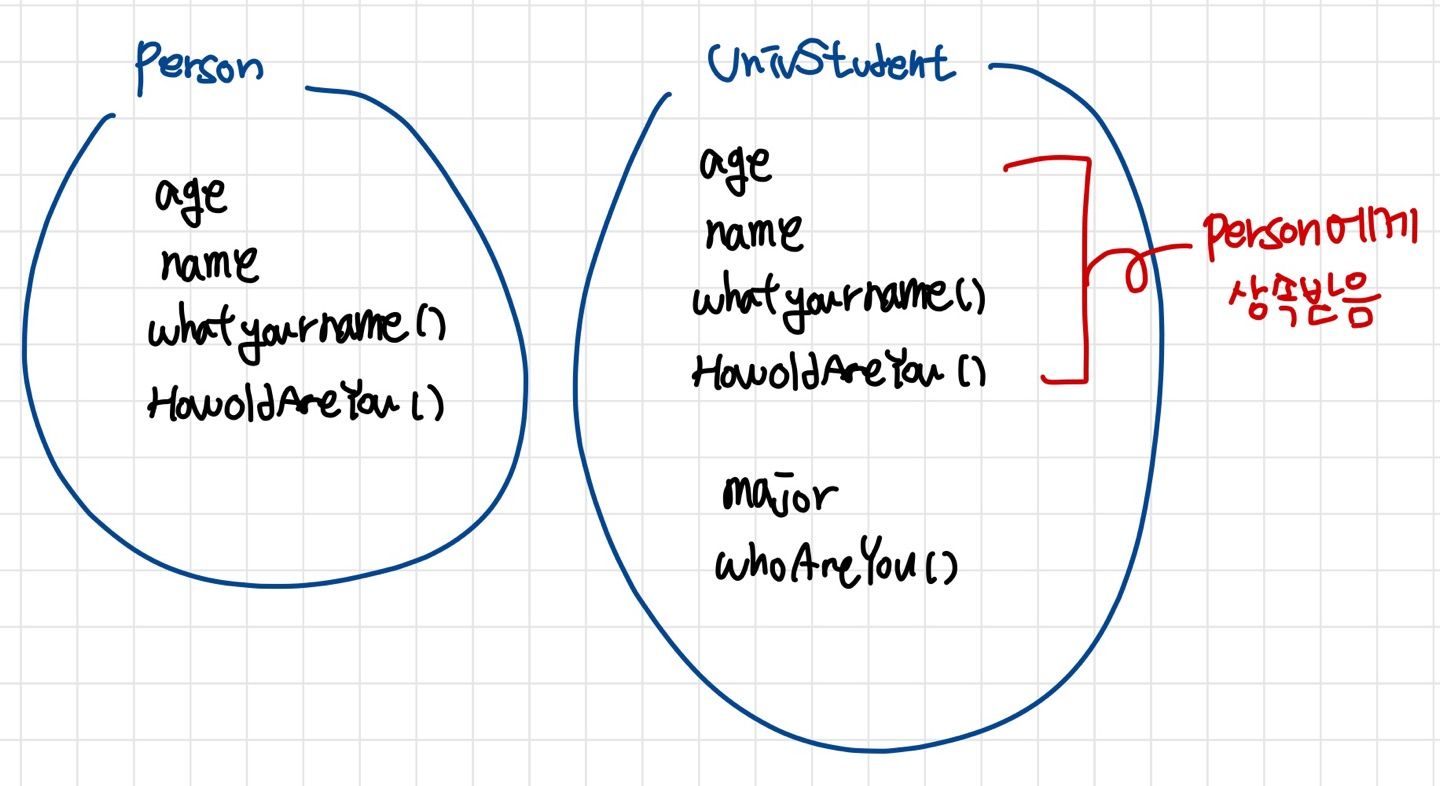
"UnivStudent" 클래스가 "Person" 클래스를 상속한다
-
UnivStudent 클래스가 Person 클래스를 상속하게 되면, UnivStudent 클래스는 Person 클래스가 지니고 있는 모든 멤버를 물려받는다.
-
즉, UnivStudent 객체에는 UnivStudent 클래스에 선언되어 있는 멤버뿐만 아니라 Person 클래스에 선언되어 있는 멤버도 존재하게 된다.
-
자식클래스의 생성자는 부모클래스의 멤버까지 초기화 해야함
- 자식클래스는 부모클래스의 생성자를 호출해서 부모클래스의 멤버를 초기화 하는 것이 좋음
- 자식클래스는 부모클래스의 private 멤버에 접근이 불가능하다
- private멤버에 접근하려면 같은 클래스에 정의된 public 함수를 통해서만 간접적으로 접근을 해야한다.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
class Person
{
private:
int age;
char name[50];
public:
Person(int myage, char* myname) : age(myage)
{
strcpy(name, myname);
}
void WhatYourname() const
{
cout << "My name is " << name << endl;
}
void HowOldAreYou() const
{
cout << "I'm " << age << " Years old" << endl;
}
};
class UnivStudent : public Person // UnivStudent클래스는 Person클래스를 상속을 받는데 접근제한 지시자가 public이다.
{
private:
char major[50];
public:
UnivStudent(char* myname, int myage, char* mymajor) : Person(myage, myname) // 자식클래스는 부모클래스의 private의 변수에 접근이 안되기 때문에 부모클래스에 호출하여 초기화
{
strcpy(major, mymajor);
}
void WhoAreYou() const
{
WhatYourname();
HowOldAreYou();
cout << "My Major is " << major << endl << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
UnivStudent ustd1("Lee", 22, "Computer eng.");
ustd1.WhoAreYou();
UnivStudent ustd2("Yoon", 25, "Electronic eng.");
ustd2.WhoAreYou();
return 0;
}
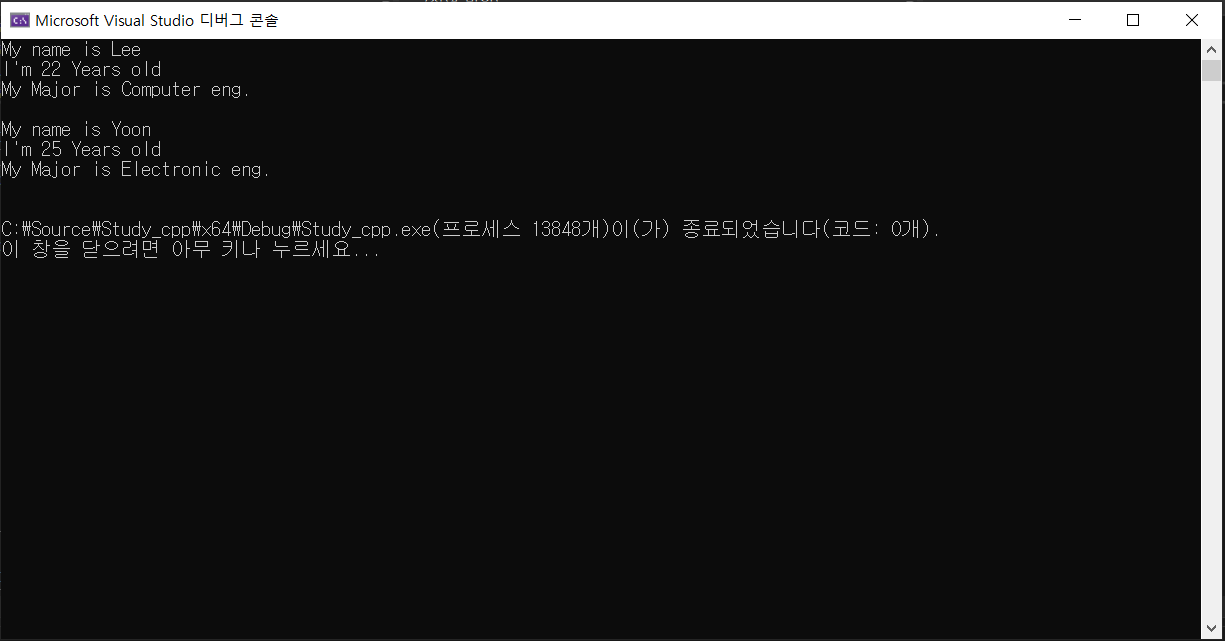
유도 클래스(자식 클래스)의 객체 생성과정
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class SoBase
{
private:
int baseNum;
public:
SoBase() : baseNum(20)
{
cout << "SoBase() " << endl;
}
SoBase(int n) : baseNum(n)
{
cout << "SoBase(int n) " << endl;
}
void ShowBaseData()
{
cout << baseNum << endl;
}
};
class SoDerived : public SoBase
{
private:
int derivNum;
public:
SoDerived() : derivNum(30)
{
cout << "DoDerived() " << endl;
}
SoDerived(int n) : derivNum(n) // 부모클래스 생성자에 의한 초기화가 안 이뤄지니 default 초기화 'SoBase() : baseNum(20)'
{
cout << "DoDerived(int n) " << endl;
}
SoDerived(int n1,int n2) : SoBase(n1), derivNum(n2) // 부모클래스 생성자 호출이 됨 'SoBase(int n) : baseNum(n)' 실행
{
cout << "SoDerived(int n1,int n2) " << endl;
}
void ShowDerivData()
{
ShowBaseData();
cout << derivNum << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
cout << "case1..... " << endl;
SoDerived dr1;
dr1.ShowDerivData();
cout << "----------------------" << endl;
cout << "case2..... " << endl;
SoDerived dr2(12);
dr2.ShowDerivData();
cout << "----------------------" << endl;
cout << "case3..... " << endl;
SoDerived dr3(23, 24);
dr3.ShowDerivData();
return 0;
}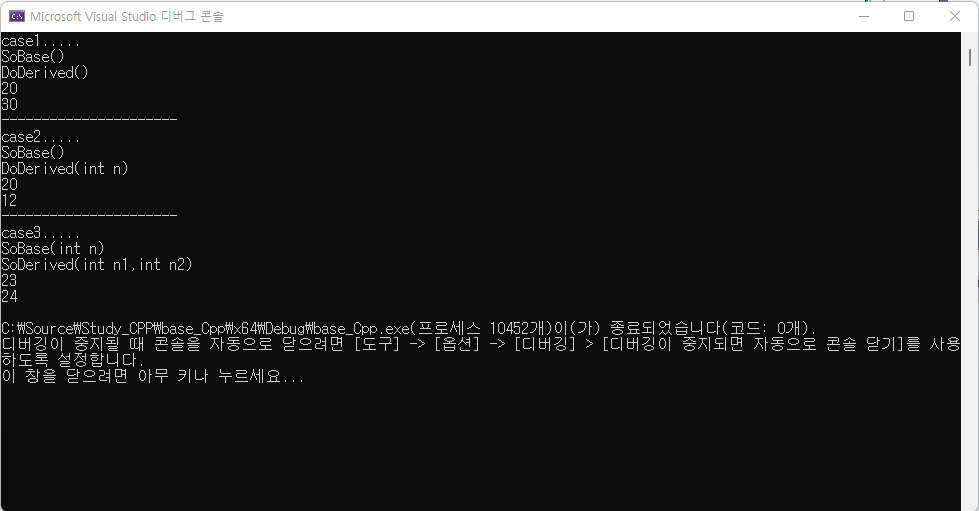
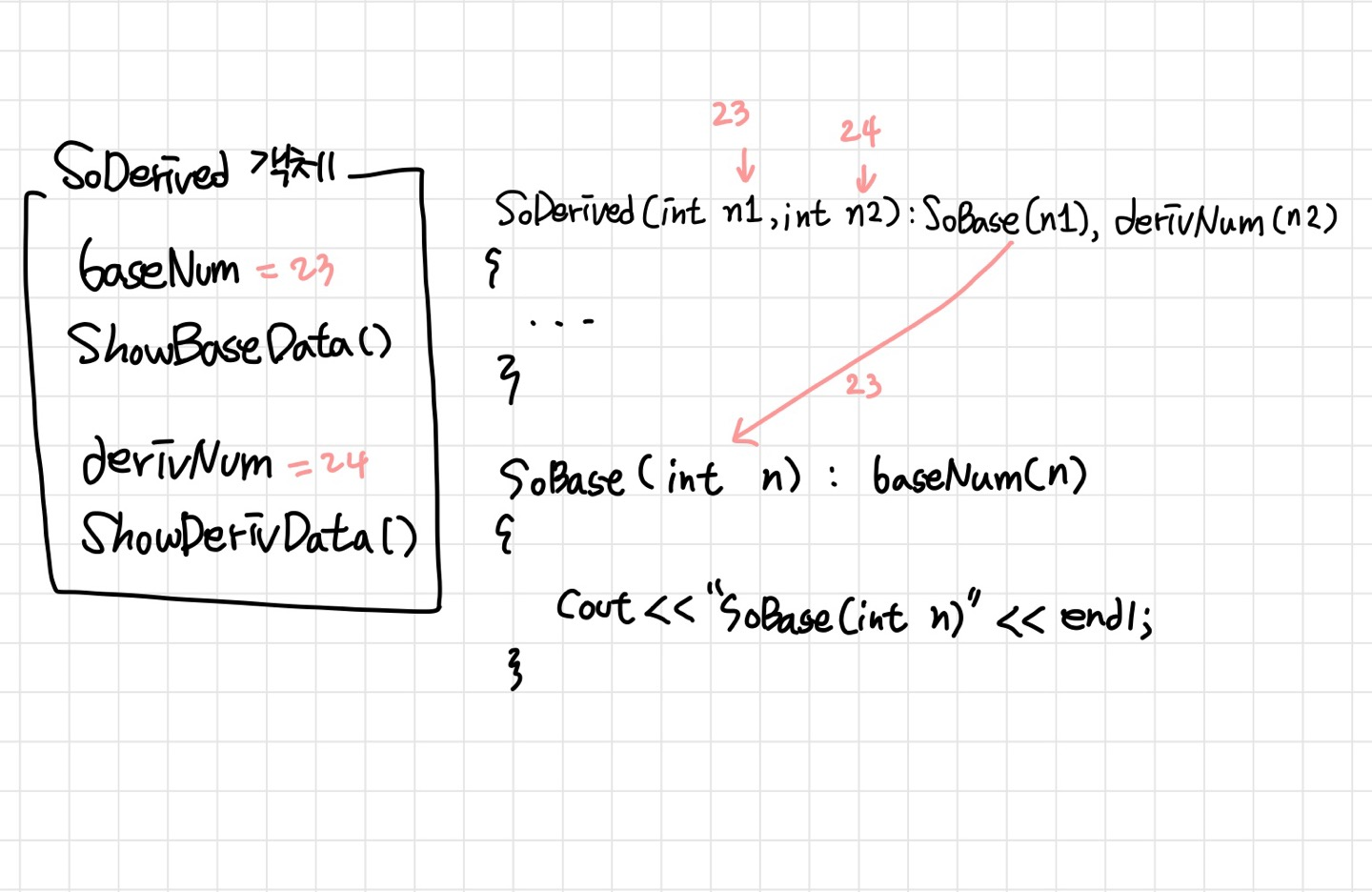
- 유도 클래스의 객체생성 과정에서 기초 클래스의 생성자는 100% 호출된다
SoDerived dr1;에서SoBase() : baseNum(20) { }와SoDerived() : derivNum(30) { }초기화- 유도 클래스의 생성자에서 기초 클래스의 생성자 호출을 명시하지 않으면, 기초 클래스의 void 생성
유도 클래스 객체의 소멸과정
유도 클래스의 객체 생성과정에서는 생성자가 두 번 호출됨을 알았으니, 유도 클래스의 객체 소멸과정에서도 소멸자가 두 번 호출됨을 유추할 수 있다.
자식 클래스가 먼저 소멸 -> 부모 클래스 소멸
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Super
{
public:
Super() {
cout << "Super () " << endl;
}
~Super() {
cout << "~Super () " << endl;
}
};
class Sub : public Super {
public:
Sub() {
cout << "Sub () " << endl;
}
~Sub() {
cout << "~Sub () " << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
cout << "------Start------" << endl;
Sub obj1;
cout << "------Stop-------" << endl;
return 0;
}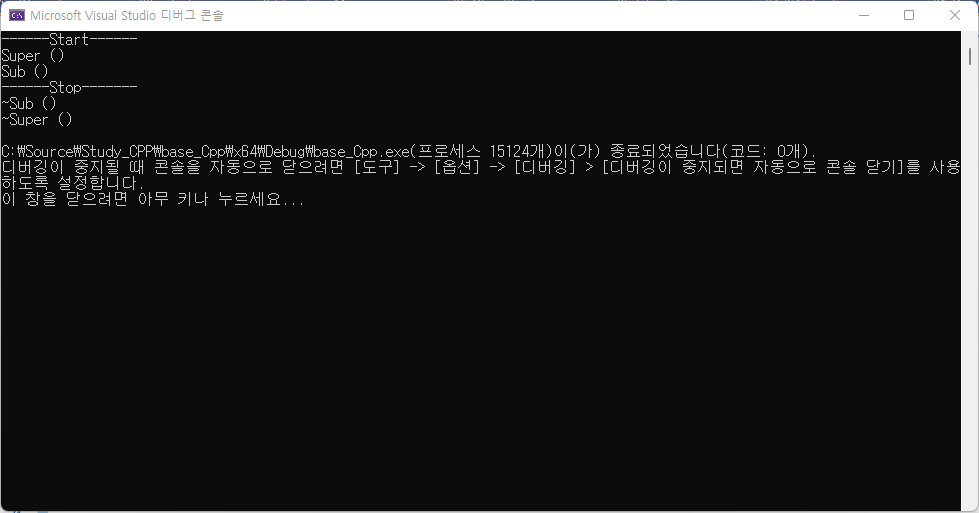
위 예제를 보면 클래스가 생성될 땐 부모클래스부터 생성되고, 소멸될 땐 자식클래스먼저 소멸된다는 것을 알 수 있다.
생성자에서 동적 할당한 메모리 공간은 소멸자에서 해제한다
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
private:
char* name;
public:
Person(char* myname) //생성자
{
name = new char[strlen(myname) + 1]; // 메모리 동적할당
strcpy(name, myname);
}
~Person() //소멸자
{
cout << name << " ~Person" << endl;
delete[] name; // 메모리 해제
}
void WhatYourName() const {
cout << "My name is " << name << endl;
}
};
class UnivStudent : public Person
{
private:
char* major;
public:
UnivStudent(char* myname, char* mymajor) : Person(myname) //생성자
{
major = new char[strlen(mymajor) + 1];// 메모리 동적할당
strcpy(major, mymajor);
}
~UnivStudent() //소멸자
{
cout << major << " ~UnivStudent" << endl;
delete[] major;// 메모리 해제
}
void WhoAreYou() const
{
WhatYourName();
cout << "My major is " << major << endl << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
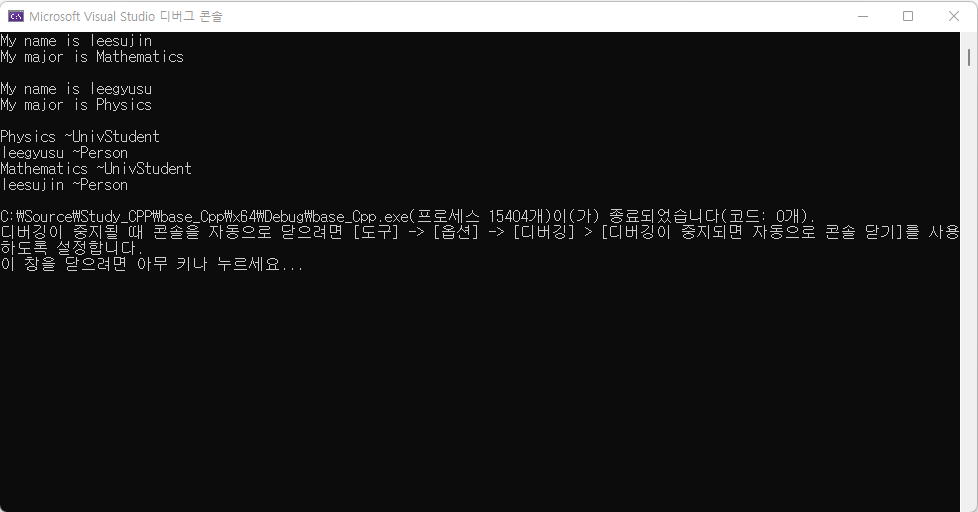
UnivStudent st1("leesujin", "Mathematics");
st1.WhoAreYou();
UnivStudent st2("leegyusu", "Physics");
st2.WhoAreYou();
return 0;
}
protected 선언과 세 가지 형태의 상속
c++ 접근제어 지시자
private < protected < public
protected 상속은 "protected보다 접근의 범위가 넓은 멤버는 protected로 변경시켜 상속"
상속을 위한 조건
"IS-A" : "일종의 ~이다."
- 포함 관계라고 생각하면 쉽다.
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class computer
{
private:
char owner[50];
public:
computer(char* name)
{
strcpy(owner, name);
}
void calculate()
{
cout << "요청 내용을 계산합니다." << endl;
}
};
class notebookcomp : public computer
{
private:
int battery;
public:
notebookcomp(char * name , int initchag) : computer(name), battery(initchag)
{ }
void charging() { battery += 5; }
void usebattery() { battery -= 5; }
void movingcal()
{
if (getbatteryinfo() < 1)
{
cout << "충전이 필요합니다." << endl;
return;
}
cout << "이동하면서 ";
calculate();
usebattery();
}
int getbatteryinfo() { return battery; }
};
class tabletnotebook : public notebookcomp
{
private:
char regstpenmodel[50];
public:
tabletnotebook(char* name, int initchag, char* pen) :notebookcomp(name, initchag)
{
strcpy(regstpenmodel, pen);
}
void write(char* peninfo)
{
if (getbatteryinfo() < 1)
{
cout << "충전이 필요합니다. " << endl;
return;
}
if (strcmp(regstpenmodel, peninfo) != 0)
{
cout << "등록된 펜이 아닙니다.";
return;
}
cout << "필기 내용을 처리합니다." << endl;
usebattery();
}
};
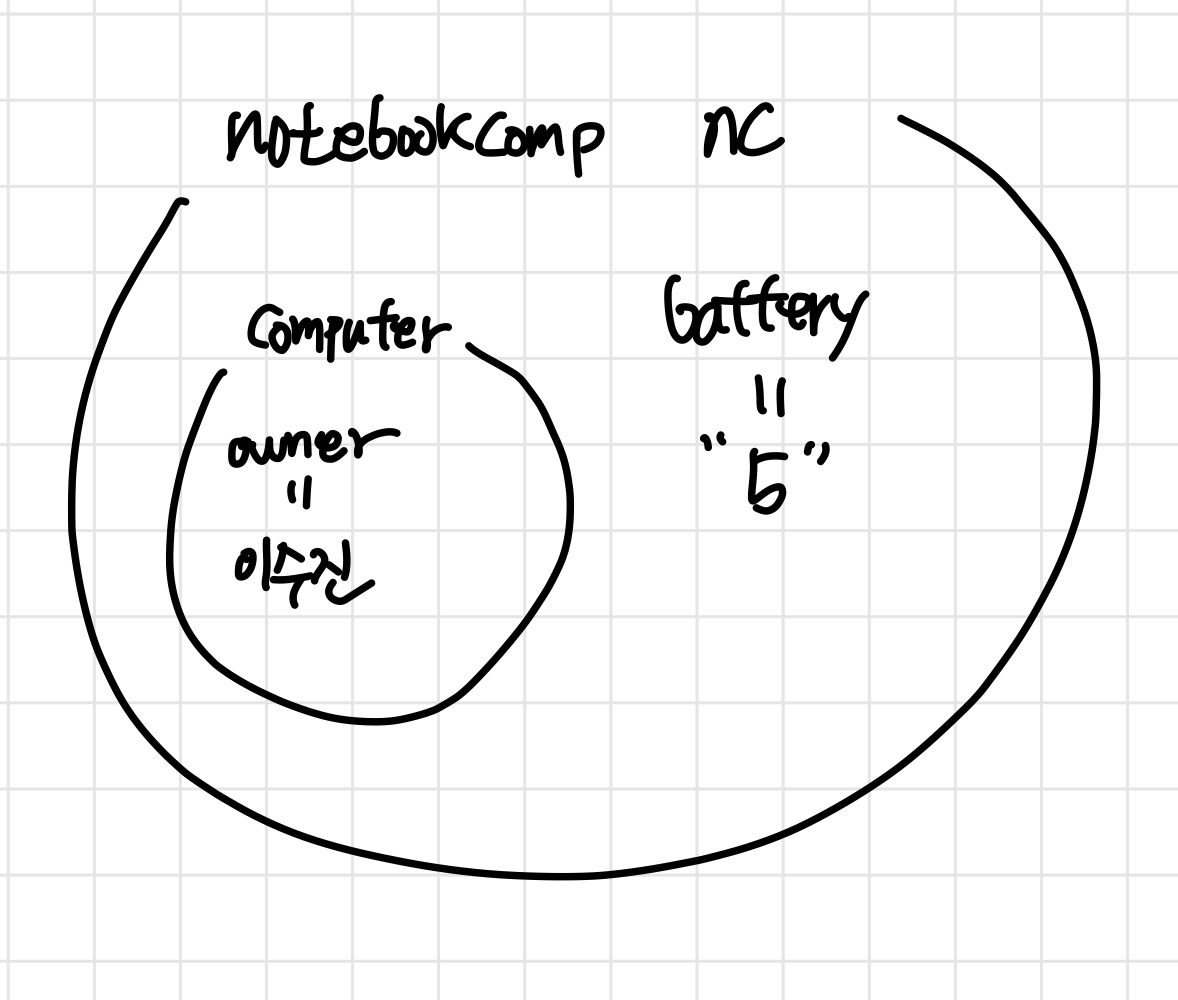
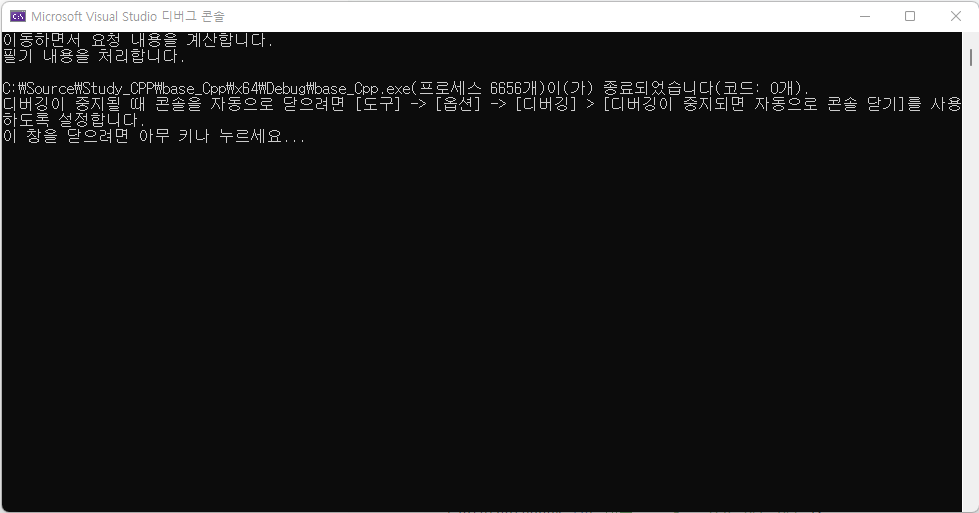
int main()
{
notebookcomp nc("이수진", 5);
tabletnotebook tn("이규수", 5, "ise-241-242");
nc.movingcal();
tn.write("ise-241-242");
return 0;
}nc 객체
"HAS-A" : "~을 소유한다"
- 소유한다는 개념으로 이해하자
- 자식클래스(유도클래스)는 기초클래스가 지닌 모든것을 소유한다
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class Gun
{
private:
int bullet;
public:
Gun(int bnum):bullet(bnum)
{ }
void Shot()
{
cout << "BBANG!" << endl;
bullet--;
}
};
class Police :public Gun
{
private:
int handcuffs;
public:
Police(int bnum,int bcuff):Gun(bnum),handcuffs(bcuff)
{ }
void PutHandcuff()
{
cout << "SNAP!" << endl;
handcuffs--;
}
};
int main()
{
Police pman(5, 3);
pman.Shot();
pman.PutHandcuff();
return 0;
}