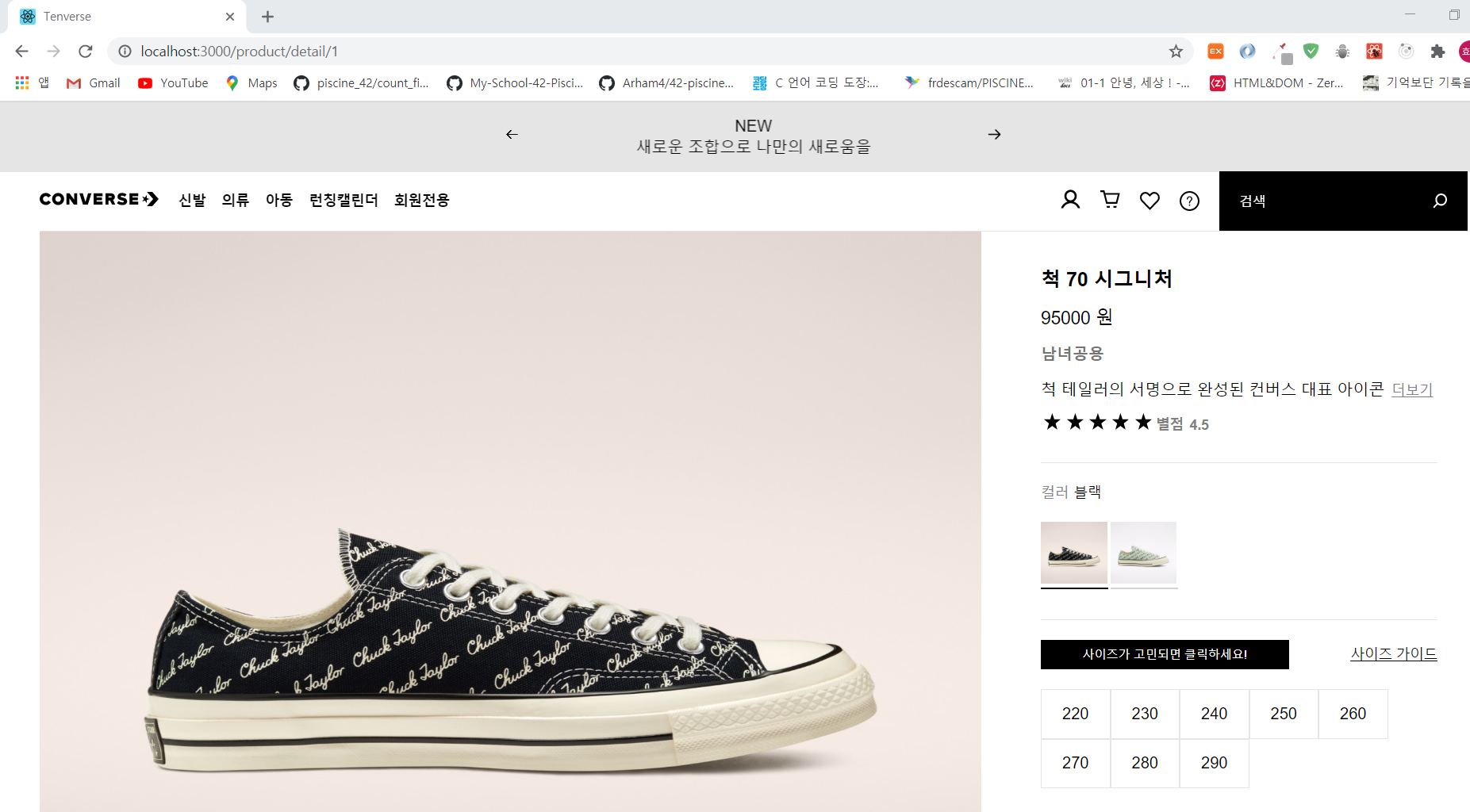
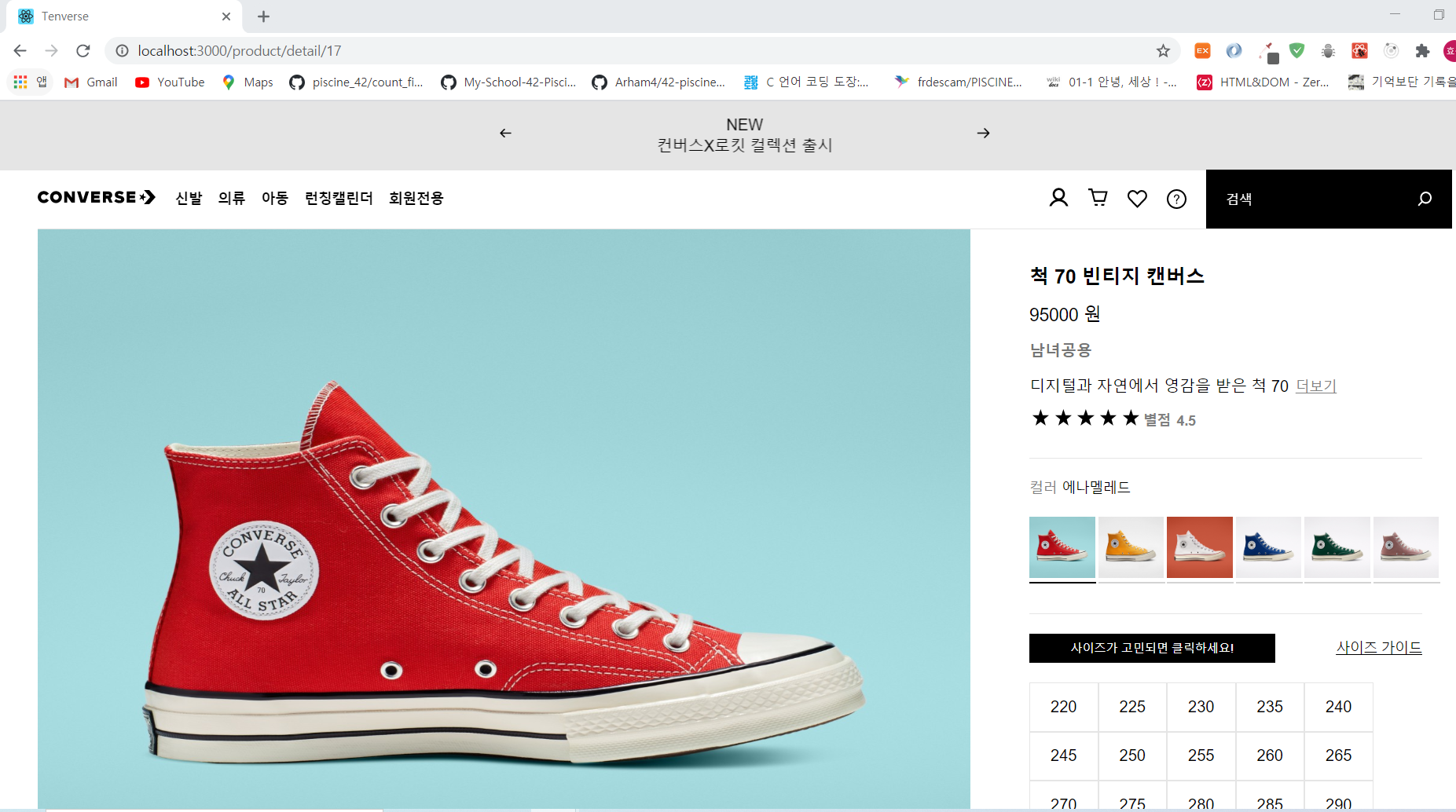
아래의 두 사진은 하나의 페이지에서 같은 형식을 유지하면서
url에 따라 받는 데이터가 달라진다. 그럴 때 사용되는 개념이유동라우터라는 개념이다.
Routes.js
class Routes extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<Router>
<Switch>
<Route exact path="/login" component={Login} />
<Route exact path="/product/detail/:id" component={ProductDetail} />
</Switch>
</Router>
)
}
}-
Routes.js에서 페이지의 형식이 재사용 되는 경우가 아니라면login과 같이path를 설정해주지만,url에 따라 사이트의 내용이 바뀌어야 하는 경우에는 경로 뒤에:과 임의의 변수를 하나 지정해주면 된다.id가 아닌 다른 변수명을 사용해도 되지만,id를 사용하는 것이 컨벤션이다. -
위의 두 사진중 아래에 해당되는 페이지에서 콘솔에
console.log(this.props)를 찍어봤다.
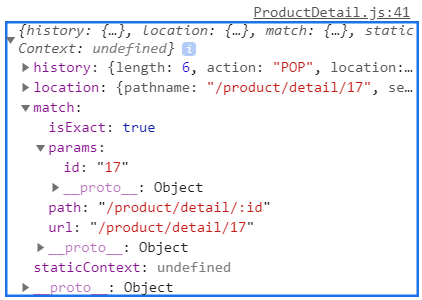
-
페이지마다 계속해서 바뀌는
url의 엔드포인트가id의 키값으로 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.Route.js에서 지정한id는this.props.match.params.id안에 담아져 있는 것이다. -
그러므로, 백엔드와
fetch로 통신할 때, 마지막의id값만 변경해주면 됐다. -
처음에 페이지는
componentDidMount에서 fetch로 데이터를 받아오고,id에 해당되는 부분을urlId변수에 담아서 그 부분만 변경될 수 있게 했다.
componentDidMount() {
const urlId = this.props.match.params.id;
fetch(`${shoeDetailAPI}${urlId}`)
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((res) => {
this.setState({
product: res.product,
});
});
console.log(this.props);
}- 나중에
url이 바뀔 때는, 새로render가 되어야 하므로,componentDidMount가 아닌,componentDidUpdate에서fetch를 해줘야 한다. componentDidMount와 다른 점은, 이전의url과 다른 경우에만fetch를 해줘야 한다는 조건문을 포함시켜야 한다. 조건문을 추가하지 않으면,url이 바뀌지 않은 경우에도 계속해서fetch를 하고 무한 루프에 빠질수 있다.
componentDidUpdate(prevProps) {
const urlId = this.props.match.params.id;
const prevUrlId = prevProps.match.params.id;
if (urlId !== prevUrlId) {
fetch(`${shoeDetailAPI}${urlId}`)
.then((res) => res.json())
.then((res) => {
this.setState({
product: res.product,
});
});
}
}- 이제
url이 이전url과 다르게 변경이 되면componentDidUpdate에서 새로fetch를 해서 새로운api주소로부터 정보를 받게 될 것이다.
