예외처리
- try : 예외를 발견한다
try { // 예외발생 예상지역 } - catch : 예외를 잡는다
catch(처리할 예외의 종류 명시) { //예외처리 코드의 삽입 } - throw : 예외를 던진다
- 예외가 발생했음을 알리는 문장의 구성에서 사용됨
throw expn;에서 expn은 변수, 상수, 객체 등 표현 가능한 모든 데이터가 될 수 있다.- 예외상황에 대한 정보를 담은 의미있는 데이터여야 한다.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
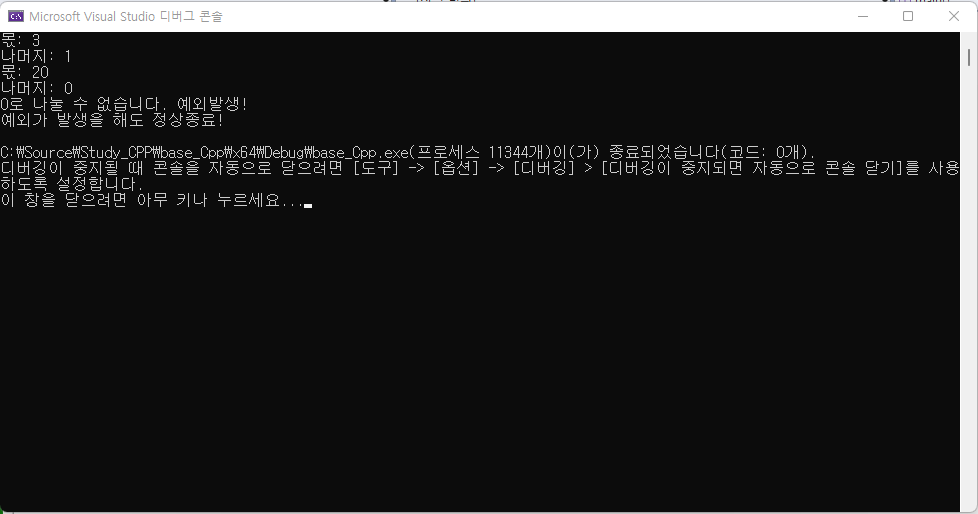
int a, b, c, d;
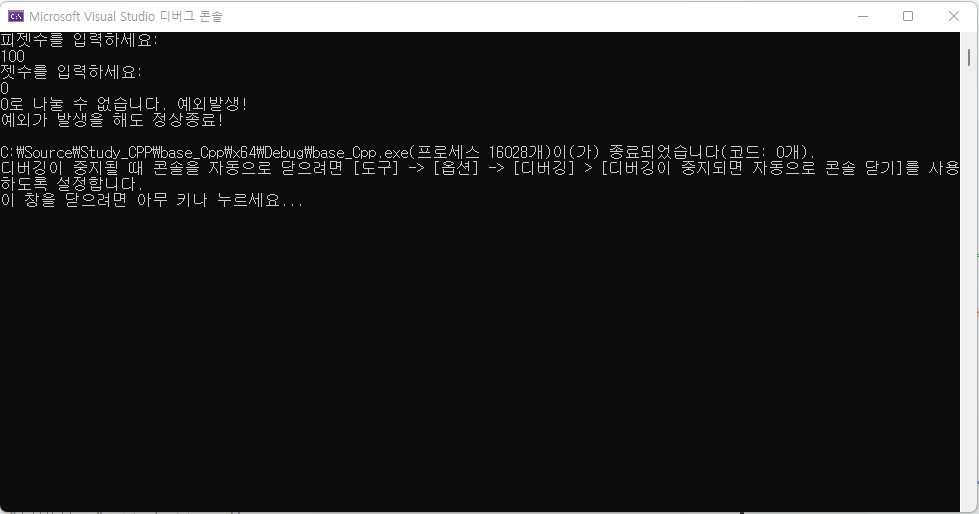
cout << "피젯수를 입력하세요: " << endl;
cin >> a;
cout << "젯수를 입력하세요: " << endl;
cin >> b;
try {
if (b == 0) throw b; // 예외가 발생되면 b를 던지고 catch가 잡음
c = a / b;
cout << "몫: " << c << endl;
d = a % b;
cout << "나머지: " << d << endl;
}
catch (int ex) {
cout << ex << "로 나눌 수 없습니다. 예외발생!" << endl;
cout << "예외가 발생을 해도 정상종료!" << endl;
return 0;
}
}
메인 함수 밖에서 예외가 발생할 때
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int divide(int a,int b)
{
int c, d;
if (b == 0) throw b;
c = a / b;
cout << "몫: " << c << endl;
d = a % b;
cout << "나머지: " << d << endl;
}
int main()
{
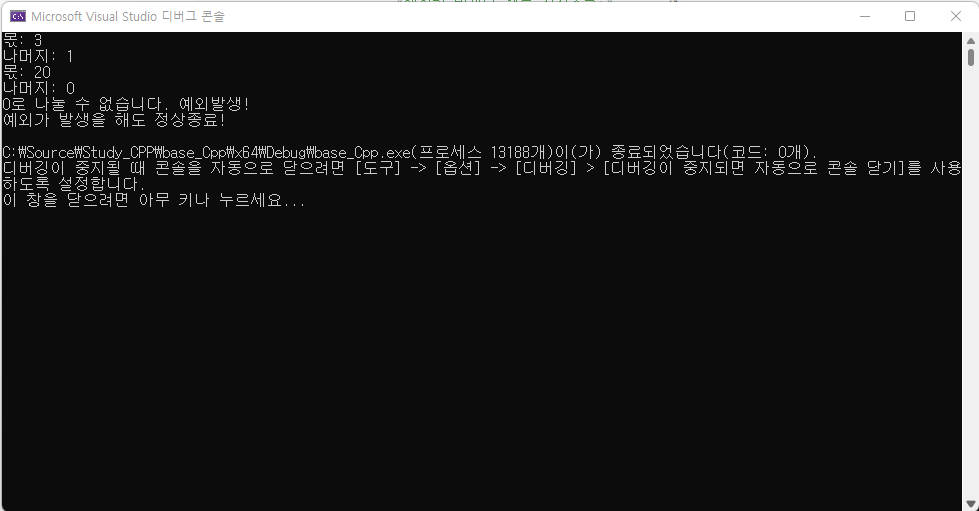
try {
divide(10, 3);
divide(100, 5);
divide(3, 0);
}
catch (int ex) {
cout << ex << "로 나눌 수 없습니다. 예외발생!" << endl;
cout << "예외가 발생을 해도 정상종료!" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
지역함수 안에서 예외처리
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int divide(int a, int b)
{
int c, d;
try
{
if (b == 0) throw b;
c = a / b;
cout << "몫: " << c << endl;
d = a % b;
cout << "나머지: " << d << endl;
}
catch (int ex) {
cout << ex << "로 나눌 수 없습니다. 예외발생!" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
divide(10, 3);
divide(100, 5);
divide(3, 0);
cout << "예외가 발생을 해도 정상종료!" << endl;
return 0;
}