정의
도로 교통망 같은 곳에서 나타날 수 있는 그래프에서 꼭짓점 간의 최단 경로를 찾는 알고리즘
그래프의 최단 경로를 찾는 문제
-
하나의 정점에서 다른 하나의 정점까지의 최단 경로를 구하는 문제(single source and single destination shortest path problem)
-
하나의 정점에서 다른 모든 정점까지의 최단 경로를 구하는 문제(single source shortest path problem) => 다익스트라
-
하나의 목적지로가는 모든 최단 경로를 구하는 문제(single destination shortest path problem)
-
모든 최단 경로를 구하는 문제(All pairs shortest path problem)
제한
- 간선들은 모두 양의 가중치를 가진다.
기본 로직(Array)
- 시간 복잡도 : (V는 정점의 개수)
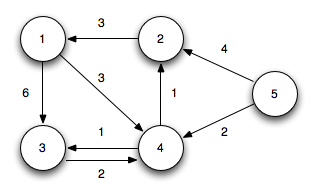
시작 정점을 5로 두고 시작한다.
5번의 가중치를 0으로 두고 아직 나머지의 가중치는 모르니 무한대로 둔다.
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 |
5번 노드에서 경로가 짧은 정점을 고른다.
5-2 경로의 경우 와 4 중 짧은 것을 고른다.
즉 dist[2] = Math.min(dist[2], dist[5] + adj[5][2])이 된다. 이는 dist[5] + adj[5][2], 4이다.
5-4 경로도 마찬가지로 2가 된다.
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | ||||
| 0 | 2 | 4 |
그리고 2의 가중치를 가진 4번 노드는 가장 짧으므로 해당 노드에서 인접한 노드를 찾는다.
인접 노드는 2와 3이다.
위의 공식과 같이 갱신해준다.
3번 노드의 경우 와 dist[4] + adj[4][3] 즉 2+1로 3이다.
2번 노드의 경우 4와 dist[4] + adj[4][2] 즉 2+1 로 3이다.
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | ||||
| 0 | 2 | 4 | ||
| 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
3과 2 둘다 가중치가 같다. 3에서 인접한 노드는 4
dist[4] 와 dist[3]+adj[3][4] 중 작은 것은 기존 값이다.
갱신하지 않는다.
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | ||||
| 0 | 2 | 4 | ||
| 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
2에서 인접한 노드는 1 하나이다.
와 dist[2] + adj[2][1] 즉 3+3=6이다.
1에서 인접한 노드는 4와 3
계산해도 갱신되지 않는다.
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | ||||
| 0 | 2 | 4 | ||
| 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 | |
| 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 6 |
결과는 다음과 같다.
BFS와 유사한 느낌으로 탐색한다는 것을 알 수 있다.
우선순위 큐(Heap)을 이용한 다익스트라
- 시간복잡도 : (V는 정점의 개수, E는 한 정점의 주변 노드)

모든 정점들을 우선순위 큐에 넣는다.
우선순위는 가중치이다.
기본적으로 우선순위 큐에 넣을 때 5를 제외한 나머지 정점들은 가중치를 무한대로 둔다.
- Priority Queue
| Index | 가중치 | 이전 정점 |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0 | -1 |
| 4 | NULL | |
| 3 | NULL | |
| 2 | NULL | |
| 1 | NULL |
- dist 배열
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 |
큐에서 가장 위의 값을 꺼낸다.
기존 배열의 값과 비교하여, 같거나 크면 연산한다.
0으로 둘다 같으므로, 5와 인접한 정점을 찾고, dist 배열보다 작은 가중치라면 Queue에 넣고 배열도 갱신해준다.
| Index | 가중치 | 이전 정점 |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | 2 | 5 |
| 2 | 4 | 5 |
| 4 | NULL | |
| 3 | NULL | |
| 2 | NULL | |
| 1 | NULL |
- dist 배열
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2 | 4 |
큐에서 값을 꺼내어 기존 배열과 비교하는 위의 연산을 수행한다.
4를 꺼내었을때의 결과는 인접한 2와 3을 연산하는 것이다.
| Index | 가중치 | 이전 정점 |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 3 | 3 | 4 |
| 2 | 4 | 5 |
| 4 | NULL | |
| 3 | NULL | |
| 2 | NULL | |
| 1 | NULL |
- dist 배열
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
큐에서 값을 꺼내어 기존 배열과 비교하는 위의 연산을 수행한다.
2를 꺼내었을때의 결과는 인접한 1을 연산하는 것이다.
우선순위가 가중치이기 때문에 6인 1번 노드는 아래로 내려간다.
| Index | 가중치 | 이전 정점 |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 3 | 4 |
| 2 | 4 | 5 |
| 1 | 6 | 2 |
| 4 | NULL | |
| 3 | NULL | |
| 2 | NULL | |
| 1 | NULL |
- dist 배열
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 6 |
큐에서 값을 꺼내어 기존 배열과 비교하는 위의 연산을 수행한다.
3를 꺼내었을때의 결과는 인접한 4를 연산하는 것이다.
4를 연산했을 때는 3번의 가중치 3과 3->4의 거리 2를 더한 5인데,
이는 dist[4]보다 크므로 queue에 넣지 않고 배열의 갱신도 하지 않는다.
| Index | 가중치 | 이전 정점 |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4 | 5 |
| 1 | 6 | 2 |
| 4 | NULL | |
| 3 | NULL | |
| 2 | NULL | |
| 1 | NULL |
- dist 배열
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 6 |
남은 Queue의 가중치들은 배열의 값들보다 크다.
Queue가 빌 때까지 확인해주며 제거하면 현재의 dist배열을 볼 수 있다.
예제 문제 - 백준 1753번
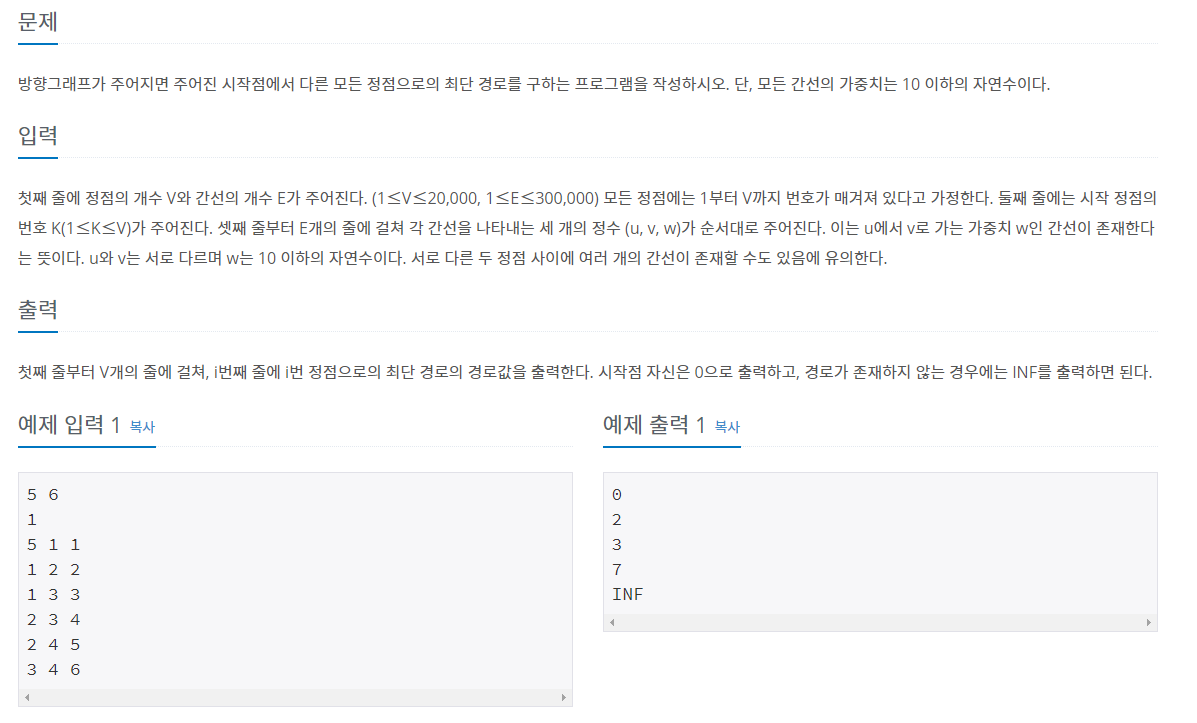
코드 - JAVA
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Main {
static ArrayList<Edge>[] adj;
static boolean[] check;
static int[] dist;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer stringTokenizer = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int V = Integer.parseInt(stringTokenizer.nextToken());
int E = Integer.parseInt(stringTokenizer.nextToken());
int start = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
adj = new ArrayList[V+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= V; i++)
adj[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0; i<E; i++){
stringTokenizer = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int u = Integer.parseInt(stringTokenizer.nextToken());
int v = Integer.parseInt(stringTokenizer.nextToken());
int w = Integer.parseInt(stringTokenizer.nextToken());
adj[u].add(new Edge(v,w));
}
check = new boolean[V+1];
dist = new int[V+1];
dijkstra(start);
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for(int i=1; i<=V; i++){
if(dist[i]!=Integer.MAX_VALUE)
stringBuilder.append(dist[i] + "\n");
else
stringBuilder.append("INF\n");
}
System.out.print(stringBuilder.toString());
}
public static void dijkstra(int start){
PriorityQueue<Edge> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
Arrays.fill(dist,Integer.MAX_VALUE);
priorityQueue.add(new Edge(start,0));
dist[start] = 0;
while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()) {
Edge edge = priorityQueue.poll();
int destination = edge.destination;
if(check[destination])
continue;
else
check[edge.destination] = true;
for (Edge next : adj[destination]) {
if (dist[next.destination] >= dist[destination] + next.weight) {
dist[next.destination] = dist[destination] + next.weight;
priorityQueue.add(new Edge(next.destination,dist[next.destination]));
}
}
}
}
}
class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> {
int destination;
int weight;
public Edge(int destination, int weight) {
this.destination = destination;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Edge o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return Integer.compare(this.weight, o.weight);
}
}
설명에서는 언급하지 않았지만, visit배열같은 방문을 체크하는 배열을 만들어 체크해주어야한다.
