다음 큰 숫자
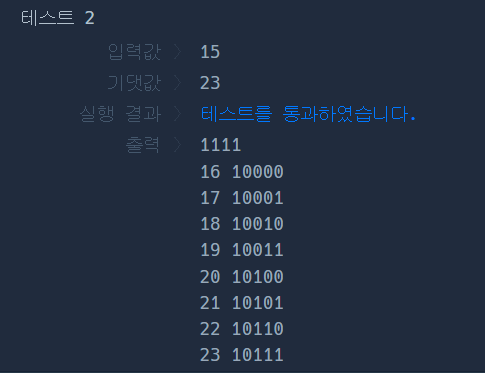
아니나 다를까 너무 정직한 풀이라서 시간이 오래 걸린다.
다른 사람 풀이를 보니 bitCount()라는 메소드가 있다.
Integer.bitCount(int x) : 입력된 32비트 정수의 1의 개수를 계산합니다.
Long.bitCount(long x) : 입력된 64비트 정수의 1의 개수를 계산합니다.
하드웨어 수준에서 최적화된 거라 수행속도도 빠르다고 한다.
1차 풀이
class Solution {
public int solution(int n) {
int answer = 0;
String binaryString = Integer.toBinaryString(n);
int count = 0, temp;
int i, j;
System.out.println(binaryString);
//이렇게 하면 시간이 너무 오래 걸릴거 같은데....
for(i = 0; i < binaryString.length(); i++){
if(binaryString.charAt(i) == '1'){
count++;
}
}
while(true){
n++;
String tempBinaryString = Integer.toBinaryString(n);
temp = 0;
System.out.println(n + " " + tempBinaryString);
for(i = 0; i < tempBinaryString.length(); i++){
if(tempBinaryString.charAt(i) == '1'){
temp++;
}
}
if(temp == count){
answer = n;
break;
}
}
return answer;
}
}2차 풀이
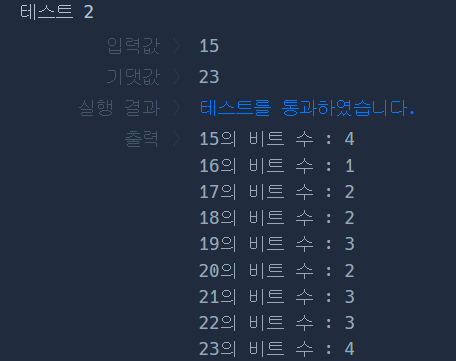
확실히 조금 더 빠르긴 하다.
class Solution {
public int solution(int n) {
int answer = 0;
int count = 0, temp = 0;
count = Integer.bitCount(n);
System.out.println(n + "의 비트 수 : " + count);
while(temp != count){
n++;
temp = Integer.bitCount(n);
System.out.println(n + "의 비트 수 : " + temp);
}
answer = n;
return answer;
}
}