각 요소가 줄을 이뤄 세워져있고 그 요소들이 자신보다 낮은 무엇인가를 몇 개나 볼 수 있는가에 대한 문제는 거의
스택이라고 보면 된다.
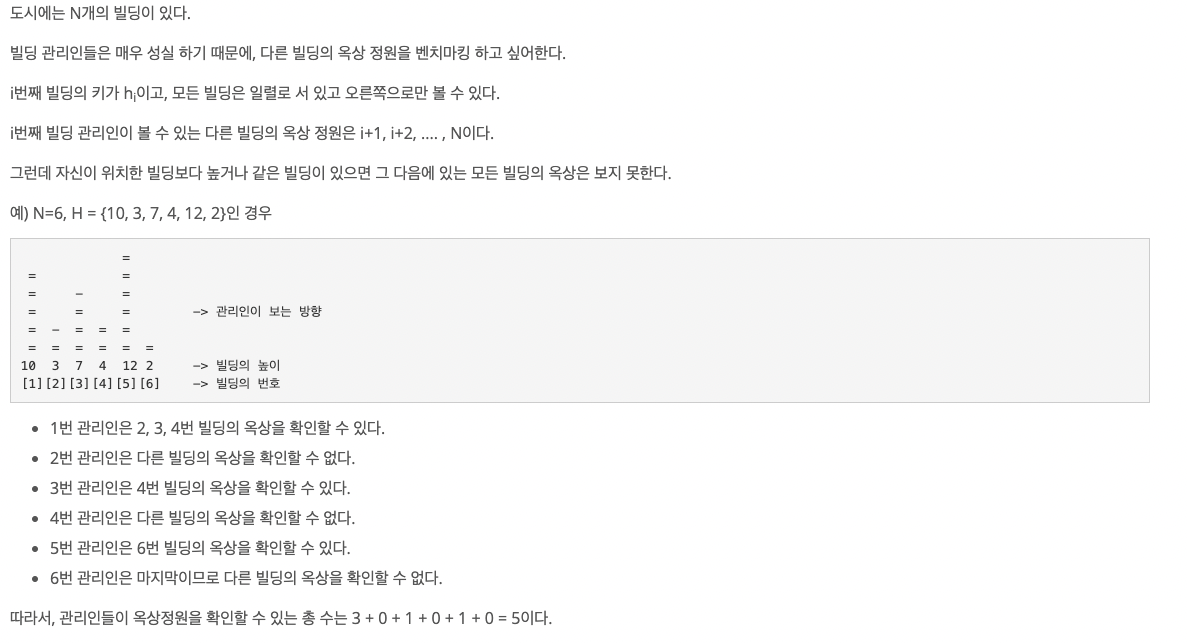
접근 방법
- 문제를 풀어내고 다른 사람들의 풀이를 보니깐(다 똑같음) 배열의 처음부터 스택에 넣어주면서
size로 더해준다. - 필자는 이런생각은 못했고, 배열의 뒷부분부터 넣어주면서 문제를 풀었다.
- 입력값의 뒷부분부터 넣어주면서
while문을 돌려줬다. stack에는pair로값과index를 넣어준다.cnt배열에는 값이stack의top과 비교할 때, 들어온 값이 더 큰 경우 자신이 벤치마킹할 수 있는 값들의 개수를 넣어주는 배열.stack의top은 자신보다 큰 값이 들어오면pop되기에cnt배열이 있는 것.
접했던 오류
- 80000개의 배열이 내림차순인 경우
int범위를 넘어서는 부분long long int로 바꿔줌.
💻 전체 코드
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
#define endl "\n"
long long int cnt[80001];
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int N;
vector<int> input;
stack<pair<int, int> > s;
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N;i++)
{
int num;
cin >> num;
input.push_back(num);
}
long long int answer = 0;
for (int i = N - 1; i >= 0;i--)
{
while (!s.empty() && s.top().first < input[i])
{
answer += (cnt[s.top().second] + 1);
cnt[i] += cnt[s.top().second]+1;
s.pop();
}
s.push(make_pair(input[i], i));
}
cout << answer << endl;
}