지난 이야기
[Back-end] Kotlin Spring boot으로 간단한 REST API를 만들어보자 - 3
지난 번에는 스프링 부트를 이용하여 간단한 CRUD API를 만들어봤습니다.
이번엔 만든 API를 안드로이드에 연동하는 것을 보여드리겠습니다.
IP 확인
일반적으로 만든 API를 AWS같은 걸로 배포해야 사용할 수 있기 때문에
저는 배포하지 않고사용하기 위해서 localhost 그대로 이용하겠습니다
ipconfig
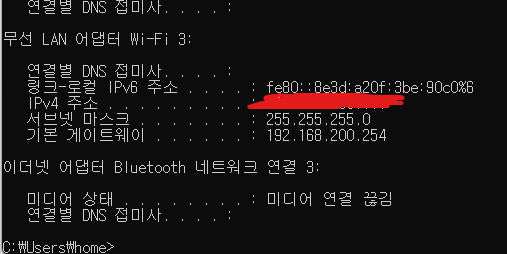
맥일 경우에는 와이파이를 들어가서 세부사항을 확인해주세요.

해당 IP 주소를 이용해서
모바일 웹에서 x.x.x.x:8080 으로 localhost에 잘 접속 되는지 확인해봅시다.
(사진)
잘 나오는군요
CRUD Service
interface CrudService {
@GET("/posts")
suspend fun readById(id: Int): Response<Entity>
@GET("/posts")
suspend fun read(): Response<List<Entity>>
@POST
suspend fun create(name: String, age: Int)
@PUT("/{id}")
suspend fun update(id: Int, name: String, age: Int)
@DELETE("/{id}")
suspend fun delete(@Path("id") id: Int)
}레트로핏에서 사용할 인터페이스를 만들어줍니다.
Retrofit 연동
const val BASE_URL = "http://yourIP:8080"
private val okHttpClient = OkHttpClient.Builder()
.addInterceptor(HttpLoggingInterceptor().apply {
level = HttpLoggingInterceptor.Level.BODY
}) // Add your interceptor here
.build()
val apiService: CrudService = Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl(BASE_URL)
.client(okHttpClient)
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())
.build()
.create(CrudService::class.java)
해당 IP 주소로 연동해줍시다.
IP는 자신의 IP를 입력해줍시다.
참고로 컴퓨터와 안드로이드 폰의 접속한 네트워크가 같아야 localhost가 가능하니
꼭 주의해주세요!
DataSource
class CrudDataSourceImpl(private val crudService: CrudService) : CrudDataSource {
override suspend fun create(name: String, age: Int) {
crudService.create(name, age)
}
override suspend fun read(): List<Entity> {
val response = crudService.read()
Log.e("123","no")
if (!response.isSuccessful) return emptyList()
Log.e("123","ok ${response.body()}")
return response.body() ?: emptyList()
}
override suspend fun readById(id: Int): Entity {
val response = crudService.readById(id)
if (response.isSuccessful) return Entity(0, "", 0)
return response.body() ?: Entity(0, "", 0)
}
override suspend fun update(id: Int, name: String, age: Int) {
crudService.update(id, name, age)
}
override suspend fun delete(id: Int) {
crudService.delete(id)
}
}http response를 처리하고 값을 넘겨주는 클래스입니다.
ViewModel
class MainViewModel(private val dataSource: CrudDataSource) : ViewModel() {
private val _state = MutableStateFlow<UIState>(UIState.Idle)
val state get() = _state
fun create(name: String, age: Int) = viewModelScope.launch {
dataSource.create(name, age)
}
fun read() = viewModelScope.launch {
_state.value = UIState.Success(dataSource.read())
}
fun readById(id: Int) = viewModelScope.launch {
_state.value = UIState.SuccessOne(dataSource.readById(id))
}
fun update(id: Int, name: String, age: Int) = viewModelScope.launch {
dataSource.update(id, name, age)
read()
}
fun delete(id: Int) = viewModelScope.launch {
dataSource.delete(id)
read()
}
}
이제 뷰에서 사용할 뷰모델을 만들어줍니다.
Screen
@Composable
fun ReadView(data: UIState.Success) {
Text(text = data.data.toString())
}
@Composable
fun CRUDScreen(viewModel: MainViewModel) {
val state = viewModel.state.collectAsState()
LaunchedEffect(Unit){
viewModel.read()
}
when(state.value){
is UIState.Idle -> {}
is UIState.Loading -> {}
is UIState.Success -> ReadView(state.value as UIState.Success)
is UIState.SuccessOne -> {}
}
}
일단 API가 연동되는지 확인하기 위한게 목적이니 read 기능만 확인하도록 하겠습니다.
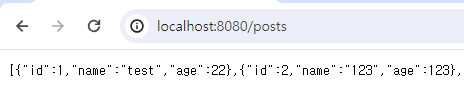
일단 스프링부트 어플리케이션을 실행해서 잘나오는지 확인해 줍시다.
잘 나오는 것을 확인했으면 안드로이드 어플을 실행해볼까요?
만약 정상적으로 동작한다면
데이터베이스에서 모든 데이터를 불러와서 화면에 출력할 것입니다.
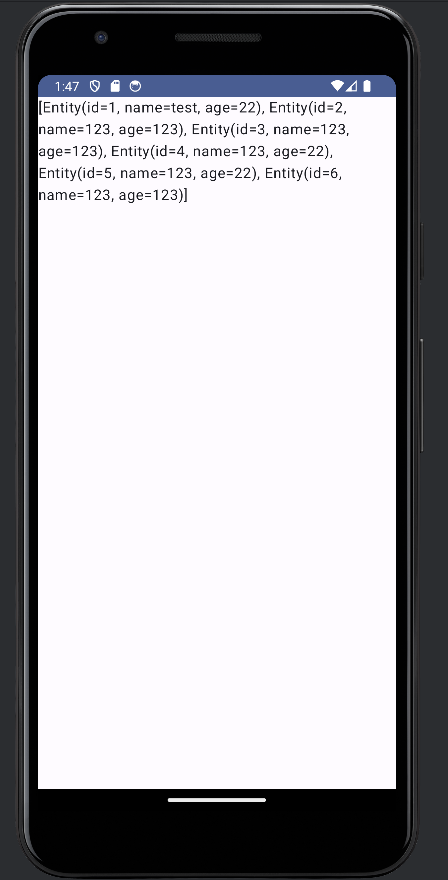
제대로 잘 연동 되었네요!
Service(API) -> DataSource -> ViewModel -> Screen 순으로 데이터가
전달됩니다.
하고 싶은 말
직접 간단한 API를 만들고 연동해보니 신기하네요..
백엔드는 간간히 취미로 계속 해야겠습니다. ㅎㅎ
다음엔 Webflux로 리액티브를 적용해보도록 하겠습니다.
