Easy - DFS, BFS, 탐색
RunTime : 11 ms / Memory : 18.25 MB
문제
You are given the array paths, where paths[i] = [cityAi, cityBi] means there exists a direct path going from cityAi to cityBi. Return the destination city, that is, the city without any path outgoing to another city.
It is guaranteed that the graph of paths forms a line without any loop, therefore, there will be exactly one destination city.
풀이 1. DFS 풀이
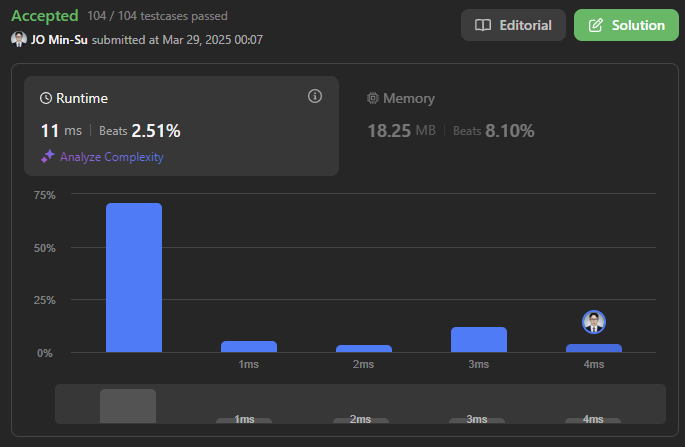
- 처음 문제를 보고 직관적으로 떠올린 풀이
- 단순하게
paths에서 연결된 노드들을 찾아 탐색한다. - 더이상 탐색할 곳이 없다면
return
class Solution:
def destCity(self, paths: List[List[str]]) -> str:
visited = [0] * len(paths)
res = ""
def dfs(std):
nonlocal res
nxt = False
for i in range(len(paths)):
if visited[i] == 0 and paths[i][0] == std:
visited[i] = 1
dfs(paths[i][1])
nxt = True
if not nxt:
res = std
dfs(paths[0][0])
return res
풀이 2. BFS 풀이
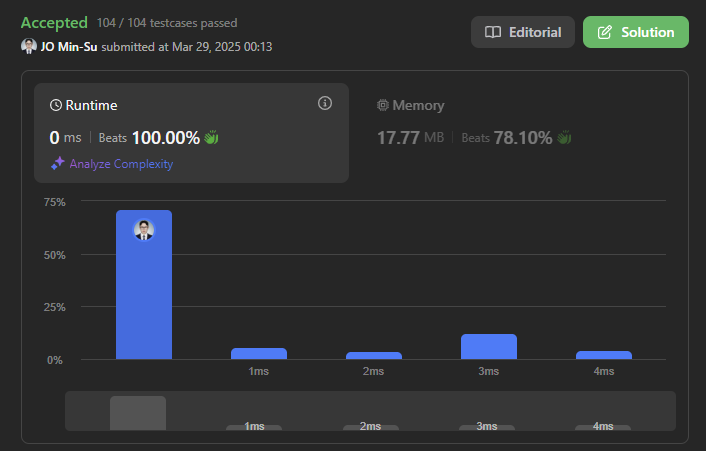
paths가 간단한 2차원 리스트 구성이기 때문에bfs도 효과적인 풀이가 될 수 있다.
from collections import deque, defaultdict
class Solution:
def destCity(self, paths: List[List[str]]) -> str:
graph = defaultdict(list)
for start, end in paths:
graph[start].append(end)
st_city = paths[0][0]
q = deque()
q.append(st_city)
dest = st_city
while q:
node = q.popleft()
dest = node
if node in graph:
for nxt in graph[node]:
q.append(nxt)
return dest
풀이 3. 직관적인 풀이
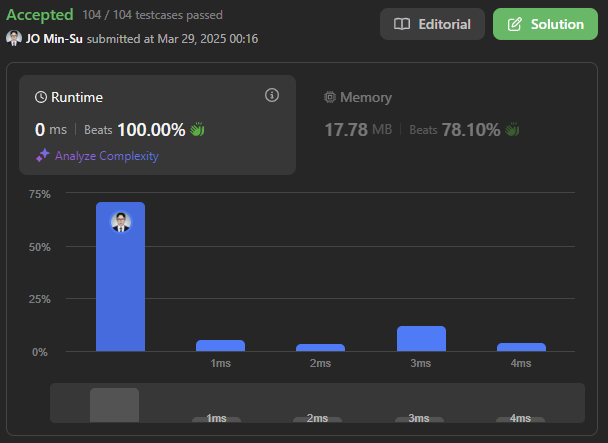
- 문제의 본질을 바라보자
- 결국
A에서 출발해B로 도착하는데,
B에서 출발하는 경로가 없다면?- 정답은 당연하게
B
- 정답은 당연하게
class Solution:
def destCity(self, paths: List[List[str]]) -> str:
start_cities = {a for a, _ in paths}
for _, b in paths:
if b not in start_cities:
return b
