1. 콜백함수
(1) 콜백함수란?
콜백함수란 전달인자로 다른 함수에 전달되는 함수로 쉽게 말하면 다른 함수가 실행을 끝낸 뒤 실행되는 CALLBACK 되는 함수를 말한다.
- 예시 (foreach, setTimeout)
// setTimeout setTimeout(function() { console.log("Hello, world!"); }, 1000); // forEach const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; numbers.forEach(function(number) { console.log(number); });
(2) 제어권
- 콜백 함수의 제어권을 넘겨받은 코드는 콜백 함수 호출 시점에 대한 제어권을 가진다.
아래 예시처럼 콜백 함수의 제어권을 넘겨받은 코드(=setInterval)가 언제 콜백함수를 호출할지 호출 시점에 대한 제어권을 가지게 되는지 확인할 수 있다! 0.3초라는 적절한 시점을 본인의 함수에 적어놓은대로 실행
1. 호출 시점
- setInterval : 반복해서 매개변수로 받은 콜백함수의 로직을 수행
var count = 0;
// timer : 콜백 내부에서 사용할 수 있는 '어떤 게 돌고있는지'
// 알려주는 id값
var timer = setInterval(function() {
console.log(count);
if(++count > 4) clearInterval(timer);
}, 300);var count = 0;
var cbFunc = function () {
console.log(count);
if (++count > 4) clearInterval(timer);
};
var timer = setInterval(cbFunc, 300); //0.3초를 간격으로 출력되게!
// 3000으로하면 3초마다 출력!
// 30000으로 하면 30초마다 ? ㄷ
// 실행 결과
// 0 (0.3sec)
// 1 (0.6sec)
// 2 (0.9sec)
// 3 (1.2sec)
// 4 (1.5sec)2. 인자
- map 함수는 각 배열 요소를 변환하여 기존 배열을 변경하지 않고, 새로운 배열을 생산 !
// map 함수에 의해 새로운 배열을 생성해서 newArr에 담고 있다.
var newArr = [10, 20, 30].map(function (currentValue, index) { //현재 값과 몇번째인지를 나타냄
console.log(currentValue, index);
return currentValue + 5;
});
console.log(newArr);
// -- 실행 결과 --
// 10 0
// 20 1
// 30 2
// [ 15, 25, 35 ]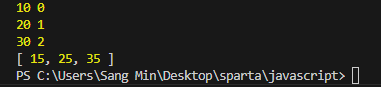
- 그럼 콜백함수에 currentValue, index의 순서를 바꾸면 어떻게 될까?
var newArr2 = [10, 20, 30].map(function (index, currentValue) {
// 순서를 바꾸면 결과는 currentValue에 5를 더한게 아닌 실제로 index에 +5 가 되는 결과가 나왔다 ㄷㄷ
console.log(index, currentValue);
return currentValue + 5;
});
console.log(newArr2);
// -- 실행 결과 --
// 10 0
// 20 1
// 30 2
// [ 5, 6, 7 ]인자에 대한 제어권은 하찮은 우리 인간따위에겐 없다.
바로 이 함수를 만든 map님 만이 콜백함수에 대한 제어권을 통제한다.👺
직접 한번 map함수 구현해보기
Array.prototype.map123 = function (callback, thisArg) {
//map 함수에서 return 할 결과 배열
var mappedarr = [];
for(var i=0; i<this.length; i++) {
// call의 첫 번째 인자는 thisArg가 존재하는 경우는 그 객체, 없으면 전역객체
// call의 두 번째 인자는 this가 배열일 것(호출의 주체가 배열)이므로,
// i번째 요소를 넣어서 인자로 전달
var mappedvalue = callback.call(thisArg || global, this[i]);
mappedarr[i] = mappedvalue;
}
return mappedarr;
};
var newarr = [1, 2, 3].map123(function (number){
return number * 2;
});
console.log(newarr);(3) 콜백함수는 함수다 !
- 콜백 함수로 어떤 객체의 메서드를 전달하더라도, 그 메서드는 메서드가 아닌 함수로 호출한다.
var obj = {
vals: [1, 2, 3],
logValues: function(v, i) {
console.log(this, v, i);
}
};
//method로써 호출
obj.logValues(1, 2);
//callback => obj를 this로 하는 메서드를 그대로 전달한게 아니다
//단지, obj.logValues가 가리키는 함수만 전달한거에요(obj 객체와는 연관 x)
[4, 5, 6].forEach(obj.logValues);(4) 콜백 함수 내부의 this에 다른 값 바인딩하기
- 전통적 방식 예시)
var obj1 = {
name: 'obj1',
func: function() {
var self = this; //이 부분!
return function () {
console.log(self.name); // 위에있는 this 부분
};
}
};
// 단순히 함수만 전달한 것이기 때문에, obj1 객체와는 상관이 x
// 메서드가 아닌 함수로서 호출한 것과 동일하죠.
var callback = obj1.func();
setTimeout(callback, 1000);
//-------------------------------------------
// obj1의 func를 직접 아래에 대입해보면 조금 더 보기 쉽다!
var obj2 = {
name: 'obj2',
func: obj1.func
};
var callback2 = obj2.func();
setTimeout(callback2, 1500); // 1.5초 뒤에 obj2 출력됨 !
// 역시, obj1의 func를 직접 아래에 대입해보면 조금 더 보기 쉽다!
var obj3 = { name: 'obj3' };
var callback3 = obj1.func.call(obj3);
setTimeout(callback3, 2000); // 2초 뒤에 obj3 출력됨 !- 위 방법은 조금 번거 롭긴 해도 this를 우회적으로나마 활용해 원하는 객체를 바라 보게 하였다. 하지만 위 예시보다 더 쉽게 해결하는 bind 메서드를 활용하는 방법을 알아보자!
var obj1 = {
name: 'obj1',
func: function () {
console.log(this.name);
}
};
//함수 자체를 obj1에 바인딩
//obj1.func를 실행할 때 무조건 this는 obj1로 고정!
setTimeout(obj1.func.bind(obj1), 1000); // 1초뒤 obj1 출력 !
var obj2 = { name: 'obj2' };
//함수 자체를 obj2에 바인딩
//obj1.func를 실행할 때 무조건 this는 obj2로 고정!
setTimeout(obj1.func.bind(obj2), 1500); // 1.5초뒤 obj2 출력 !(5) 콜백 지옥과 비동기 제어😂
1. callback hell이란?
-
콜백 함수를 익명 함수로 전달하는 과정이 반복되어 코드의 들여쓰기 수준이 헬 수준인 경우를 말한다!!
-
주로 이벤트 처리 및 서버 통신과 같은 비동기적 작업을 수행할 때 발생한다..
2. 동기와 비동기
동기 : synchronous
-
현재 실행중인 코드가 끝나야 다음 코드를 실행하는 방식
비동기 : synchronous => async라고 흔히 부른다
-
실행 중인 코드의 완료 여부와 무관하게 즉시 다음 코드로 넘어가는 방식
(setTimeout, addEventListner 등)3. 콜백지옥의 예시와 해결방안🤗
-
콜백지옥 예시) 가독성이 매우 좋지 않은 모습..
setTimeout(
function (name) {
var coffeeList = name;
console.log(coffeeList);
setTimeout(
function (name) {
coffeeList += ", " + name;
console.log(coffeeList);
setTimeout(
function (name) {
coffeeList += ", " + name;
console.log(coffeeList);
setTimeout(
function (name) {
coffeeList += ", " + name;
console.log(coffeeList); //--------------------------------------------->>
},
500,
"카페라떼"
);
},
500,
"카페모카"
);
},
500,
"아메리카노"
);
},
500,
"에스프레소"
);- 위와 같은 가독성 문제를 해결 하는 첫번째 방법은 바로 기명함수로 변환하는것!
var coffeeList = '';
var addEspresso = function (name) {
coffeeList = name;
console.log(coffeeList);
setTimeout(addAmericano, 500, '아메리카노');
};
var addAmericano = function (name) {
coffeeList += ', ' + name;
console.log(coffeeList);
setTimeout(addMocha, 500, '카페모카');
};
var addMocha = function (name) {
coffeeList += ', ' + name;
console.log(coffeeList);
setTimeout(addLatte, 500, '카페라떼');
};
var addLatte = function (name) {
coffeeList += ', ' + name;
console.log(coffeeList);
};
setTimeout(addEspresso, 500, '에스프레소'); // 그나마 가독성이 좋아졌지만..
// 아쉽지만 위 코드는 근본적인 해결책은 아니다. 비동기 작업의 동기적 표현이 필요 !!비동기 작업의 동기적 표현- promise
- Promise 는 비동기 처리에 대해 처리가 끝나면 알려달라는 약속!!
- new 연산자로 호출한 Promise의 인자로 넘어가는 콜백은 바로 실행
- 그 내부의 resolve (or reject) 함수를 호출하는 구문이 있을 경우 reslove 와 reject 둘중 하나가 실행되기 전까지 다음 오류로 넘어가지 않음 !!
- 따라서, 비동기작업이 완료될 때 비로소 resolve, reject 호출한다.
비동기 - > 동기적 표현 예시 🙀
new Promise(function (resolve) {
setTimeout(function () {
var name = '에스프레소';
console.log(name);
resolve(name);
}, 500);
}).then(function (prevName) {
return new Promise(function (resolve) {
setTimeout(function () {
var name = prevName + ', 아메리카노';
console.log(name);
resolve(name);
}, 500);
});
}).then(function (prevName) {
return new Promise(function (resolve) {
setTimeout(function () {
var name = prevName + ', 카페모카';
console.log(name);
resolve(name);
}, 500);
});
}).then(function (prevName) {
return new Promise(function (resolve) {
setTimeout(function () {
var na`me = prevName + ', 카페라떼';
console.log(name);
resolve(name);
}, 500);
});
});비동기 작업의 동기적 표현 - Generator
-
*가 붙은 함수가 제너레이터 함수! 제너레이터 함수는 실행하면, Iterator 객체가 반환(next()를 가지고 있음)된다.
iterator 은 객체는 next 메서드로 순환 할 수 있는 객체 -
iterator 객체는 next 메서드로 순환 할 수 있는 객체 next 메서드 호출 시 Generator 함수 내부에서 yield에서 STEP 이후 다시 next 메서드를 호출하면 멈췄던 부분 -> 그 다음의 yield 까지 실행 후 stop !! 즉 비동기 작업이 완료되는 시점마다 next 메서드를 호출해주면 Generator 함수 내부소스가 위 -> 아래로 순차적으로 진행됨😀
-
아래 실제 예시를 보자
var addCoffee = function (prevName, name) {
setTimeout(function () {
coffeeMaker.next(prevName ? prevName + ', ' + name : name);
}, 500);
};
var coffeeGenerator = function* () { // -> 별표가 붙어있음 !!
var espresso = yield addCoffee('', '에스프레소');
console.log(espresso);
var americano = yield addCoffee(espresso, '아메리카노');
console.log(americano);
var mocha = yield addCoffee(americano, '카페모카');
console.log(mocha);
var latte = yield addCoffee(mocha, '카페라떼');
console.log(latte);
};
var coffeeMaker = coffeeGenerator();
coffeeMaker.next();비동기 작업의 동기적 표현 - Promise + Async(비동기)/await(기다리다)
- ES2017에서 새롭게 추가된 async/await 문을 이용하였으며, Promise ~ then과 동일한 효과를 얻을 수 있다.
var addCoffee = function (name) {
return new Promise(function (resolve) {
setTimeout(function(){
resolve(name);
}, 500);
});
};
var coffeeMaker = async function () {
//var coffeeMaker = async () => {
var coffeeList = '';
var _addCoffee = async function (name) {
coffeeList += (coffeeList ? ', ' : '') + await addCoffee(name);
};
// promise를 반환하는 함수인 경우, await를 만나면 무족너 끝날 때 까지 기다린다.
//_addcoffee("에스프레소") 이 로직이 실행되는데 100초가 결렸다.
await _addCoffee('에스프레소');
// console.log는 100초 뒤 실행
console.log(coffeeList);
await _addCoffee('아메리카노');
console.log(coffeeList);
await _addCoffee('카페모카');
console.log(coffeeList);
await _addCoffee('카페라떼');
console.log(coffeeList);
};
coffeeMaker();