백준 1639 c++ : 구현, DFS
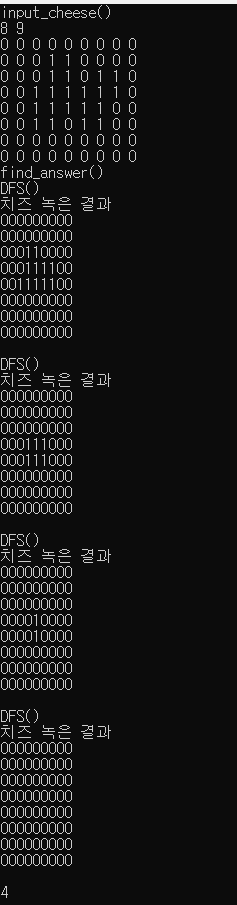
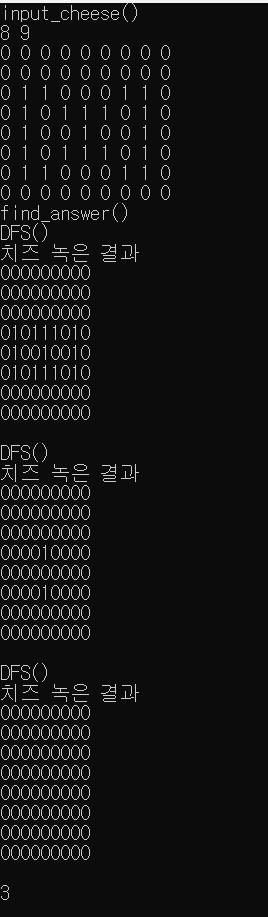
다른 사람들 풀이보다는 비효율적인 부분이 많다.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void input_cheese(vector<vector<bool>>& cheese);
int find_answer(vector<vector<bool>>& cheese);
void DFS(vector<vector<bool>>& cheese, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int y, int x);
bool find_remain_cheese(vector<vector<bool>>& cheese);
bool is_it_melt(vector<vector<bool>>& cheese, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int y, int x);
int main(void) {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
vector<vector<bool>> cheese;
input_cheese(cheese);
cout << find_answer(cheese) << "\n";
return 0;
}
void input_cheese(vector<vector<bool>>& cheese) {
cout << "input_cheese()\n";
int N, M, i, j;
bool temp;
cin >> N >> M;
cheese.resize(N, vector<bool>(M, false));
/*
새로운 요소를 추가할 것이지만, 크기를 미리 조정할 필요는 없을 때 → reserve()
벡터의 크기를 강제적으로 조정하고, 새 요소를 특정 값으로 초기화할 때 → resize()
*/
for (i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < M; j++) {
cin >> temp;
cheese[i][j] = temp;
}
}
return;
}
int find_answer(vector<vector<bool>>& cheese) {
cout << "find_answer()\n";
int N = cheese.size(), M = cheese[0].size(), i, j, count = 0;
bool dfsExecuted;
while (1) {
vector<vector<bool>> visited(N, vector<bool>(M, false));
if (!find_remain_cheese(cheese)) {//남은 치즈가 존재하는지 판단
break;
}
dfsExecuted = false;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if (cheese[i][j] == false && visited[i][j] == false) {
DFS(cheese, visited, i, j);
dfsExecuted = true;
break;
}
}
if (dfsExecuted) {
break;
}
}
vector<pair<int, int>> melt;//바로 녹여버리면 안될듯?
for (i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < M; j++) {
//녹아야 하는 치즈 판단
if (cheese[i][j] == true && visited[i][j] == false && is_it_melt(cheese, visited, i, j)) {
melt.push_back({ j, i });
}
}
}
for (pair<int, int> coordinate : melt) {//치즈 녹이기
cheese[coordinate.second][coordinate.first] = false;//녹았음
visited[coordinate.second][coordinate.first] = true;
}
cout << "치즈 녹은 결과\n";
for (i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < M; j++) {
cout << (cheese[i][j] ? 1 : 0);
}
cout << "\n";
}
cout << "\n";
count++;
}
return count;
}
bool find_remain_cheese(vector<vector<bool>>& cheese) {
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < cheese.size(); i++) {
for (j = 0; j < cheese[i].size(); j++) {
if (cheese[i][j]) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
void DFS(vector<vector<bool>>& cheese, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int y, int x) {
cout << "DFS()\n";
int N = cheese.size(), M = cheese[0].size(), i, j;
vector<pair<int, int>> direction{ {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1} };
stack <pair<int, int>> st;
int current_x, current_y, next_x, next_y;
st.push({ x, y });
visited[y][x] = true;
while (!st.empty()) {
current_x = st.top().first;
current_y = st.top().second;
st.pop();
for (i = 0; i < direction.size(); i++) {
next_x = current_x + direction[i].first;
next_y = current_y + direction[i].second;
if ((next_x >= 0 && next_x < M) && (next_y >= 0 && next_y < N)//범위 내에 있고
&& (!visited[next_y][next_x])//방문한 적 없고
&& (cheese[next_y][next_x] == false)) {//치즈가 아니고
st.push({ next_x, next_y });
visited[next_y][next_x] = true;
}
}
}
for (i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < M; j++) {
cout << (visited[i][j] ? 0 : 1);
}
cout << "\n";
}
cout << "\n";
return;
}
bool is_it_melt(vector<vector<bool>>& cheese, vector<vector<bool>>& visited, int y, int x) {
int count = 0;
vector<pair<int, int>> direction{ {1, 0},{0, 1},{-1, 0},{0, -1} };
int N = cheese.size(), M = cheese[0].size(), i, next_x, next_y;
for (i = 0; i < direction.size(); i++) {
next_x = x + direction[i].first;
next_y = y + direction[i].second;
if ((next_x >= 0 && next_x < M) && (next_y >= 0 && next_y < N) &&//범위 내에 있고
(visited[next_y][next_x] == true) && (cheese[next_y][next_x] == false)) {//DFS로 연결된 공기
count++;
}
}
if (count >= 2) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}