The world of cryptocurrency is exciting, offering new investment opportunities and a glimpse into the future of finance. However, for a beginner, figuring out how to buy cryptocurrency safely—navigating terms like Bitcoin, Ethereum, exchanges, and wallets—can feel overwhelming and even a little risky. The good news is that with the right knowledge and a cautious approach, you can confidently take your first steps into crypto investing. This guide will walk you through the essential steps to buy cryptocurrency safely, ensuring you protect your assets from the start.
Understanding the Landscape: Key Terms for Safe Crypto Buying
Before diving in, let's clarify a few crucial concepts. Knowing these will help you make informed decisions and understand where potential risks lie.
- Cryptocurrency: Digital or virtual tokens that use cryptography for security. They operate on a decentralized technology called blockchain.
- Blockchain: A distributed, immutable ledger that records transactions. Its decentralized nature is a key security feature but also means there's no central authority to appeal to if things go wrong.
- Exchanges: Platforms where you can buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies. They are the most common way for beginners to purchase crypto.
- Brokers: Simplified platforms that offer an easier interface for buying crypto, often interacting with exchanges behind the scenes. They might have limitations on moving your crypto.
- Wallets: Digital tools used to store your cryptocurrency. They come in various forms (hot, cold, software, hardware), each with different security implications. Understanding wallets is crucial for safety.
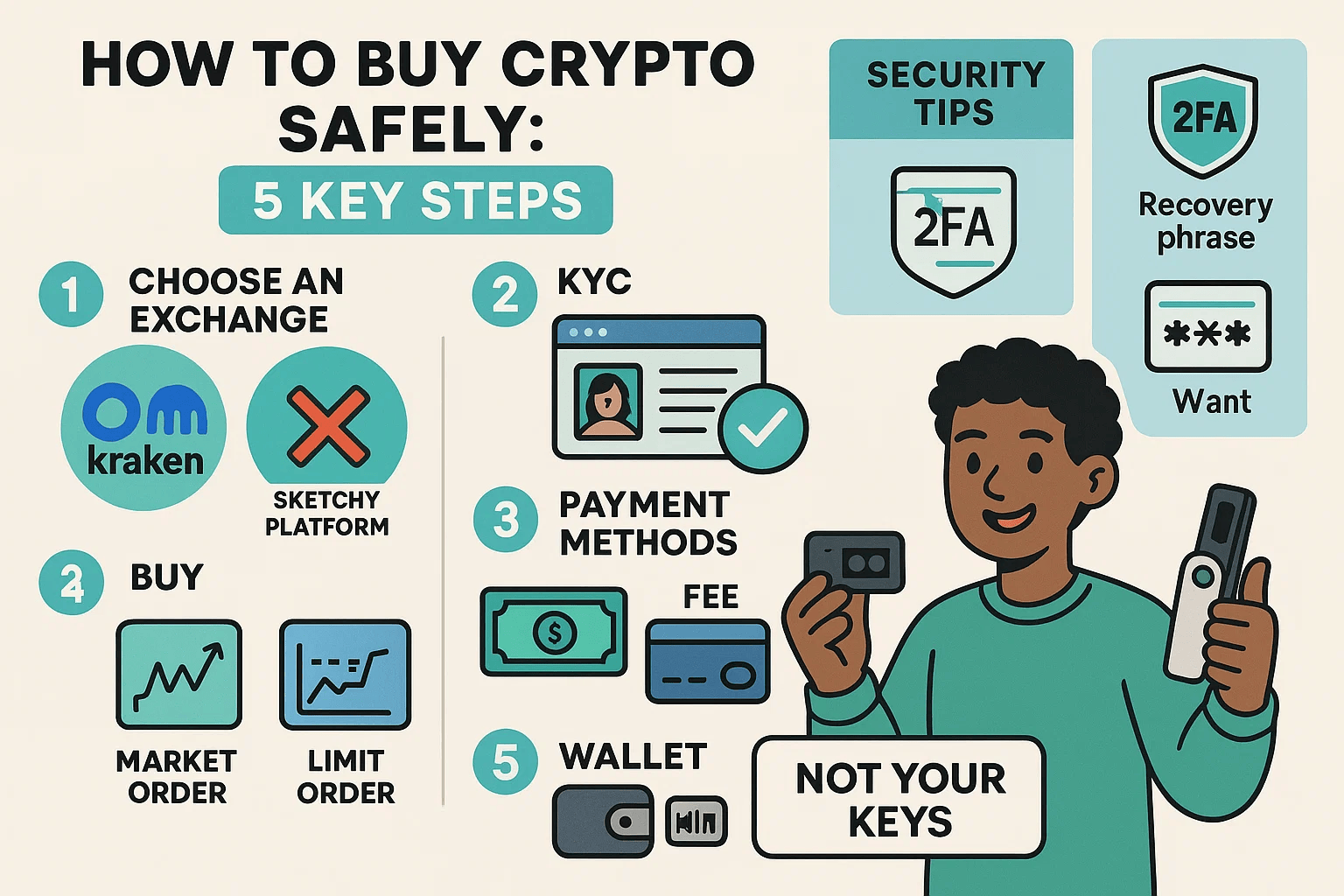
Step 1: Choosing a Secure and Reputable Platform
Your first major decision is selecting where to buy your cryptocurrency. This choice significantly impacts your security. You'll generally choose between a cryptocurrency exchange or a crypto broker.
What Is a Cryptocurrency Exchange?
A cryptocurrency exchange is a dedicated platform for trading digital assets.
- Pros: Often offer a wider variety of cryptocurrencies, more advanced trading features, and potentially lower fees for standard trades.
- Cons for Beginners: Can be complex and intimidating. The security of your crypto often relies on the exchange's own security measures if you leave your assets there.
- Examples: Coinbase, Binance, Kraken, Gemini.
What Is a Cryptocurrency Broker?
Brokers provide a simpler, more user-friendly interface for buying cryptocurrency.
- Pros: Easier to navigate for beginners.
- Cons for Beginners: May charge higher fees or build costs into the spread. Crucially, some brokers (like Robinhood or SoFi, as mentioned in the Forbes article) may not allow you to move your crypto off their platform to a personal wallet, which limits your control and security options.
- Examples: Robinhood, SoFi, eToro.
Key Safety Features to Look For in a Platform:
Regardless of whether you choose an exchange or a broker, prioritize these safety features:
- Security Measures: Look for platforms that offer Two-Factor Authentication (2FA), cold storage for a majority of customer funds, and insurance policies against hacks (though these are rare and may not cover individual losses).
- Regulatory Compliance: Platforms that comply with regulations in your jurisdiction (e.g., FinCEN registration in the U.S.) are generally more trustworthy.
- Reputation & Reviews: Research the platform's history. Look for user reviews focusing on security, customer support, and ease of fund withdrawal.
- Transparency: Clear information about fees, security practices, and how they handle user assets.
- Fiat On-Ramps: Ensure the platform allows you to deposit traditional currency (like USD, EUR) from your bank account. Some exchanges only allow crypto-to-crypto trades.
For beginners focused on safety, an exchange that allows you to withdraw your crypto to a personal wallet is generally a better long-term choice, even if it has a slightly steeper learning curve.
Step 2: Creating Your Account Securely
Once you've selected a platform, you'll need to create an account. This process itself is a critical security checkpoint.
- Use a Strong, Unique Password: Do not reuse passwords from other accounts. Use a password manager to generate and store complex passwords.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) Immediately: This is non-negotiable for security. 2FA adds an extra layer of protection by requiring a second form of verification (e.g., a code from an authenticator app like Google Authenticator or Authy) in addition to your password. Avoid SMS-based 2FA if possible, as it's more vulnerable to SIM-swapping attacks.
- Secure Your Email Account: The email linked to your crypto account is a prime target. Ensure it also has a strong, unique password and 2FA enabled.
Understanding the Verification Process (KYC)
Reputable platforms will require you to verify your identity, a process known as Know Your Customer (KYC). This typically involves providing:
- Personal information (name, address, date of birth)
- A copy of a government-issued ID (driver's license, passport)
- Sometimes, a selfie to match your ID photo.
While sharing personal data might feel intrusive, KYC is a crucial anti-fraud measure and a sign of a compliant, more secure platform. It helps prevent money laundering and illicit activities. Platforms that don't require KYC might seem convenient but can be riskier.
Step 3: Funding Your Account Safely
With your account set up and secured, you'll need to deposit funds.
Safe Deposit Methods:
- Bank Transfer (ACH or Wire): Generally considered a secure way to deposit funds. ACH transfers might take a few days to clear, while wire transfers are often faster but may cost more.
- Debit Card: Can be convenient for smaller amounts, but ensure you're on the legitimate platform's site (check for HTTPS and the correct domain).
A Word of Warning on Credit Cards:
While some platforms allow credit card deposits, this is generally not recommended for beginners and carries significant risks:
- High Fees: Credit card companies often treat crypto purchases as cash advances, which come with hefty fees (e.g., 3-5% from the card issuer) and higher interest rates. The exchange may also charge its own deposit fee.
- Debt Risk: Investing in volatile assets like cryptocurrency with borrowed money is extremely risky. If the market drops, you could be left with debt you can't easily repay.
- Impulse Buys: The ease of credit can lead to investing more than you can afford to lose.
Stick to depositing funds you already have and can afford to risk.
Step 4: Making Your First Crypto Purchase (and Common Pitfalls)
Once your funds are available, you're ready to buy.
- Choose Your Cryptocurrency: For beginners, starting with well-established cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC) or Ethereum (ETH) is often advised due to their larger market capitalization, longer track record, and more extensive resources available for research.
- Understand Ticker Symbols: Each cryptocurrency has a unique ticker symbol (e.g., BTC for Bitcoin, ETH for Ethereum, DOGE for Dogecoin). Double-check this before purchasing.
- Start Small: Only invest what you can afford to lose. Cryptocurrency markets are highly volatile. Beginners should start with small amounts to understand the process and market fluctuations without significant financial risk.
- Fractional Shares: You don't need to buy a whole Bitcoin or Ethereum. Most platforms allow you to purchase fractions of a coin, making it accessible even with a small budget.
Avoiding FOMO and Emotional Investing:
The "Fear Of Missing Out" (FOMO) can lead to impulsive decisions. Resist the urge to buy a cryptocurrency just because its price is skyrocketing or because you saw it hyped on social media.
- Do Your Own Research (DYOR): Understand what you're investing in. Don't rely solely on tips from friends or online influencers.
- Avoid "Pump and Dump" Schemes: Be wary of lesser-known coins being aggressively promoted online. These can be schemes to inflate the price artificially before the promoters sell off, leaving new investors with losses.
Step 5: Securing Your Cryptocurrency After Purchase
This is arguably the most critical step for long-term safety. Where you store your crypto after buying it matters immensely.
Exchange Wallets: Convenience vs. Risk
When you buy crypto on an exchange, it's typically held in a wallet managed by the exchange.
- Convenience: Easy to access for trading.
- Risk: You don't truly control the private keys to this crypto. If the exchange gets hacked, goes bankrupt, or restricts withdrawals, you could lose your assets. The saying in crypto is: "Not your keys, not your coins." While major exchanges have robust security, they remain a target.
Personal Crypto Wallets: Taking Control
For enhanced security, especially for amounts you don't plan to trade actively, consider moving your crypto to a personal wallet.
- Hot Wallets (Software Wallets): These are software programs or mobile apps that store your crypto. They are connected to the internet.
- Pros: More secure than leaving crypto on an exchange (you control the keys), convenient for frequent use.
- Cons: Still vulnerable to online threats like malware or phishing if your device is compromised.
- Examples: Exodus, Trust Wallet, MetaMask (primarily for Ethereum and compatible tokens).
- Cold Wallets (Hardware Wallets): These are physical devices (like a USB stick) that store your private keys offline.
- Pros: The most secure option as they are isolated from internet-based attacks.
- Cons: Less convenient for quick transactions, have an upfront cost. Can be lost or damaged if not handled carefully (though recovery is possible with the seed phrase).
- Examples: Ledger Nano S/X, Trezor Model T.
Protecting Your Private Keys and Seed Phrases:
When you set up a personal wallet (hot or cold), you'll be given a private key and/or a seed phrase (recovery phrase).
- This is the master key to your crypto. Anyone with access to it can access your funds.
- Guard it meticulously. Write it down on paper (or multiple papers stored in different secure locations), or use a metal seed storage solution.
- Never store it digitally (e.g., in a text file on your computer, in an email, or in cloud storage).
- Never share it with anyone. Legitimate support will never ask for your seed phrase.
Bonus: Common Crypto Scams for Beginners to Avoid
Awareness is your first line of defense against scams:
- Phishing Scams: Fake emails, texts, or websites designed to look like legitimate platforms to steal your login credentials or private keys. Always double-check URLs and be wary of unsolicited communications.
- Giveaway Scams: Promises of "send 1 ETH, get 2 ETH back" are always scams, often promoted by hacked social media accounts of public figures.
- Impersonation Scams: Scammers posing as support staff from exchanges or wallet providers, asking for your seed phrase or remote access to your computer.
- Fake Mobile Apps: Malicious apps mimicking legitimate crypto wallets or exchanges. Only download apps from official app stores and verify the developer.
- Investment Scams (Ponzi/Pyramid Schemes): Promises of unrealistically high, guaranteed returns.
Alternative (Potentially Safer) Routes for Crypto Exposure
If direct crypto purchase feels too risky, consider these:
- Crypto Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): These are becoming available in some regions (like Bitcoin ETFs in the U.S.). They allow you to invest in cryptocurrency through a traditional brokerage account, offering diversification and regulatory oversight. However, you don't own the underlying crypto directly.
- Stocks of Companies in the Crypto Space: Investing in publicly traded companies involved in blockchain technology, crypto mining (e.g., Nvidia, as mentioned by Forbes), or those holding significant crypto assets (e.g., PayPal, Square). This offers indirect exposure with the familiarity of stock market investing.
Conclusion
Buying cryptocurrency as a beginner can be a rewarding experience, but prioritizing safety is paramount. By choosing reputable platforms, implementing strong security practices for your accounts, understanding the risks associated with different storage methods, and being vigilant against scams, you can navigate the crypto world more confidently.
Remember to start small, only invest what you can afford to lose, and continuously educate yourself. The cryptocurrency landscape is always evolving, and staying informed is key to protecting your investments.
Ready to take the next step with a deeper understanding? Explore more insights and guides on how to buy cryptocurrency at CryptoCrafted.org.
