함수 오버라이딩
함수 오버로딩이 함수의 중복 정의라면 함수 오버라이딩은 함수의 재정의이다
오버라이딩은 상속 받았을 때 부모클래스의 함수를 사용하지 않고 다른 기능을 실행할 때 함수를 자식클래스에 같은 이름, 매개변수로 재정의해서 사용하는 것.
함수 오버로딩
- 메소드 이름이 같아야 한다
- 반환형이 같아도 되고 달라도 됨
- 파라미터 개수가 달라야 함
- 파라미터 개수가 같을 경우, 자료형이 달라야 함
함수 오버라이딩
- 오버라이드 하고자 하는 메소드가 상위 클래스에 존재해야 함
- 메소드 이름이 같아야 함
- 메소드 파라미터 개수, 파라미터의 자료형이 같아야 함
- 메소드 리턴형이 같아야 함
- 상위 메소드와 동일하거나 내용이 추가되야 함
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
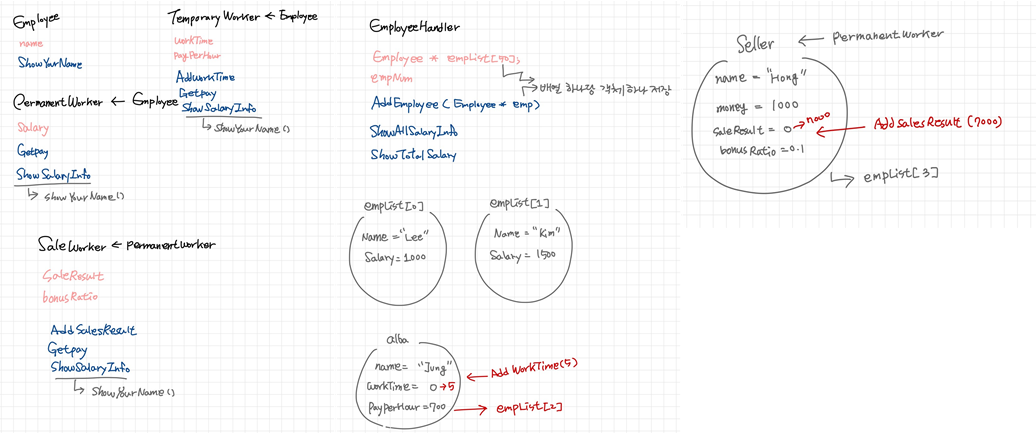
class Employee
{
private:
char name[100];
public:
Employee(const char* name)
{
strcpy(this->name, name);
}
void ShowYourName() const // 함수 상수화(name값 즉, 함수안에 내용이 변경되지 않음)
{
cout << "name: " << name << endl;
}
virtual int GetPay() const
{
return 0;
}
virtual void ShowSalaryInfo() const
{
}
};
class PermanentWorker :public Employee
{
private:
int salary;
public:
PermanentWorker(const char*name,int money):Employee(name),salary(money)
{ }
int GetPay() const // 함수 오버라이딩 ... 자식 클래스의 오버라이딩 된 메소드에 의해 가려짐
{
return salary;
}
void ShowSalaryInfo() const // 함수 오버라이딩
{
ShowYourName();
cout << "salary: " << GetPay() << endl << endl;
}
};
class TemporaryWorker : public Employee
{
private:
int workTime;
int payPerHour;
public:
TemporaryWorker(const char * name, int pay):Employee(name),workTime(0),payPerHour(pay)
{ }
void AddWorkTime(int time)
{
workTime += time;
}
int GetPay() const
{
return workTime * payPerHour;
}
void ShowSalaryInfo() const
{
ShowYourName();
cout << "salary: " << GetPay() << endl << endl; // GetPay()는 저장되지 않고 호출만 되니 임시객체이다
}
};
class SaleWorker : public PermanentWorker
{
private:
int saleResult;
double bonusRatio;
public:
SaleWorker(const char * name,int money,double ratio):PermanentWorker(name,money),saleResult(0),bonusRatio(ratio)
{ }
void AddSalesResult(int value)
{
saleResult += value;
}
int GetPay() const // 함수 오버라이딩
{
return PermanentWorker::GetPay() + (int)(saleResult * bonusRatio);
}
void ShowsalaryInfo() const // 함수 오버라이딩
{
ShowYourName();
cout << "salary : " << GetPay() << endl << endl;
}
};
class EmployeeHandler
{
private:
Employee* empList[50]; // 포인터 배열 : 포인터를 저장한다
int empNum;
public:
EmployeeHandler() : empNum(0)
{ }
void AddEmployee(Employee* emp)
{
empList[empNum++] = emp;
}
void ShowAllSalaryInfo() const
{
for (int i = 0; i < empNum; i++)
empList[i]->ShowSalaryInfo();
}
void ShowTotalSalary() const
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < empNum; i++)
{
sum += empList[i]->GetPay();
}
cout << "salary sum : " << sum << endl;
}
~EmployeeHandler()
{
for (int i = 0;i < empNum;i++)
{
delete empList[i];
}
}
};
int main()
{
// 직원관리를 목적으로 설계된 컨트롤 클래스의 객체생성
EmployeeHandler handler;
// 정규직 등록
handler.AddEmployee(new PermanentWorker("Lee", 1000));
handler.AddEmployee(new PermanentWorker("Kim", 1500));
//임시직 등록
TemporaryWorker* alba = new TemporaryWorker("Jung", 700);
alba->AddWorkTime(5);
handler.AddEmployee(alba);
//영업직 등록
SaleWorker* seller = new SaleWorker("Hong", 1000, 0.1);
seller->AddSalesResult(7000); // '->' 포인터로 접근하는 경우
handler.AddEmployee(seller); // '.' 객체를 통해 접근하는 경우
// 이번 달에 지불해야 할 급여
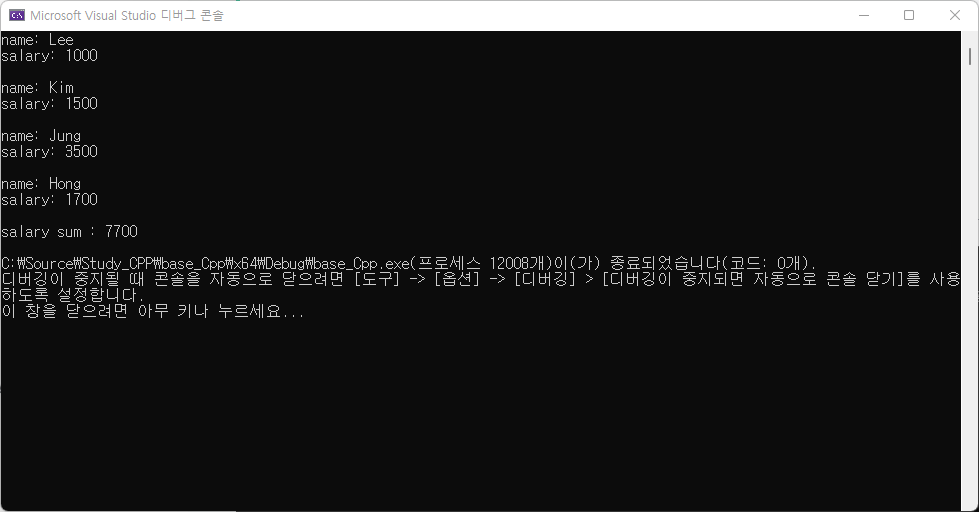
handler.ShowAllSalaryInfo();
// 이번 달에 지불해야 할 급여의 총합
handler.ShowTotalSalary();
return 0;
}
- SalesWorker클래스의 ShowSalaryInfo함수는 PermanentWorker 클래스의 ShowSalaryInfo 함수와 동일한데,
SalesWorker 클래스에서 ShowSalaryInfo 함수를 오버라이딩 한 이유
- PermanentWorker 클래스의 ShowSalaryInfo 함수 내에서 호출되는 GetPay 함수는 PermanentWorker 클래스에 정의된 GetPay 함수의 호출로 이어진다.
따라서 SalesWorker 클래스에 정의된 GetPay 함수가 호출되도록 SalesWorker클래스에 별도의 ShowSalaryInfo 함수를 정의해야한다