백준 16173 java : 구현, DFS
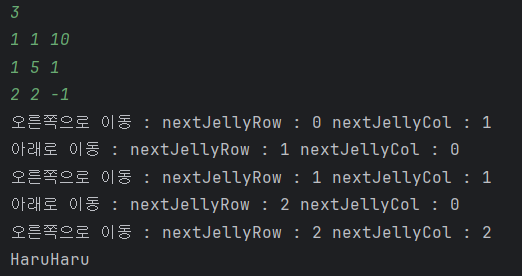
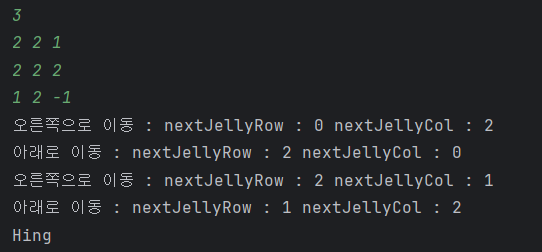
왜 DFS를 썼는가?
크기가 작기 때문에 브루트포스 또는 DFS가 둘 다 가능할 거라 생각된다. 그러나, N값이 3이상으로 확장되는 경우를 상정해서 DFS로 구현했다.
DFS는 BFS와 달리 최단 경로가 아니라 어떻게든 도착하는 경로가 존재하는지 여부를 확인할 수 있다.
또한 DFS는 브루트포스와 달리 필요없는 이동을 줄일 수 있다.
왜 재귀 말고 스택을 사용했는가?
DFS를 구현하는 방법에 재귀방식과 스택방식이 있다. 재귀는 코드가 간결하지만 속도가 느리고, 메모리초과가 발생할 수 있다. 스택은 코드가 복잡한 대신 속도가 상대적으로 빠르고 메모리를 상대적으로 절약할 수 있다.
또한 스택을 사용하면 BFS를 구현하는 방식인 큐 방식과 코드가 거의 유사해서 활용하기 좋다. 그러나 일부의 경우 스택 방식은 꺼내는 순서가 고정돼 순서가 정해진 경로 탐색에서 불이익이 있을 수 있다.
예시 : 백준 24481 : https://velog.io/@magicdrill/%EB%B0%B1%EC%A4%80-24481-java-%EA%B7%B8%EB%9E%98%ED%94%84-DFS
왜 방문 처리를 하는가?
처음에 방문처리 없이 구현해 틀렸는데, 문제를 다시 읽어보면 map에 저장되는 값은 마지막을 제외하면 0부터 10이다. 만약 현재 쩰리가 위치한 곳의 값이 0이면, 쩰리의 다음 위치는 그 위치 그대로다. 이때 방문처리 코드가 없다면 그 위치를 계속 스택에 집어넣어서 메모리 초과가 발생한다. 그러므로 한번 도착한 곳은 방문처리를 해 불필요한 이동과 메모리초과를 방지하자.
import java.util.*;
public class bj16173 {
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
static int N;
static int [][] map;
static class Location{
int row;
int col;
Location(int row, int col){
this.row = row;
this.col = col;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
inputData();
System.out.println(findAnswer());
}
public static void inputData(){
int i, j;
N = sc.nextInt();
map = new int[N][N];
for(i = 0; i < N; i++){
for(j = 0; j < N; j++){
map[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
}
public static String findAnswer(){
int currentJellyRow = 0, currentJellyCol = 0;
int nextJellyRow = 0, nextJellyCol = 0;
int step;
int i, j;
//갈 수 있냐 없냐니까 DFS?
//근데 아무리 커도 3*3이니까 브루트포스도 될 듯
Stack<Location> st;
st = new Stack<>();
boolean [][] visited = new boolean[N][N];
st.add(new Location(currentJellyRow, currentJellyCol));
while(!st.isEmpty()){
Location current = st.pop();
currentJellyRow = current.row;
currentJellyCol = current.col;
visited[currentJellyRow][currentJellyCol] = true;
if(currentJellyRow == N-1 && currentJellyCol == N-1){
return "HaruHaru";
}
step = map[currentJellyRow][currentJellyCol];
//오른쪽으로 가기
if(currentJellyCol + step < N && !visited[currentJellyRow][currentJellyCol + step]){
nextJellyRow = currentJellyRow;
nextJellyCol = currentJellyCol + step;
visited[nextJellyRow][nextJellyCol] = true;
System.out.println("오른쪽으로 이동 : nextJellyRow : " + nextJellyRow + " nextJellyCol : " + nextJellyCol);
st.add(new Location(nextJellyRow, nextJellyCol));
}
//아래쪽으로 가기
if(currentJellyRow + step < N && !visited[currentJellyRow + step][currentJellyCol]){
nextJellyRow = currentJellyRow + step;
nextJellyCol = currentJellyCol;
visited[nextJellyRow][nextJellyCol] = true;
System.out.println("아래로 이동 : nextJellyRow : " + nextJellyRow + " nextJellyCol : " + nextJellyCol);
st.add(new Location(nextJellyRow, nextJellyCol));
}
}
return "Hing";
}
}