🧡 9장 집합 연산자
-
오라클의 집합 연산자는 서로 다른 두 개의 결과를 연산을 통해 새로운 결과를 추출한다.
-
수학의 정석 1장에서 배운 집합의 셈(합집합, 교집합, 차집합)과 비슷한 개념이다.
-
- 집합 연산자의 종류
: 집합 연산자는 4가지 종류가 있다.
-
UNION: 두 집합을 더해서 결과를 출력. 중복 값 제거하고 정렬함
-
UNION ALL: 두 집합을 더해서 결과를 출력. 중복 값 제거 안하고 정렬 안함
-
INTERSECT: 두 집합의 교집합 결과를 출력. 정렬함.
-
MINUS: 두 집합의 차집합 결과를 출력. 쿼리의 순서 중요함
-
- 연산자 사용 조건
-
(1)두 집합의 SELECT 절에 오는 칼럼의 개수가 동일해야 한다.
SELECT 리스트의 표현식은 개수가 일치해야 합니다. -
(2)두 집합의 SELECT 절에 오는 칼럼의 데이터형이 동일해야 한다.
후속 query에 있는 각 열의 데이터 유형은 첫 번째 query에 있는 상응하는 열의 데이터 유형과 일치해야 합니다. -
(3) 두 집합의 칼럼명은 달라도 상관없다.
-
(4) 실행 순서를 변경하는 데 괄호를 사용할 수 있습니다.
-
(5) ORDER BY 절은 명령문의 맨 끝에만 올 수 있습니다.
-
(6) 중복 행은 UNION ALL 외에는 자동으로 제거합니다.
-
(7) 첫 번째 query의 열 이름이 결과에 머리글로 표시됩니다.
-
(8) UNION ALL의 경우를 제외하고 출력은 기본적으로 첫 번째 열을 기준으로 오름차순으로 정렬됩니다
-
- 부가 설명 (1) UNION / UNION ALL
-
UNION, UNION ALL 모두 두 집합을 더해서 결과를 출력.
-
UNION은 두 결과에서 중복된 값을 제거하고 출력
-
UNION ALL은 중복되는 값까지 전부 다 출력.
-
- 연산자 별 예시
-
(1)
UNION ALL
- 질의) 학력정보 테이블에서 대학명이 대구대인 사람의 정보와 창원대인 사람의 결과를 UNION ALL
SELECT 대학교명, 전공명 FROM 학력정보
WHERE 대학교명 = '대구대'
UNION ALL
SELECT 대학교명, 전공명 FROM 학력정보
WHERE 대학교명 = '창원대'=> 중복된 항목 제거 X 및 정렬 X
- (2) UNION
- 질의) 학력정보 테이블에서 대학명이 대구대인 사람의 정보와 창원대인 사람의 결과를 UNION ALL
SELECT 대학교명, 전공명 FROM 학력정보
WHERE 대학교명 = '대구대'
UNION
SELECT 대학교명, 전공명 FROM 학력정보
WHERE 대학교명 = '창원대'=> 중복된 항목 제거 O 및 전공 명 오름차순 정렬 O
- (3) INTERSECT
질의) 학력정보 테이블에서 대학명이 대구대인 모든 라인과,
- 대학명이 대구대이면서 전공명이 행정학인 라인을 INTERSECT
SELECT 대학교명, 전공명 FROM 학력정보
WHERE 대학교명 = '대구대'
INTERSECT
SELECT 대학교명, 전공명 FROM 학력정보
WHERE 대학교명 = '창원대'
AND 전공명 = '행정학'=>두 개의 쿼리의 교집합인 ROW 만 출력됨.
(근데 사실 INTERSECT는 굳이 쓸 필요가 있나 싶음.
단순히 WHERE 조건절로 해결 가능해 보임.)
- (4) MINUS
질의) 학력정보 테이블에서 대학명이 대구대인 모든 라인과,
- 대학명이 대구대이면서 전공명이 행정학인 라인을 MINUS
=> INTERSECT와 정 반대의 결과를 출력.
10장 sql을 활용한 집계 및 분석
ref. rollup
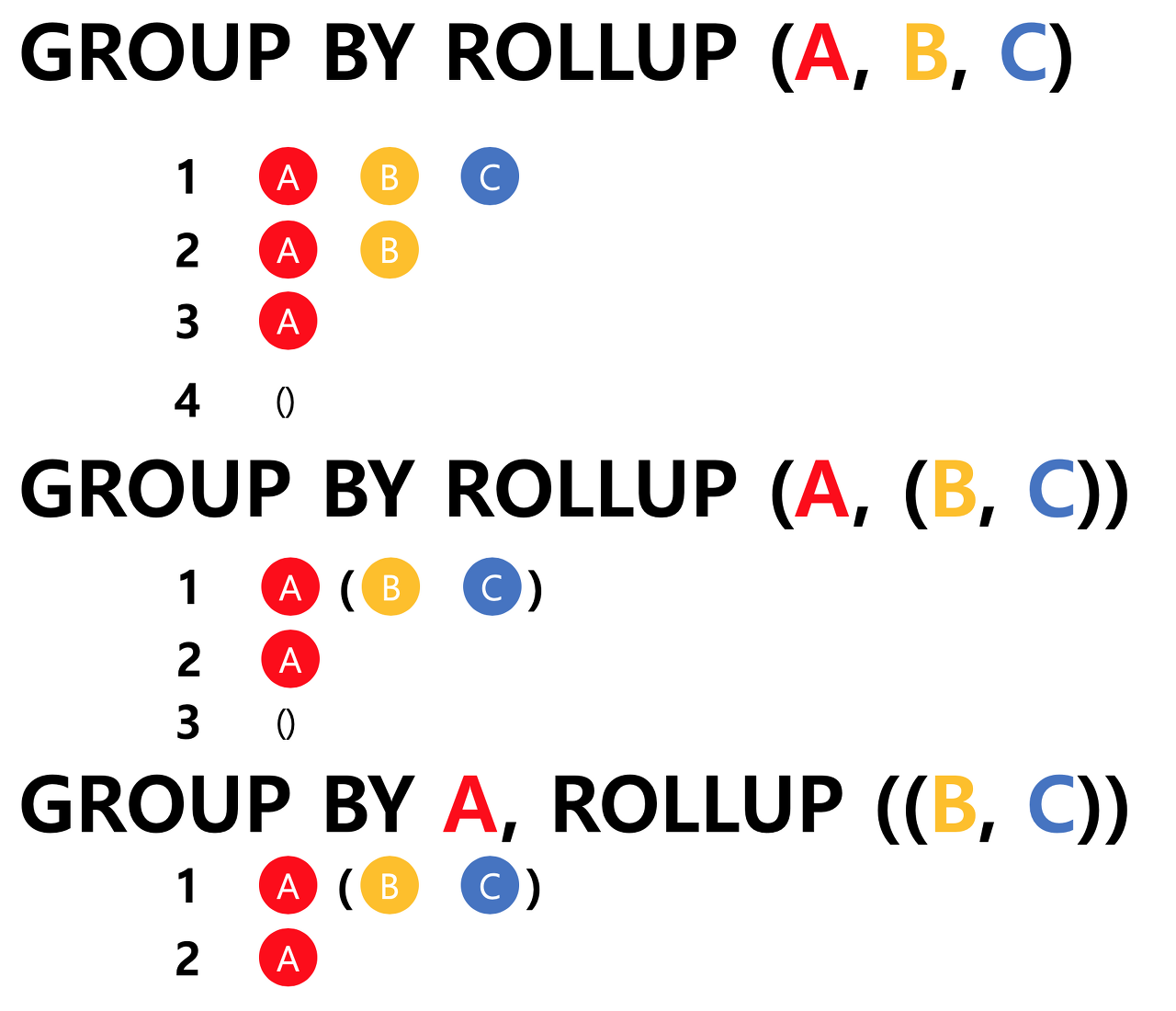
- ROLLUP의 인자로 들어온 칼럼을 오른쪽부터 하나씩 빼면서 GROUP을 만듭니다.
- "()"의 의미는 GROUP이 없는 즉, 전체에 대한 결과를 출력한다는 뜻 입니다. EX(SUM 함수 사용하면 전체 SUM 구한다는 뜻)
- 괄호로 묶여져 있는 컬럼은 하나로 본다는 뜻 입니다.
- ROLLUP 이전에 일반 컬럼과 GROUP BY 한다면, 일반 컬럼은 끝까지 남습니다.
컬럼개수 +1 의 개수 그룹핑
https://myjamong.tistory.com/191
실습_sql developer
ora1 계정 내 입력
ora1
8-1) 평균 급여 이상을 받는 '모든' 사원의 사원 번호, 성 및 급여를 출력하는 쿼리를 작성합니다.
급여의 오름차순으로 결과를 정렬합니다.
select employee_id, last_name, salary
from employees
where salary > (select avg(salary) from employees)
order by salary;
8-2) '성에 문자 "u"가 포함된' 사원과 같은 '부서'에 근무하는 모든 사원의 사원 번호와 성을 출력하는 쿼리를 작성합니다.
select employee_id, last_name
from employees
where department_id in (select department_id from employees where last_name like '%u%');
8-3) 부서 위치 ID(location_id) 가 1700인 사원의 성, 부서 ID 및 작업 ID를 출력하는 쿼리를 작성하세요
select last_name, department_id, job_id
from employees
where department_id in (select department_id from departments where location_id = 1700);
8-4) king(last_name) 에게 보고하는 모든 사원의 성과 급여를 표시하는 보고서를 작성
=매니저가 king인 모든 사원의 last_name, salary 작성
select last_name, salary
from employees
where manager_id in (select employee_id from employees where lower(last_name) = 'king');
8-5) executive 부서의 사원에 대해 부서ID, 성 및 직무 ID를 출력하는 쿼리 작성
select department_id, last_name, job_id
from employees
where department_id in (select department_id from departments where lower(department_name) = 'executive');
8-6) '평균보다 많은 급여를 받고' 성(last_name)에 문자 "u"가 포함된 사원이 '속한 부서에서' 근무하는 사원 정보를 출력하는 쿼리를 작성하세요.
오답)
select employee_id, last_name, salary
from employees
where department_id in (select department_id from employees where last_name like '%u%')
and salary > (select avg(salary) from employees);
cf. 8-2) '성에 문자 "u"가 포함된' 사원과 '같은 부서에 근무하는' '모든 사원'의 사원 번호와 성을 출력하는 쿼리를 작성합니다.
8-7) 커미션을 받는 사원의 부서 번호 및 급여 '둘 다 일치하는' 사원 정보를 출력하는 쿼리를 작성하세요 (다중열 서브쿼리)
select last_name, department_id, salary
from employees
where (department_id, salary) in (select department_id , salary from employees where commission_pct is not null);
8-8) 관리자가 아닌 사원을 출력하는 쿼리를 작성하세요 (not in 연산자 활용)
select last_name
from employees
where employee_id
not in (select manager_id from employees where manager_id is not null);
8-9) '사원이 없는' 모든 부서의 부서번호(department_id), 부서명(department_name)을 출력하는쿼리문을 작성하시오
select department_id, department_name, manager_id, location_id
from departments
where department_id in (select department_id from departments where department_id is null);
오답)
select *
from departments
where department_id not in (select department_id from employees where department_id is not null);
8-10) 어려움
소속 부서의 평균 급여보다 많이 받는 사원을 출력하는 쿼리 작성 .
사원의 성(last_name), 급여(salary), 부서 ID (department_id), '소속 부서의 평균 급여'(cf. 전체 부서의 평균 급여) 표시.
평균 급여 순으로 정렬, 평균 급여는 소수점 아래 2자리로 반올림하여 표시
출력 행 as 사용
select ename, salary, deptno,
select(avg(sal) from employees where department_id in (select department_id from employees)) dept_avg
from employees
where sal > (select avg(sal) from employees) ;
오답) 특정 부서 소속 ->셀프 조인 위한 테이블 분리, 알리아스 지정
select e.last_name ename, e.salary salary, e.department_id deptno, round(avg(a.salary),2) dept_avg
from employees e, employees a
where e.department_id = a.department_id
and e.salary > (select avg(salary) from employees where department_id = e.department_id)
group by e.last_name e.salary e.department_id
order by avg(a.salary);
8-11) 관리자가 아닌 사원 정보를 출력하는 쿼리를 exists 연산자를 이용해 작성
select employee_id, last_name
from employees
where employee_id not in (select manager_id from employees where manager_id is not null);
select employee_id, last_name
from employees
where not exists (select 1 from employees);
오답)
select employee_id, last_name
from employees o
where not exists (select 1 from employees e where o.employee_id = e.employee_id);
8-12) 모든 사원의 사원 ID, 성 및 부서 이름을 표시하는 쿼리를 작성합니다. 부서 이름 순서로 정렬합니다. 스칼라 서브쿼리를 사용하여 부서 이름을 표시하시오.
select employee_id, last_name,
(select department_name from departments where ) department
from employees;
오답)
select employee_id, last_name,
(select department_name from departments d where d.department_id = e.department_id) department
from employees e
order by department ;
8-13) 부서의 총 급여가 회사 전체 총급여의 8분의 1(1/8)을 초과하는 부서의 이름과 해당 부서의 총 급여를 표시하는 쿼리를 작성합니다. 부서별 총 급여를 구하는 부분은 with 절로 작성합니다.
with summary
(select department_name, sum(d.sal) dept_total
from departments d
where sal > (select sum(sal)*1/8 from employees e where e.department_id = d.department_id)
select department_name, dept_total from summary;
오답)
with summary as
(select d.department_name, sum(e.salary) dept_total
from employees e, departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id
group by d.department_name)
select department_name, dept_total
from summary
where sum(e.salary)> (select sum(dept_total)*1/8 from summary);
-- 9장 집합 연산자
-- union
--두 집합의 SELECT 절에 오는 칼럼의 개수가 동일해야 한다.
--select employee_id, job_id, department_id
--from employees
--union
--select employee_id, job_id
--from job_history;
select employee_id, job_id, department_id
from employees
union
select employee_id, job_id, department_id
from job_history;
--union all
select employee_id, job_id, department_id
from employees
union all
select employee_id, job_id, department_id
from job_history;
select employee_id, job_id, department_id
from job_history
union all
select employee_id, job_id, department_id
from employees;
select employee_id, last_name
from employees
union all
select department_id, department_name
from departments;
--두 집합의 SELECT 절에 오는 칼럼의 데이터형이 동일해야 한다.
--select employee_id, salary
--from employees
--union all
--select department_id, department_name
--from departments;
select employee_id, to_char(salary)
from employees
union all
select department_id, department_name
from departments;
select employee_id, salary, to_char(null)
from employees
union
select to_number(null), department_id, department_name
from departments;
--sql_실습
select deptno, ename, sal
from emp
where deptno in (10, 30)
union
select deptno, ename, sal from emp
where deptno in (20, 30) ;
select deptno, ename, sal from emp
where deptno in (10, 30)
union all
select deptno, ename, sal from emp
where deptno in (20, 30);
-- 질문 사항 (결과값이 다르게 나오는 이유?)
--8-9) '사원이 없는' 모든 부서의 부서번호(department_id), 부서명(department_name)을 출력하는쿼리문을 작성하시오
--
select *
from departments
where department_id in (select department_id from employees where department_id is null);
-- in/not in 연산식에서 null이 있으면 반환하지 않음
--오답)
select *
from departments
where department_id
not in
(select nvl(department_id,1) from employees);
-- nvl -> null이 반환되면 in연산식에서는 false가 돼서 반환되는 값이 없는데,
-- nvl을 써서 특정한 값을 반환하도록 함
select *
from departments
where department_id
not in (select department_id from employees where department_id is not null);
--9장 연습문제 풀이
--9-1)
select cust_id, prod_id
from sales_2000_11
intersect
select cust_id, prod_id
from sales_2000_12;
--9-2)
select cust_id, prod_id
from sales_2000_12
minus
select cust_id, prod_id
from sales_2000_11;
--9-3)
select cust_id, prod_id
from sales_2000_11
where cust_id = 173
union
select cust_id, prod_id
from sales_2000_12
where cust_id = 173;
--9-4)
select to_char(hire_date, 'yyyy') as hiredate, sum(salary) as sum_sal
from employees
group by to_char(hire_date, 'yyyy')
union
select 'total :', sum(salary) -- 전체 총합을 특정 문자열의 행으로 삽입함으로 그룹핑 불필요
from employees
order by hiredate;
-- select 보다 group by 먼저 실행되므로, select 에 기재한 as는 group by 절에 사용 불가
-- 리터럴 문자를 사용하면 특정 문자열을 행에 추가할 수 있음
--select 'what', sum(salary)
--from employees
--order by to_char(hire_date, 'yyyy');
--9-5)
select employee_id, last_name, department_id
from employees
where department_id = 10
union all
select employee_id, last_name, department_id
from employees
where department_id = 50
union all
select employee_id, last_name, department_id
from employees
where department_id = 20;
--
select employee_id, last_name, department_id
from employees
where department_id in (10, 50, 20);
-- 집합 연산자 사용시 주의 사항
-- order by 절은 마지막에만 사용
--select deptno, empno, ename, sal
--from emp
--where deptno in (10, 30)
--order by ename
--union
--select deptno, empno, ename, sal
--from emp
--where deptno in (20, 30)
--order by ename;
--
select deptno, empno, ename, sal
from emp
where deptno in (10, 30)
union
select deptno, empno, ename, sal
from emp
where deptno in (20, 30)
order by ename;
--
--
SELECT b.employee_id, a.department_name, b.job_id, 'now'
FROM departments a, employees b
WHERE a.department_id(+) = b.department_id
UNION ALL
SELECT b.employee_id, a.department_name, b.job_id, 'history'
FROM departments a, job_history b
WHERE a.department_id = b.department_id
order by 1;
/
-- 가독성을 위해 with 절 사용
WITH a AS
(select department_id, department_name from departments)
SELECT b.employee_id, a.department_name, b.job_id, 'now'
FROM a, employees b
WHERE a.department_id(+) = b.department_id
UNION ALL
SELECT b.employee_id, a.department_name, b.job_id, 'history'
FROM a, job_history b
WHERE a.department_id = b.department_id
order by 1
/
-- 10장. sql을 활용한 집계 및 분석
select department_id, job_id, sum(salary)
from employees
group by department_id, job_id;
select department_id, job_id, sum(salary)
from employees
group by rollup(department_id, job_id);
-- rollup은 괄호 안 컬럼에 대해 오른쪽 끝 컬럼부터 왼쪽 방향으로 진행하며, 컬럼의 set를 반환
-- (department_id, job_id) / job_id / department_id 각각 그룹핑
-- 10 (null) 4400 행은 department_id 기준 그룹핑 실행한 값
-- ROLLUP의 인자로 들어온 칼럼을 오른쪽부터 하나씩 빼면서 GROUP을 만듭니다.
-- 60번 빼고
-- union all 사용
select department_id, job_id, sum(salary)
from employees
group by department_id, job_id
union all
select department_id, null, sum(salary)
from employees
group by department_id
union all
select null, null, sum(salary)
from employees
group by ();
-- null은 형 변환 불필요
-- rollup(job_id)
-- department_id, job_id
-- department_id
-- 전체() 별 그룹핑(grand total) 누락
select department_id, job_id, sum(salary)
from employees
group by department_id,rollup(job_id);
select department_id, job_id, sum(salary)
from employees
group by job_id,rollup(department_id);
-- 부서별 급여 합만 출력
select deptno, empno, sum(sal)
from emp
group by deptno, rollup(empno);
-- 전체 급여 합만 출력
select deptno, empno, ename, sum(sal) s_sal
from emp
group by rollup ((ename, deptno, empno));
-- (ename, deptno, empno)
-- () grand total
--부서별 합계와 전체 grand total 출력
select deptno, empno, ename, sum(sal) s_sal
from emp
group by rollup (deptno, (ename, empno));
-- 그룹핑
--deptno, empno, ename
--deptno
--() grand total
-- cube 연산자= 인자 갯수 ^2 만큼 그룹 개수 생성 (부분 집합 개념 유사)
select department_id, job_id, sum(salary)
from employees
where department_id < 60
group by cube (department_id, job_id);
-- GROUPING SETS
-- 단일 인자로 인한 그룹핑은 포함하지 않고, 복수 인자로 그룹핑하는 경우 활용 가능 (부분 집합 중 일부로 그룹화)
SELECT department_id, job_id, manager_id, AVG(salary)
FROM employees
GROUP BY GROUPING SETS ((department_id, job_id, manager_id),
(department_id, manager_id),
(job_id, manager_id));
select department_id, job_id, manager_id, avg(salary)
from employees
group by grouping sets ( (department_id, job_id), (job_id, manager_id));
--group by grouping sets (a, b, c)
--group by a
--union all
--group by b
--union all
--group by c
--group by grouping sets (a, (b, c))
--a, (b,c) 2개 인자로 그룹핑 후 union all 연산 결과값과 동일
select deptno, empno, ename, sum(sal) s_sal
from emp
group by grouping sets (deptno, rollup(ename, empno))
order by s_sal;
-- 4개 인자로 그룹핑 후 union all 연산 결과값과 동일
--deptno
--ename, empno
--ename
--()
select deptno, null, null, sum(sal) s_sal
from emp
group by deptno
union all
select null, ename, empno, sum(sal) s_sal
from emp
group by ename, empno
union all
select null, ename, null, sum(sal) s_sal
from emp
group by ename
union all
select null, null, null, sum(sal) s_sal
from emp
group by ()
order by s_sal;
-- GROUPING Function : 예제
SELECT department_id, job_id, sum(salary),
GROUPING(department_id), GROUPING(job_id)
FROM employees
WHERE department_id <= 30
GROUP BY ROLLUP(department_id, job_id);
-- GROUPING Function 활용, having 절에 조건 부여해 grand total 제외 가능
SELECT department_id, job_id, sum(salary),
GROUPING(department_id), GROUPING(job_id)
FROM employees
WHERE department_id <= 30
GROUP BY ROLLUP(department_id, job_id)
having GROUPING(department_id) != 1;
--grand total 제외 (1) ROLLUP 일부 컬럼에만 부여
SELECT DEPARTMENT_ID,
JOB_ID, SUM(SALARY)
FROM EMPLOYEES
WHERE DEPARTMENT_ID <= 30
GROUP BY DEPARTMENT_ID, ROLLUP(JOB_ID);
--grand total 제외 (2) grouping_function, having 절 활용
SELECT DEPARTMENT_ID,
JOB_ID, SUM(SALARY)
FROM EMPLOYEES
WHERE DEPARTMENT_ID <= 30
GROUP BY ROLLUP(DEPARTMENT_ID, JOB_ID)
HAVING GROUPING(DEPARTMENT_ID) = 0;
SELECT department_id, job_id, sum(salary),
GROUPING(department_id), GROUPING(job_id)
FROM employees
WHERE department_id <= 30
GROUP BY ROLLUP(department_id, job_id)
having GROUPING(department_id) != 1;
-- 총계만 출력
-- 전체 급여 합만 출력 (1)
--select deptno, empno, ename, sum(sal) s_sal
--from emp
--group by rollup ((ename, deptno, empno));
-- grand_total만 출력
SELECT department_id, job_id, sum(salary),
GROUPING(department_id), GROUPING(job_id)
FROM employees
GROUP BY ROLLUP(department_id, job_id)
having GROUPING(department_id) = GROUPING(job_id);
-- grand_total, sub_total 출력
SELECT department_id, job_id, sum(salary),GROUPING(department_id), GROUPING(job_id)
FROM employees
GROUP BY ROLLUP(department_id, job_id)
having case when GROUPING(department_id) =1 then '총계';
when GROUPING(job_id)=1 then '소계';
-- grand_total 총계, sub_total 소계 출력
select decode(grouping(department_id),0,to_char(department_id),'총계') department_id,
decode(grouping(job_id),0,job_id,'소계') job_id, sum(salary),
grouping(department_id), grouping(job_id)
from employees
group by rollup(department_id, job_id);
--select case when grouping(department_id) =1 then '총계' department_id,
-- case when grouping(job_id)=1 then '소계' job_id, sum(salary),
-- grouping(department_id), grouping(job_id)
--from employees
--group by rollup(department_id, job_id);
SELECT
(case when grouping(department_id) = 1 then '총계' else to_char(department_id) end) as department_id,
(case when grouping(job_id) = 1 and grouping(department_id) = 1 then ' '
when grouping(job_id) = 1 then '소계' else job_id end) as job_id,
sum(salary)
FROM employees
GROUP BY ROLLUP(department_id, job_id);
-- 분석 함수
-- SELECT 절과 ORDER BY 절에서만 사용 가능합니다
-- 분석함수의 분석 대상 정의 -> over 절
-- OVER( ) : SELECT 명령 수행 결과 전체를 분석 대상(window)으로 합니다.
-- GROUP BY 절을 사용하지 않고,
-- 조회된 각 행에 그룹으로 집계된 값을 표시할 때 OVER 절과 함께 PARTITION BY 절을 사용하면 된다.
-- over () 은 전체 행을 분석대상으로 고려
-- count (*) over () 행 별로(건건이) 갯수를 세서 디스플레이
-- sum(sal) ... group by job
-- sum(sal) over (partition by job)
SELECT department_id, employee_id, last_name,
COUNT(*) all_cnt
FROM employees
WHERE department_id = 50
group by department_id, employee_id, last_name;
-- group by 한 행당 연산 진행 -> 1 추출
SELECT department_id, employee_id, last_name,
COUNT(*) OVER() AS all_cnt
FROM employees
WHERE department_id = 50;
--OVER()?
--COUNT의 범위를 () 안의 값으로 지정
--아무것도 없으면 테이블 전체에 대한 내용
--그래서 테이블 전체에 대한 카운트 진행-> 5TEST 계정 내 입력
TEST
select count(*)
from sales
where cust_id <= 10
group by cust_id;
SELECT cust_id, sum(COUNT(amount_sold)) over() AS total_cnt
from sales
where cust_id <= 10
group by cust_id;
--OVER()?
--COUNT의 범위를 () 안의 값으로 지정
--아무것도 없으면 테이블 전체에 대한 내용
--그래서 테이블 전체에 대한 카운트 진행-> 5
--
SELECT employee_id, department_id, salary,
SUM(salary) OVER(PARTITION BY department_id) AS dept_sal
FROM employees;
-- SELECT employee_id, department_id, salary, SUM(salary) AS dept_sal
-- FROM employees
-- group by employee_id, department_id, salary;
SELECT employee_id, department_id, salary,
round(avg(salary) OVER(PARTITION BY department_id), 0) AS dept_sal
FROM employees;
SELECT employee_id, job_id, salary,
round(avg(salary) OVER(PARTITION BY job_id), 0) AS dept_sal
FROM employees;
SELECT employee_id, department_id, job_id, salary,
round(avg(salary) OVER(PARTITION BY department_id, job_id), 0) AS dept_sal
FROM employees;
-- sal의 누적값 계산
SELECT employee_id, salary,
SUM(salary) OVER(ORDER BY employee_id) AS total_sal
FROM employees;
-- 분석 대상(window)는 본인을 포함해서 위쪽 sal을 누적으로 더해나가겠다
-- +) partition by , order by를 함께 사용 가능
SELECT employee_id, salary,
SUM(salary) OVER(ORDER BY employee_id desc) AS total_sal
FROM employees;
-- +) partition by , order by를 함께 사용 가능 (해당 부서 안에 order by를 실행, 부서별 누적값 추출)
SELECT department_id,employee_id, salary,
SUM(salary) OVER(partition BY department_id order by employee_id asc) AS total_sal
FROM employees;
-- 실습 교재 68p
-- 분석 함수 실행 순서는 가장 마지막임
--※ 잘못 작성된 명령어 -- 분석함수는 가장 마지막에 수행되므로 81 년생들의 평균임
--- 그룹핑 후 분석함수 실행 (평균 산출시 누락된 값 존재)
SQL>
SELECT empno, ename, sal, hiredate, deptno,
ROUND(AVG(sal) OVER(PARTITION BY deptno),2) AS AVG_SAL
FROM emp
WHERE hiredate BETWEEN TO_DATE('1981/01/01','YYYY/MM/DD')
AND TO_DATE('1981/12/31','YYYY/MM/DD');
---> 인라인 뷰 사용 필
--- EMP 테이블에서 1981 년에 입사한 사원 정보와 소속 부서의 평균 급여를 출력합니다.
SELECT empno, ename, sal, hiredate, deptno, avg_sal,
FROM (SELECT empno, ename, sal, hiredate, deptno, ROUND(AVG(sal) OVER(PARTITION BY deptno),2)
AS AVG_SAL
FROM emp)
WHERE hiredate BETWEEN TO_DATE('1981/01/01','YYYY/MM/DD')
AND T O_DATE('1981/12/31','YYYY/MM/DD') ;
--첫 row 부터 자기 자신 (커런트 로) 까지 sal 합계 구하겠다
--UNBOUNDED PRECEDING : 윈도우의 시작 위치가 첫번째 ROW
--
-- UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING : 윈도우의 마지막 위치가 마지막 ROW
--
-- CURRENT ROW : 윈도우의 시작 위치가 현재 ROW
-- ROW : 부분집합인 윈도우 크기를 물리적인 단위로 행 집합을 지정
SELECT employee_id, salary,
SUM(salary) OVER(ORDER BY employee_id ROWS
BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING
AND CURRENT ROW) AS sum_sal
FROM employees;
-- RANGE : 논리적인 주소에 의해 행 집합을 지정
-- hiredate=2001/01/13, 입사일 4/13~10/13의 avg(sal) 출력
-- 4/13~10/13에 입사한 동기들의 평균 sal을 알고 싶어!!
SELECT employee_id, TO_CHAR(hire_date, 'YYYY/MM/DD') hiredate, salary,
AVG(salary) OVER(ORDER BY hire_date RANGE
BETWEEN INTERVAL '3' MONTH PRECEDING
AND INTERVAL '3' MONTH FOLLOWING) AS avg_sal
FROM employees;
-- rank 는 order by와 함께 사용 필
SELECT employee_id, department_id, salary,
RANK() OVER(ORDER BY salary DESC) "Rank"
FROM employees;
-- 부서별 순위 출력
SELECT employee_id, department_id, salary,
RANK() OVER(PARTITION BY department_id
ORDER BY salary DESC) "Rank"
FROM employees;
--DENSE_RANK()
SELECT employee_id, department_id, salary,
DENSE_RANK() OVER(ORDER BY salary DESC) "Dense_Rank"
FROM employees;
--ROW_NUMBER()
SELECT employee_id, department_id, salary,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(ORDER BY salary DESC) "Row_Number"
FROM employees;
-- RANK(), DENSE_RANK(), ROW_NUMBER() 비교
SELECT employee_id, department_id, salary,
RANK() OVER (ORDER BY salary DESC) "Rank",
DENSE_RANK() OVER (ORDER BY salary DESC) "Dense_Rank",
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(ORDER BY salary DESC) "Row_Number"
FROM employees;
--
-- cume_dist : 누적 분포(상위 %) 나타냄
-- sal desc : sal 이 높은 순으로 정렬
-- ntile(5) : 5개 그룹으로 분할
select ename, sal,
round(cume_dist() over(order by sal desc),2) cume_dist,
ntile(5) over(order by sal desc) grade
from emp;
-- 분석함수 마다 over 절 붙여야 수행됨
-- Aggregate Family
SELECT employee_id, department_id, salary,
SUM(salary) OVER() sum,
TRUNC( AVG(salary) OVER() ) avg,
MIN(salary) OVER() min,
MAX(salary) OVER() max
FROM employees;
--OVER()
--COUNT의 범위를 () 안의 값으로 지정
--아무것도 없으면 테이블 전체에 대한 내용으로 연산 진행
--cf. group by 한 행당 연산 진행
--SUM(salary) OVER() sum ->테이블 전체의 salary의 총계를 반환
--cf.
--SELECT employee_id, department_id, salary, SUM(salary) sum
--FROM employees
--group by employee_id, department_id, salary;
---> (employee_id, department_id, salary) 당 하나의 salary의 소계를 반환
-- 각 Window에서 하나의 행 만을 추출하려는 경우(FIRST/LAST) (인라인뷰 대체 가능)
--MAX(last_name) KEEP (DENSE_RANK FIRST
--ORDER BY salary DESC) max_ename,
--sal 순위 1인 last_name을 가져오되, sal의 공동 순위 존재 시(공동 1위) max 통해 여러개의 last_name 을 asc 진행
--MIN(last_name) KEEP (DENSE_RANK LAST
--ORDER BY salary DESC) min_ename
--sal 순위 꼴등인 last_name을 가져오되, sal의 공동 순위 존재 시(공동 꼴찌) min 통해 여러개의 last_name 을 asc 진행
SELECT department_id,
MAX(last_name) KEEP (DENSE_RANK FIRST
ORDER BY salary DESC) max_ename,
MIN(last_name) KEEP (DENSE_RANK LAST
ORDER BY salary DESC) min_ename
FROM employees
GROUP BY department_id;
--
SELECT department_id, last_name, salary ,
MAX(last_name) KEEP (DENSE_RANK FIRST
ORDER BY salary DESC) over(partition by department_id) max_ename,
MIN(last_name) KEEP (DENSE_RANK LAST
ORDER BY salary DESC) over(partition by department_id) min_ename
FROM employees;
--OVER 절은 분석대상(window) 뒤에 서술 필, 단독 사용 불가
---- +) partition by , order by를 함께 사용 가능 (해당 부서 안에 order by를 실행, 부서별 누적값 추출)
--SELECT department_id,employee_id, salary,
-- SUM(salary) OVER(partition BY department_id order by employee_id asc) AS total_sal
--FROM employees;
-- sql lag, lead 함수로 이전행과 다음행 조회하기
-- 이전 또는 이후 행의 데이터를 함께 조회할 수 있는 기능
-- 이전 행의 값과 현재 값을 비교하거나 계산시 유용
-- 5일 전 소비 값과 현재 소비값을 비교해서 오른 행에만 값 출력 (lag 함수 사용)
-- select *, lag(spending, 5) over (order by date) as lag_spending from table;
-- 5일 후 소비 값과 현재 소비값을 비교해서 오른 행에만 값 출력 (lead 함수 사용)
-- select *, lead(spending, 5) over (order by date) as lead_spending from table;
-- LAG()
SELECT employee_id, salary,
LAG(salary, 5, 0) OVER(ORDER BY employee_id) "Before_Salary"
FROM employees;
-- LEAD()
SELECT employee_id, salary,
LEAD(salary, 19, 0) OVER(ORDER BY employee_id) "Next_Salary"
FROM employees;