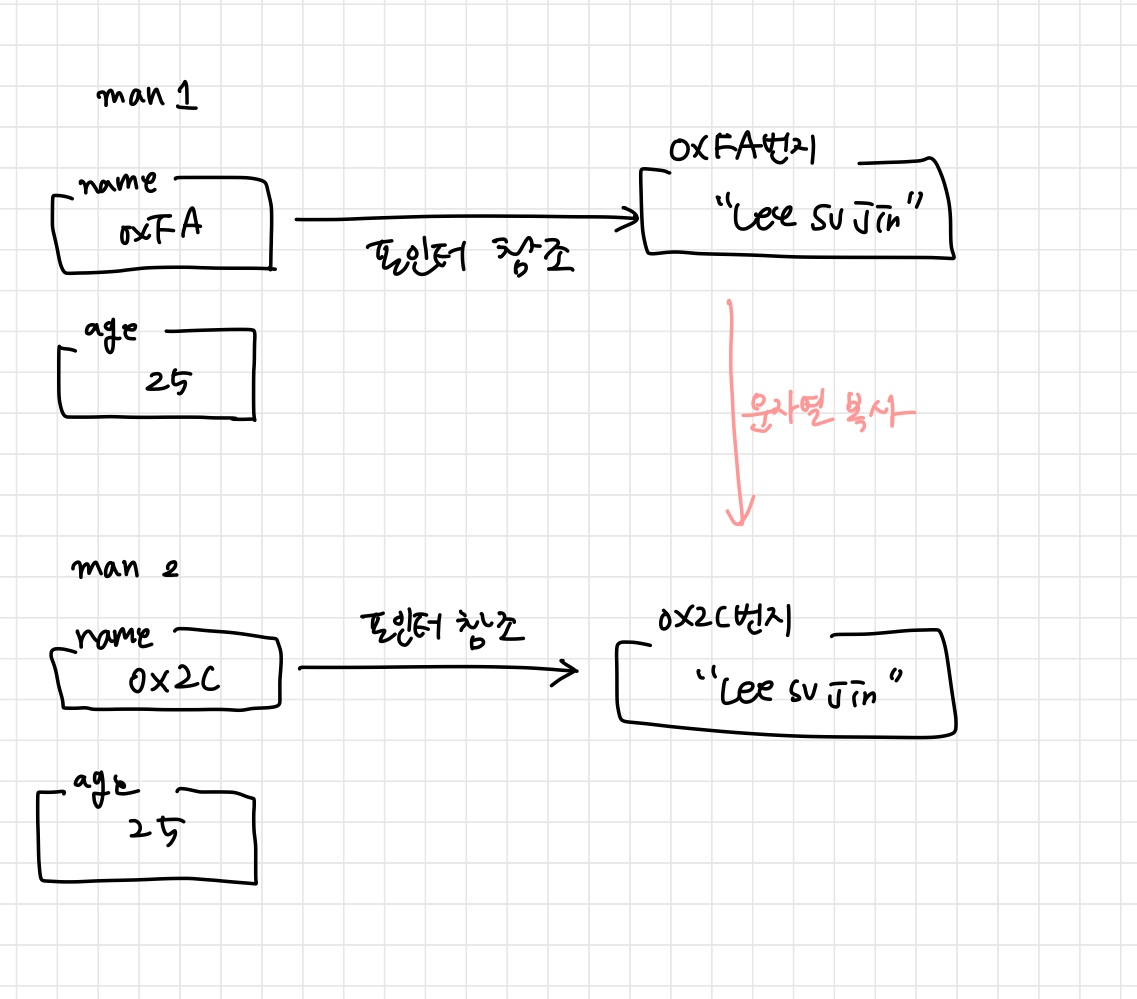
깊은복사
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
class Person
{
private:
char* name;
int age;
public:
Person(char* name, int age)
{
int len = (int)strlen(name) + 1;
this->name = new char[len];
strcpy(this->name, name);
this-> age = age;
}
explicit Person(const Person& copy)
{
cout << "복사생성자 호출" << endl;
this->name = new char[strlen(copy.name) + 1];
strcpy(this->name, copy.name);
this->age = copy.age;
}
void ShowPersonInfo() const
{
cout << "이름: " << this->name << endl;
cout << "나이: " << this->age << endl;
}
~Person()
{
delete[] this->name;
cout << "Called destructor" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Person man1("Lee su jin", 25);
Person man2(man1);
man1.ShowPersonInfo();
man2.ShowPersonInfo();
return 0;
}오류 없이 잘 실행 됨

복사 생성자의 호출 시점
- case1 : 기존에 생성된 객체를 이용해서 새로운 객체를 초기화하는 경우
SoSimple obj2=obj1;
- case2 : Call-by-value 방식의 함수호출 과정에서 객체를 인자로 전달하는 경우(매개변수가 객체일 때)
SoSimple SimpleFuncObj(SoSimple ob) {...}
- case3 : 객체를 반환하되, 참조형으로 반환하지 않는 경우
return ob;
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class SoSimple
{
private:
int num;
public:
SoSimple(int n) : num(n)
{ }
SoSimple(const SoSimple& copy) : num(copy.num)
{
cout << "Called SoSimple(const SoSimple& copy)" << endl;
}
SoSimple& AddNum(int n)
{
num += n;
return *this;
}
void ShowData()
{
cout << "num: " << num << endl;
}
};
SoSimple SimpleFuncObj(SoSimple ob)
{
cout << "return 이전" << endl;
return ob;
}
int main()
{
SoSimple obj(7);
SimpleFuncObj(obj).AddNum(30).ShowData(); // 임시객체에 저장된 값에 30증가됨 ... 구문이 끝나면 초기상태로 돌아감
obj.ShowData();
return 0;
}
- 디버깅해보기
객체가 사라지는 시기는?
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Temporary
{
private:
int num;
public:
Temporary(int n) : num(n)
{
cout << "create obj: " << num << endl;
}
~Temporary()
{
cout << "destroy obj: " << num << endl;
}
void ShowTempInfo()
{
cout << "My num is " << num << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Temporary(100); // 객체의 이름이 없으니 임시객체... 생성자 호출 됨...소멸자도 호출 됨
cout << "********after make!" << endl << endl;
Temporary(200).ShowTempInfo();
cout << "********after make!" << endl << endl;
const Temporary &ref=Temporary(300);
cout << "********end of main!" << endl << endl;
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class SoSimple
{
private:
int num;
public:
SoSimple(int n) : num(n)
{
cout << "New Object: " << this << endl;
}
SoSimple(const SoSimple& copy) : num(copy.num)
{
cout << "New Copy: " << this << endl;
}
~SoSimple()
{
cout << "Destroy obj: " << this << endl;
}
};
SoSimple SimpleFuncObj(SoSimple ob)
{
cout << "Parm ADR: " << &ob << endl;
return ob;
}
int main()
{
SoSimple obj(7);
SimpleFuncObj(obj);
cout << endl;
SoSimple tempRef = SimpleFuncObj(obj);
cout << "Return Obj " << &tempRef << endl;
return 0;
}
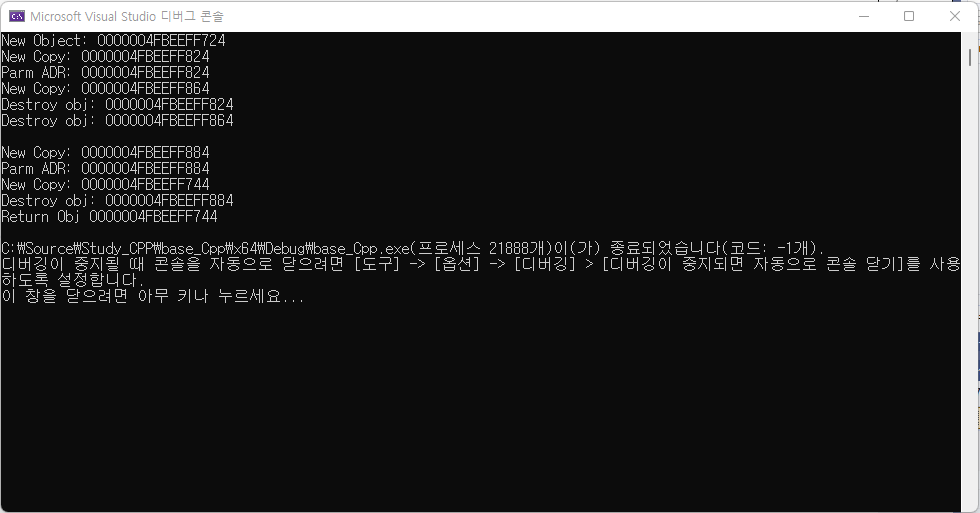
추가 설명